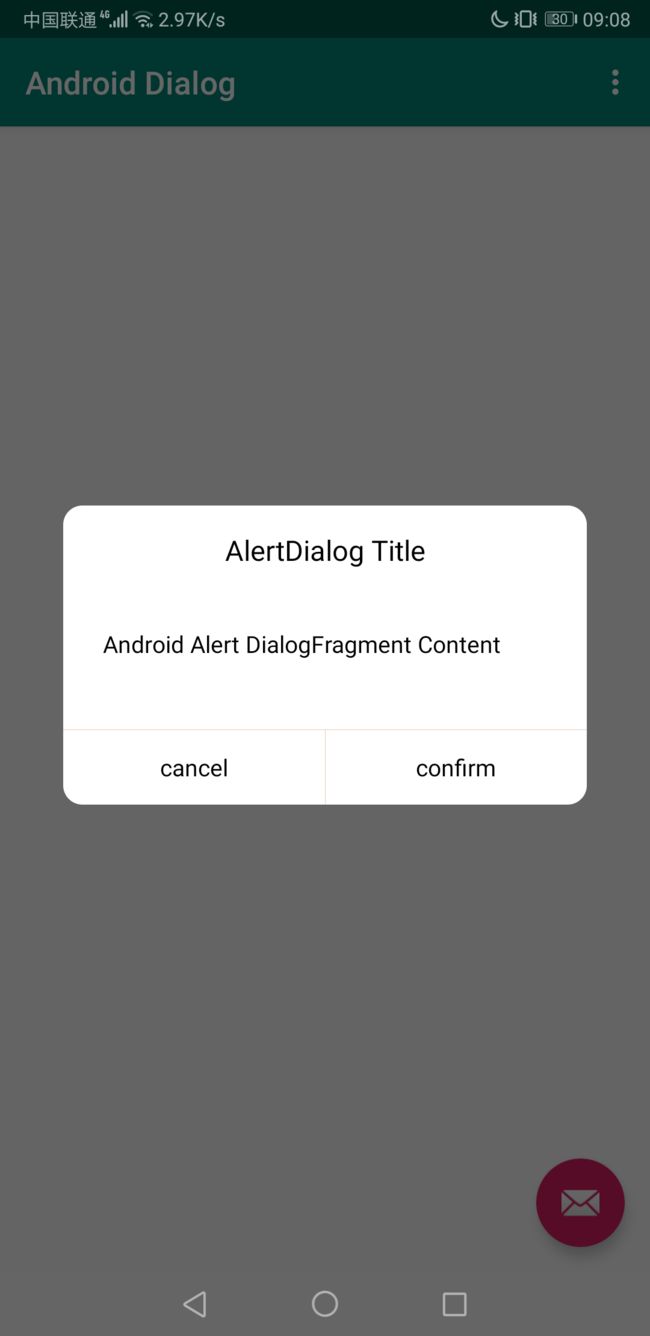
一、什么是宏函数?通过宏定义的函数是宏函数。如下,编译器在预处理阶段会将Add(x,y)替换为((x)*(y))#defineAdd(x,y)((x)*(y))#defineAdd(x,y)((x)*(y))intmain(){inta=10;intb=20;intd=10;intc=Add(a+d,b)*2;cout<
谢谢你们,爱你们!
鹿游儿
昨天家人去泡温泉,二个孩子也带着去,出发前一晚,匆匆下班,赶回家和孩子一起收拾。饭后,我拿出笔和本子(上次去澳门时做手帐的本子)写下了1\2\3\4\5\6\7\8\9,让后让小壹去思考,带什么出发去旅游呢?她在对应的数字旁边画上了,泳衣、泳圈、肖恩、内衣内裤、tapuy、拖鞋……画完后,就让她自己对着这个本子,将要带的,一一带上,没想到这次带的书还是这本《便便工厂》(晚上姑婆发照片过来,妹妹累得
爬山后遗症
璃绛
爬山,攀登,一步一步走向制高点,是一种挑战。成功抵达是一种无法言语的快乐,在山顶吹吹风,看看风景,这是从未有过的体验。然而,爬山一时爽,下山腿打颤,颠簸的路,一路向下走,腿部力量不够,走起来抖到不行,停不下来了!第二天必定腿疼,浑身酸痛,坐立难安!
