Reference
- This is good: http://blog.igevin.info/posts/git-cheat-sheet/
Some random stuff
在 GitHub 上 fork 到自己的仓库,如 docker_user/docker_practice,然后 clone 到本地,并设置用户信息。
$ git clone [email protected]:docker_user/docker_practice.git
$ cd docker_practice
$ git config user.name "yourname"
$ git config user.email "your email"修改代码后提交,并推送到自己的仓库。
$ #do some change on the content
$ git commit -am "Fix issue #1: change helo to hello"
$ git push在 GitHub 网站上提交 pull request。
定期使用项目仓库内容更新自己仓库内容。
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/yeasy/docker_practice
$ git fetch upstream
$ git checkout master
$ git rebase upstream/master
$ git push -f origin master
Merge branch
Simple Solution:
git checkout master
git pull origin master
git merge test
git push origin master
Upper operations have two issues:
More complicated Solution:
This is one very practice question, but all before answers are not practical.
Like
git checkout master
git pull origin master
git merge test
git push origin master
Upper operations have two issues:
it's not one safety way, cause we don't know is there any conflicts between test branch and master branch
it would "squeeze" all test commits into one merge commit on master, that is to say on master branch, we can't see the all change logs of test branch
So, when we suspect there would some conflicts, we can have following git operations:
git checkout test
git pull
git checkout master
git pull
git merge --no-ff --no-commit test
Test merge before commit, avoid a fast-forward commit by --no-ff,
If conflicts notified, we can run git status to check details about the conflicts and try to solve
git status
Once we solve the conflicts, or there is not any conflicts, we commit and push them
git commit -m 'merge test branch'
git push
But this way will lose the changes history logged in test branch, and it would make master branch to be hard for other developers to understand the history of the project.
So the best method is we have to use Rebase instead of Merge (suppose, when in this time, we have solved the branches conflicts).
Following is one simple sample, for advanced operations, please refer to http://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Rebasing
git checkout master
git pull
git checkout test
git pull
git rebase -i master
git checkout master
git merge test
Yeap, when you have uppers done, the Test branch's all commits will be moved onto the head of Master branch. The major benefit of rebasing is that you get a liner and much cleaner project history.
The only thing you need to avoid is: never use rebase on public branch, like master branch.
like following operation:
git checkout master
git rebase -i test
never do these operations.
Details for https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/merging-vs-rebasing/the-golden-rule-of-rebasing
appendix:
if you are not sure the rebasing operations, please refer to: https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Rebasing
Git ignore
# put this in the directory where you want git to ignore everything but the directory sturcture
# Ignore everything in this directory
*
# Except this file
!.gitignore
Git Flow
https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/
Tutorial
Based on http://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0013739516305929606dd18361248578c67b8067c8c017b000
Git on local machine
版本退回
- check log
git log
- git 使用
HEAD表示当前版本。HEAD^HEAD^^表示前一个,2个版本。
git reset --hard HEAD^
- can use
commit idto placeHEADto a particular version
git reset --hard 3628164
git resest --hard commit_id
- can use
git reflogto track all the command
git reflog
ea34578 HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to HEAD^
3628164 HEAD@{1}: commit: append GPL
ea34578 HEAD@{2}: commit: add distributed
cb926e7 HEAD@{3}: commit (initial): wrote a readme file
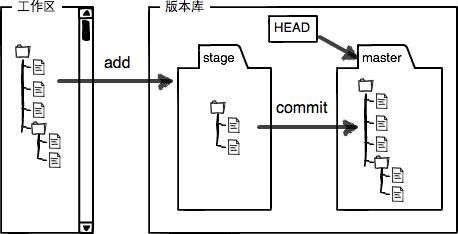
Working directory and Repository
工作区(Working Directory)
就是你在电脑里能看到的目录,比如我的learngit文件夹就是一个工作区版本库(Repository)
工作区有一个隐藏目录.git,这个不算工作区,而是Git的版本库。
Git的版本库里存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是称为stage(或者叫index)的暂存区,还有Git为我们自动创建的第一个分支master,以及指向master的一个指针叫HEAD.
