本篇内容主要讲解其他关于Service内容:
- 前台服务以及通知发送
- 服务Service与线程Thread的区别
- Android 5.0以上的隐式启动服务问题以及解决方案
1. 前台服务以及通知发送
前台服务被认为是用户主动意识到的一种服务,因此在内存不足时,系统也不会考虑将其终止。 前台服务必须为状态栏提供通知,状态栏位于“正在进行”标题下方,这意味着除非服务停止或从前台删除,否则不能清除通知。例如将从服务播放音乐的音乐播放器设置为在前台运行,这是因为用户明确意识到其操作。 状态栏中的通知可能表示正在播放的歌曲,并允许用户启动 Activity 来与音乐播放器进行交互。需要设置服务运行于前台, 我们该如何才能实现呢?
Android官方给我们提供了两个方法,分别是startForeground()和stopForeground(),这两个方式解析如下:
- startForeground(int id, Notification notification)
该方法的作用是把当前服务设置为前台服务,其中id参数代表唯一标识通知的整型数,需要注意的是提供给 startForeground() 的整型 ID 不得为 0,而notification是一个状态栏的通知。 - stopForeground(boolean removeNotification)
该方法是用来从前台删除服务,此方法传入一个布尔值,指示是否也删除状态栏通知,true为删除。 注意该方法并不会停止服务。 但是,如果在服务正在前台运行时将其停止,则通知也会被删除。
下面我们结合一个简单案例来使用以上两个方法,ForegroundService代码如下:
class ForegroundService : Service() {
companion object {
const val NOTIFICATION_DOWNLOAD_PROGRESS_ID = 0x01
}
override fun onBind(intent: Intent?): IBinder? {
return null
}
private fun createNotification() {
//使用兼容版本
val builder = NotificationCompat.Builder(this)
//设置状态栏的通知图标
builder.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
//设置通知栏横条的图标
builder.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.mipmap.ic_launcher_round))
//禁止用户点击删除按钮删除
builder.setAutoCancel(false)
//禁止滑动删除
builder.setOngoing(true)
//右上角的时间显示
builder.setShowWhen(true)
//设置通知栏的标题内容
builder.setContentTitle("I am Foreground Service!!!")
//创建通知
val notification = builder.build()
//设置为前台服务
startForeground(NOTIFICATION_DOWNLOAD_PROGRESS_ID, notification);
}
override fun onStartCommand(intent: Intent, flags: Int, startId: Int): Int {
val i = intent.extras.getInt("cmd")
when (i) {
0 -> createNotification()
1 -> stopForeground(true)
}
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
stopForeground(true)
}
}
在ForegroundService类中,创建了一个notification的通知,并通过启动Service时传递过来的参数判断是启动前台服务还是关闭前台服务,最后在onDestroy方法被调用时,也应该移除前台服务。以下是ForegroundActivity的实现:
class ForegroundActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_foreground)
val intent = Intent(this, ForegroundService::class.java)
startForegroundBtn.setOnClickListener {
intent.putExtra("cmd",0)
startService(intent)
}
stopForegroundBtn.setOnClickListener {
intent.putExtra("cmd",1)
startService(intent)
}
}
}
效果比较简单,点击启动前台服务,通知栏会弹出一个通知消息,点击关闭前台服务时消失。
2. 服务Service与线程Thread的区别
2.1 概念区分
- Thread 是程序执行的最小单元,它是分配CPU的基本单位,android系统中UI线程也是线程的一种,当然Thread还可以用于执行一些耗时异步的操作。
- Service是Android的一种机制,服务是运行在主线程上的,它是由系统进程托管。它与其他组件之间的通信类似于client和server,是一种轻量级的IPC通信,这种通信的载体是binder,它是在linux层交换信息的一种IPC,而所谓的Service后台任务只不过是指没有UI的组件罢了。
2.2 执行任务区分
- 在android系统中,线程一般指的是工作线程(即后台线程),而主线程是一种特殊的工作线程,它负责将事件分派给相应的用户界面小工具,如绘图事件及事件响应,因此为了保证应用 UI 的响应能力主线程上不可执行耗时操作。如果执行的操作不能很快完成,则应确保它们在单独的工作线程执行。
- Service 则是android系统中的组件,一般情况下它运行于主线程中,因此在Service中是不可以执行耗时操作的,否则系统会报ANR异常,之所以称Service为后台服务,大部分原因是它本身没有UI,用户无法感知(当然也可以利用某些手段让用户知道),但如果需要让Service执行耗时任务,可在Service中开启单独线程去执行。
2.3 使用场景区分
- 当要执行耗时的网络或者数据库查询以及其他阻塞UI线程或密集使用CPU的任务时,都应该使用工作线程(Thread),这样才能保证UI线程不被占用而影响用户体验。
- 在应用程序中,如果需要长时间的在后台运行,而且不需要交互的情况下,使用服务。比如播放音乐,通过Service+Notification方式在后台执行同时在通知栏显示着。
2.4 两者的最佳使用方式
在大部分情况下,Thread和Service都会结合着使用,比如下载文件,一般会通过Service在后台执行+Notification在通知栏显示+Thread异步下载,再如应用程序会维持一个Service来从网络中获取推送服务。在Android官方看来也是如此,所以官网提供了一个Thread与Service的结合来方便我们执行后台耗时任务,它就是IntentService,当然 IntentService并不适用于所有的场景,但它的优点是使用方便、代码简洁,不需要我们创建Service实例并同时也创建线程,某些场景下还是非常赞的!由于IntentService是单个worker thread,所以任务需要排队,因此不适合大多数的多任务情况。
说到底,两者没有任何关系
3. Android 5.0以上的隐式启动问题
先来了解一下什么是隐式启动和显示启动:
- 显示启动
val intent = Intent(this, ForegroundService::class.java)
startService(intent)