《策划经理回忆录之二》
路基雅虎
话说三年变六年,飘了,飘了……眨眼,2013年5月,老吴回到了他的家乡——油城从新开启他的工作幻想症生涯。很庆幸,这是一家很有追求,同时敢于尝试的,且实力不容低调的新星房企——金源置业(前身泰源置业)更值得庆幸的是第一个盘就是油城十路的标杆之一:金源盛世。2013年5月,到2015年11月,两年的陪伴,迎来了一场大爆发。2000个筹,5万/筹,直接回笼1个亿!!!这……让我开始认真审视这座看似五线
swagger访问路径
igotyback
swagger
Swagger2.x版本访问地址:http://{ip}:{port}/{context-path}/swagger-ui.html{ip}是你的服务器IP地址。{port}是你的应用服务端口,通常为8080。{context-path}是你的应用上下文路径,如果应用部署在根路径下,则为空。Swagger3.x版本对于Swagger3.x版本(也称为OpenAPI3)访问地址:http://{ip
扫地机类清洁产品之直流无刷电机控制
悟空胆好小
清洁服务机器人单片机人工智能
扫地机类清洁产品之直流无刷电机控制1.1前言扫地机产品有很多的电机控制,滚刷电机1个,边刷电机1-2个,清水泵电机,风机一个,部分中高端产品支持抹布功能,也就是存在抹布盘电机,还有追觅科沃斯石头等边刷抬升电机,滚刷抬升电机等的,这些电机有直流有刷电机,直接无刷电机,步进电机,电磁阀,挪动泵等不同类型。电机的原理,驱动控制方式也不行。接下来一段时间的几个文章会作个专题分析分享。直流有刷电机会自动持续
那个抄袭的大张伟
猫小努
最近一直在追《即刻电音》这个综艺,除了觉得出场节目的音乐制作人有意思之外,也觉得有两个导师挺有趣的(另外一个就忽略了吧)。孙艺兴在上一篇文章里面已经说过了,那么这篇就说说我们的大老师,大张伟吧。其实在节目刚开始大张伟出来的时候,我以为他是属于导师里面来活跃气氛负责搞笑的,毕竟孙艺兴属于卖萌卖傻卖老实的,尚雯婕一般负责装逼耍狠的,而大张伟一贯以来上综艺的形象基本上都是蹦蹦跳跳带动气氛的。谁知道,两期
2018-07-23-催眠日作业-#不一样的31天#-66小鹿
小鹿_33
预言日:人总是在逃避命运的路上,与之不期而遇。心理学上有个著名的名词,叫做自证预言;经济学上也有一个很著名的定律叫做,墨菲定律;在灵修派上,还有一个很著名的法则,叫做吸引力法则。这3个领域的词,虽然看起来不太一样,但是他们都在告诉人们一个现象:你越担心什么,就越有可能会发生什么。同样的道理,你越想得到什么,就应该要积极地去创造什么。无论是自证预言,墨菲定律还是吸引力法则,对人都有正反2个维度的影响
《大清方方案》| 第二话
谁佐清欢
和珅究竟说了些什么?竟能令堂堂九五之尊龙颜失色!此处暂且按下不表;单说这位乾隆皇帝,果真不愧是康熙从小带过的,一旦决定了要做的事,便杀伐决断毫不含糊。他当即亲自拟旨,着令和珅为钦差大臣,全权负责处理方方事件,并钦赐尚方宝剑,遇急则三品以下官员可先斩后奏。和珅身负皇上重托,岂敢有半点怠慢,当夜即率领相关人等,马不停蹄杀奔江汉。这一路上,和珅的几位幕僚一直在商讨方方事件的处置方案。有位年轻幕僚建议快刀
【一起学Rust | 设计模式】习惯语法——使用借用类型作为参数、格式化拼接字符串、构造函数
广龙宇
一起学Rust#Rust设计模式rust设计模式开发语言
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录前言一、使用借用类型作为参数二、格式化拼接字符串三、使用构造函数总结前言Rust不是传统的面向对象编程语言,它的所有特性,使其独一无二。因此,学习特定于Rust的设计模式是必要的。本系列文章为作者学习《Rust设计模式》的学习笔记以及自己的见解。因此,本系列文章的结构也与此书的结构相同(后续可能会调成结构),基本上分为三个部分
本周第二次约练
2cfbdfe28a51
中原焦点团队中24初26刘霞2021.12.3约练161次,分享第368天当事人虽然是带着问题来的,但是咨询过程中发现,她是经过自己不断地调整和努力才走到现在的,看到当事人的不容易,找到例外,发现资源,力量感也就随之而来。增强画面感,或者说重温,会给当事人带来更深刻的感受。