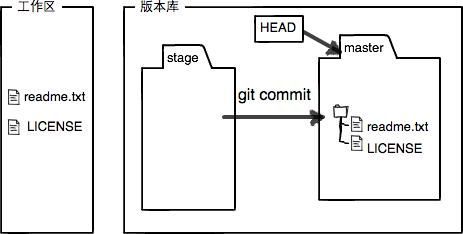
所以,git add命令实际上就是把要提交的所有修改放到暂存区(Stage),然后,执行git commit就可以一次性把暂存区的所有修改提交到分支。
一旦提交后,如果你又没有对工作区做任何修改,那么工作区就是“干净”的:
$ git status# On branch masternothing to commit (working directory clean)
Note: git commit will only commit changes that has been add into stage zone. The changes in working directory but not in stage zone will not be committed.
用git diff HEAD -- file_name 命令可以查看工作区和版本库里面最新版本的区别
git diff HEAD -- readme.txt
撤销修改
1. Discard the changes in working directory (unstaged)
git checkout -- file_name 可以丢弃工作区的修改
git checkout -- readme.txt
$ git status
# On branch master
# Changes not staged for commit:
# (use "git add ..." to update what will be committed)
# (use "git checkout -- ..." to discard changes in working directory)
#
# modified: readme.txt
#
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
命令git checkout -- readme.txt意思就是,把readme.txt文件在工作区的修改全部撤销,这里有两种情况:
一种是readme.txt自修改后还没有被放到暂存区,现在,撤销修改就回到和版本库一模一样的状态;
一种是readme.txt已经添加到暂存区后,又作了修改,现在,撤销修改就回到添加到暂存区后的状态。
总之,就是让这个文件回到最近一次git commit或git add时的状态。
2. Discard changes that already be staged
$ git status
# On branch master
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git reset HEAD ..." to unstage)
#
# modified: readme.txt
#
Git同样告诉我们,用命令git reset HEAD file_name 可以把暂存区的修改撤销掉(unstage),重新放回工作区:
$ git reset HEAD readme.txt
$ git status
# On branch master
# Changes not staged for commit:
# (use "git add ..." to update what will be committed)
# (use "git checkout -- ..." to discard changes in working directory)
#
# modified: readme.txt
#
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
After this, apply the same method to discard the changes in working directory.
$ git checkout -- readme.txt
$ git status
# On branch masternothing to commit (working directory clean)
Delete and recover file
** 1. delete file from repository**
$ rm test.txt
$ git rm test.txt
$ git commit -m "remove test.txt"
** 2. Recover deleted file **
另一种情况是删错了,因为版本库里还有呢,所以可以很轻松地把误删的文件恢复到最新版本:
$ git checkout -- test.txt
git checkout 其实是用版本库里的版本替换工作区的版本,无论工作区是修改还是删除,都可以“一键还原”。
Remote Repository
After create a new repo on GitHub, we can connect this new Github repo with our local repo, and push content to it
$ git remote add origin git@server-name:path/repo-name.git
$ git remote add origin [email protected]:michaelliao/learngit.git
请千万注意,把上面的michaelliao替换成你自己的GitHub账户名,否则,你在本地关联的就是我的远程库,关联没有问题,但是你以后推送是推不上去的,因为你的SSH Key公钥不在我的账户列表中。
添加后,远程库的名字就是origin,这是Git默认的叫法,也可以改成别的,但是origin这个名字一看就知道是远程库。
$ git push -u origin master
Counting objects: 19, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (19/19), done.
Writing objects: 100% (19/19), 13.73 KiB, done.
Total 23 (delta 6), reused 0 (delta 0)
To [email protected]:michaelliao/learngit.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch master set up to track remote branch master from origin.