- 隐式启动
需要设置一个Action,我们可以把Action的名字设置成Service的全路径名字,在这种情况下android:exported默认为true。
val serviceIntent = Intent()
serviceIntent.action = "com.wangyy.service.ForegroundService"
startService(serviceIntent)
如果在同一个应用中,两者都可以用。在不同应用时,只能用隐式启动。
Android 5.0以上的隐式启动问题
Android 5.0之后google出于安全的角度禁止了隐式声明Intent来启动Service。如果使用隐式启动Service,会出没有指明Intent的错误,如下:
Process: com.wangyy.service, PID: 4025
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to start activity ComponentInfo{com.wangyy.service/com.wangyy.service.ForegroundActivity}: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Service Intent must be explicit: Intent { act=com.wangyy.service.ForegroundService }
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2534)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2614)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:178)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1470)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:111)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:194)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5643)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:372)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:960)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:755)
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Service Intent must be explicit: Intent { act=com.wangyy.service.ForegroundService }
at android.app.ContextImpl.validateServiceIntent(ContextImpl.java:1801)
at android.app.ContextImpl.startServiceCommon(ContextImpl.java:1830)
at android.app.ContextImpl.startService(ContextImpl.java:1814)
at android.content.ContextWrapper.startService(ContextWrapper.java:516)
at com.wangyy.service.ForegroundActivity.onCreate(ForegroundActivity.kt:30)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6100)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1112)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2481)
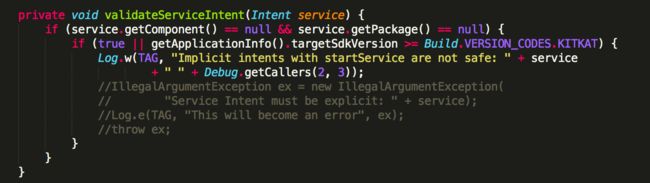
主要原因我们可以从源码中找到,这里看看Android 4.4的ContextImpl源码中的validateServiceIntent(Intent service),可知如果启动service的intent的component和package都为空并且版本大于KITKAT的时候只是报出一个警报,告诉开发者隐式声明intent去启动Service是不安全的.
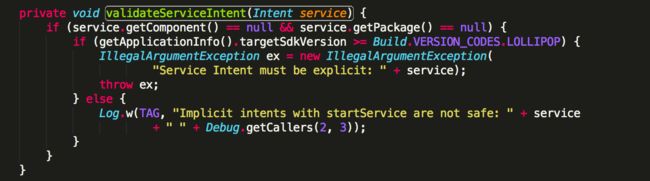
而在android5.0之后呢?我们这里看的是android6.0的源码如下:
从源码可以看出如果启动service的intent的component和package都为空并且版本大于LOLLIPOP(5.0)的时候,直接抛出异常,该异常与之前隐式启动所报的异常时一致的。那么该如何解决呢?
解决方式
- 设置Action和packageName
val serviceIntent = Intent()
serviceIntent.action = "com.wangyy.service.ForegroundService"
serviceIntent.`package` = packageName
startService(serviceIntent)
- 将隐式启动转换为显示启动
public static Intent getExplicitIntent(Context context, Intent implicitIntent) {
// Retrieve all services that can match the given intent
PackageManager pm = context.getPackageManager();
List resolveInfo = pm.queryIntentServices(implicitIntent, 0);
// Make sure only one match was found
if (resolveInfo == null || resolveInfo.size() != 1) {
return null;
}
// Get component info and create ComponentName
ResolveInfo serviceInfo = resolveInfo.get(0);
String packageName = serviceInfo.serviceInfo.packageName;
String className = serviceInfo.serviceInfo.name;
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(packageName, className);
// Create a new intent. Use the old one for extras and such reuse
Intent explicitIntent = new Intent(implicitIntent);
// Set the component to be explicit
explicitIntent.setComponent(component);
return explicitIntent;
}
关于Service的全部介绍就此完结。
源码地址:ServiceLearnDemo
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/52709857