2022-07-08
保利学府里李楚怡1307022
——保利碧桂园学府里——童梦奇趣【科学实验室】「7.9-7.10」✏玩出大智慧约99-144㎡二期全新升级力作
《庄子.达生9》
钱江潮369
【原文】孔子观于吕梁,县水三十仞,流沫四十里,鼋鼍鱼鳖之所不能游也。见一丈夫游之,以为有苦而欲死也,使弟子并流而拯之。数百步而出,被发行歌而游于塘下。孔子从而问焉,曰:“吾以子为鬼,察子则人也。请问,‘蹈水有道乎’”曰:“亡,吾无道。吾始乎故,长乎性,成乎命。与齐俱入,与汩偕出,从水之道而不为私焉。此吾所以蹈之也。”孔子曰:“何谓始乎故,长乎性,成乎命?”曰:“吾生于陵而安于陵,故也;长于水而安于
直抒《紫罗兰永恒花园外传》
雷姆的黑色童话
没看过《紫罗兰永恒花园》的我莫名的看完了《紫罗兰永恒花园外传》,又莫名的被故事中的姐妹之情狠狠地感动了的一把。感动何在:困苦中相依为命的姐妹二人被迫分离,用一个人的自由换取另一个人的幸福。之后,虽相隔不知几许依旧心心念念彼此牵挂。这种深深的姐妹情谊就是令我为之动容的所在。贝拉和泰勒分别影片开始,海天之间一个孩童凭栏眺望,手中拿着折旧的信纸。镜头一转,挑灯伏案的薇尔莉特正在打字机前奋笔疾书。这些片段
基于社交网络算法优化的二维最大熵图像分割
智能算法研学社(Jack旭)
智能优化算法应用图像分割算法php开发语言
智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码文章目录智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码1.前言2.二维最大熵阈值分割原理3.基于社交网络优化的多阈值分割4.算法结果:5.参考文献:6.Matlab代码摘要:本文介绍基于最大熵的图像分割,并且应用社交网络算法进行阈值寻优。1.前言阅读此文章前,请阅读《图像分割:直方图区域划分及信息统计介绍》htt
18-115 一切思考不能有效转化为行动,都TM是扯淡!
成长时间线
7月25号写了一篇关于为什么会断更如此严重的反思,然而,之后日更仅仅维持了一周,又出现了这次更严重的现象。从8月2号到昨天8月6号,5天!又是5天没有更文!虽然这次断更时间和上次一样,那为什么说这次更严重?因为上次之后就分析了问题的原因,以及应该如何解决,按理说应该会好转,然而,没过几天严重断更的现象再次出现,想想,经过反思,问题依然没有解决与改变,这让我有些担忧。到底是哪里出了问题,难道我就真的
直返最高等级与直返APP:无需邀请码的返利新体验
古楼
随着互联网的普及和电商的兴起,直返模式逐渐成为一种流行的商业模式。在这种模式下,消费者通过购买产品或服务,获得一定的返利,并可以分享给更多的人。其中,直返最高等级和直返APP是直返模式中的重要概念和工具。本文将详细介绍直返最高等级的概念、直返APP的使用以及与邀请码的关系。【高省】APP(高佣金领导者)是一个自用省钱佣金高,分享推广赚钱多的平台,百度有几百万篇报道,运行三年,稳定可靠。高省APP,
如果做到轻松在股市赚钱?只要坚持这三个原则。
履霜之人
大A股里向来就有七亏二平一赚的说法,能赚钱的都是少数人。否则股市就成了慈善机构,人人都有钱赚,谁还要上班?所以说亏钱是正常的,或者说是应该的。那么那些赚钱的人又是如何做到的呢?普通人能不能找到捷径去分一杯羹呢?方法是有的,但要做到需要你有极高的自律。第一,控制仓位,散户最大的问题是追涨杀跌,只要涨起来,就把钱往股票上砸,然后被套,隔天跌的受不了,又一刀切,全部割肉。来来回回间,遍体鳞伤。所以散户首
DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
特殊的拜年
飘雪的天堂
文/雪儿大年初一,家家户户没有了轰响的鞭炮声,大街上没有了人流涌动的喧闹,几乎看不到人影,变得冷冷清清。天刚亮不大会儿,村里的大喇叭响了起来:由于当前正值疾病高发期,流感流行的高峰期。同时,新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎进入第二波流行的上升期。为了自己和他人的健康安全着想,请大家尽量不要串门拜年,不要在街里走动。可以通过手机微信,视频,电话,信息拜年……今年的春节真是特别。禁止燃放鞭炮,烟花爆竹,禁止出村