由于远程库是空的,我们第一次推送master分支时,加上了-u参数,Git不但会把本地的master分支内容推送的远程新的master分支,还会把本地的master分支和远程的master分支关联起来,在以后的推送或者拉取时就可以简化命令。
从现在起,只要本地作了提交,就可以通过命令:
$ git push origin master
Branch Management
创建与合并分支
查看分支:git branch
创建分支:git branch
切换分支:git checkout
创建+切换分支:git checkout -b
合并某分支到当前分支:git merge
删除分支:git branch -d
git merge命令用于合并指定分支到当前分支。合并后,再查看readme.txt的内容,就可以看到,和dev分支的最新提交是完全一样的。
$ git merge dev
Updating d17efd8..fec145a
Fast-forward
readme.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
注意到上面的Fast-forward信息,Git告诉我们,这次合并是“快进模式”,也就是直接把master指向dev的当前提交,所以合并速度非常快。
当然,也不是每次合并都能Fast-forward,我们后面会讲其他方式的合并。
合并完成后,就可以放心地删除dev分支了.
准备合并dev分支,请注意--no-ff参数,表示禁用Fast forward:
$ git merge --no-ff -m "merge with no-ff" dev
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
readme.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
解决冲突
用带参数的git log也可以看到分支的合并情况
$ git log --graph --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit
* 59bc1cb conflict fixed
|\
| * 75a857c AND simple
* | 400b400 & simple
|/
* fec145a branch test
...
多人协作
当你从远程仓库克隆时,实际上Git自动把本地的master分支和远程的master分支对应起来了,并且,远程仓库的默认名称是origin。
要查看远程库的信息,用git remote:
$ git remote
origin
$ git remote -v
origin [email protected]:michaelliao/learngit.git (fetch)
origin [email protected]:michaelliao/learngit.git (push)
上面显示了可以抓取和推送的origin的地址。如果没有推送权限,就看不到push的地址。
推送分支
$ git push origin master
$ git push origin dev
但是,并不是一定要把本地分支往远程推送,那么,哪些分支需要推送,哪些不需要呢?
- master分支是主分支,因此要时刻与远程同步;
- dev分支是开发分支,团队所有成员都需要在上面工作,所以也需要与远程同步;
- bug分支只用于在本地修复bug,就没必要推到远程了,除非老板要看看你每周到底修复了几个bug;
- feature分支是否推到远程,取决于你是否和你的小伙伴合作在上面开发。
抓取分支
当你的小伙伴从远程库clone时,默认情况下,你的小伙伴只能看到本地的master分支。不信可以用git branch命令看看:
$ git branch
- master
现在,你的小伙伴要在dev分支上开发,就必须创建远程origin的dev分支到本地,于是他用这个命令创建本地dev分支:
$ git checkout -b dev origin/dev
现在,他就可以在dev上继续修改,然后,时不时地把dev分支push到远程:
$ git commit -m "add /usr/bin/env"
[dev 291bea8] add /usr/bin/env
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
$ git push origin dev
Counting objects: 5, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 349 bytes, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To [email protected]:michaelliao/learngit.git
fc38031..291bea8 dev -> dev
git pull也失败了,原因是没有指定本地dev分支与远程origin/dev分支的链接,根据提示,设置dev和origin/dev的链接:
$ git branch --set-upstream dev origin/dev
Branch dev set up to track remote branch dev from origin.
小结
查看远程库信息,使用git remote -v;
本地新建的分支如果不推送到远程,对其他人就是不可见的;
从本地推送分支,使用git push origin branch-name,如果推送失败,先用git pull抓取远程的新提交;
在本地创建和远程分支对应的分支,使用git checkout -b branch-name origin/branch-name,本地和远程分支的名称最好一致;
建立本地分支和远程分支的关联,使用git branch --set-upstream branch-name origin/branch-name;
从远程抓取分支,使用git pull,如果有冲突,要先处理冲突。
Tag
在Git中打标签非常简单,首先,切换到需要打标签的分支上:
$ git branch
* dev
master
$ git checkout master
Switched to branch 'master'
然后,敲命令git tag
$ git tag v1.0
可以用命令git tag查看所有标签:
$ git tag
v1.0
Add tag to history commit
$ git log --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit
6a5819e merged bug fix 101
cc17032 fix bug 101
7825a50 merge with no-ff
6224937 add merge
59bc1cb conflict fixed
400b400 & simple
75a857c AND simple
fec145a branch test
d17efd8 remove test.txt
...
$ git tag v0.9 6224937
$ git tag -a v0.1 -m "version 0.1 released" 3628164