高端密码学院笔记285
柚子_b4b4
高端幸福密码学院(高级班)幸福使者:李华第(598)期《幸福》之回归内在深层生命原动力基础篇——揭秘“激励”成长的喜悦心理案例分析主讲:刘莉一,知识扩充:成功=艰苦劳动+正确方法+少说空话。贪图省力的船夫,目标永远下游。智者的梦再美,也不如愚人实干的脚印。幸福早课堂2020.10.16星期五一笔记:1,重视和珍惜的前提是知道它的价值非常重要,当你珍惜了,你就真正定下来,真正的学到身上。2,大家需要
2020-04-12每天三百字之连接与替代
冷眼看潮
不知道是不是好为人师,有时候还真想和别人分享一下我对某些现象的看法或者解释。人类社会不断发展进步的过程,就是不断连接与替代的过程。人类发现了火并应用火以后,告别了茹毛饮血的野兽般的原始生活(火烧、烹饪替代了生食)人类用石器代替了完全手工,工具的使用使人类进步一大步。类似这样的替代还有很多,随着科技的发展,有更多的原始的事物被替代,代之以更高效、更先进的技术。在近现代,汽车替代了马车,高速公路和铁路
398顺境,逆境
戴骁勇
2018.11.27周二雾霾最近儿子进入了一段顺境期,今天表现尤其不错。今天的数学测试成绩喜人,没有出现以往的计算错误,整个卷面书写工整,附加题也在规定时间内完成且做对。为迎接体育测试的锻炼有了质的飞跃。坐位体前屈成绩突飞猛进,估测成绩能达到12cm,这和上次测试的零分来比,简直是逆袭。儿子还在不断锻炼和提升,唯恐到时候掉链子。跑步姿势在我的调教下,逐渐正规起来,速度随之也有了提升。今晚测试的50
Java实现的简单双向Map,支持重复Value
superlxw1234
java双向map
关键字:Java双向Map、DualHashBidiMap
有个需求,需要根据即时修改Map结构中的Value值,比如,将Map中所有value=V1的记录改成value=V2,key保持不变。
数据量比较大,遍历Map性能太差,这就需要根据Value先找到Key,然后去修改。
即:既要根据Key找Value,又要根据Value
PL/SQL触发器基础及例子
百合不是茶
oracle数据库触发器PL/SQL编程
触发器的简介;
触发器的定义就是说某个条件成立的时候,触发器里面所定义的语句就会被自动的执行。因此触发器不需要人为的去调用,也不能调用。触发器和过程函数类似 过程函数必须要调用,
一个表中最多只能有12个触发器类型的,触发器和过程函数相似 触发器不需要调用直接执行,
触发时间:指明触发器何时执行,该值可取:
before:表示在数据库动作之前触发
[时空与探索]穿越时空的一些问题
comsci
问题
我们还没有进行过任何数学形式上的证明,仅仅是一个猜想.....
这个猜想就是; 任何有质量的物体(哪怕只有一微克)都不可能穿越时空,该物体强行穿越时空的时候,物体的质量会与时空粒子产生反应,物体会变成暗物质,也就是说,任何物体穿越时空会变成暗物质..(暗物质就我的理
easy ui datagrid上移下移一行
商人shang
js上移下移easyuidatagrid
/**
* 向上移动一行
*
* @param dg
* @param row
*/
function moveupRow(dg, row) {
var datagrid = $(dg);
var index = datagrid.datagrid("getRowIndex", row);
if (isFirstRow(dg, row)) {
Java反射
oloz
反射
本人菜鸟,今天恰好有时间,写写博客,总结复习一下java反射方面的知识,欢迎大家探讨交流学习指教
首先看看java中的Class
package demo;
public class ClassTest {
/*先了解java中的Class*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任何一个类都
springMVC 使用JSR-303 Validation验证
杨白白
springmvc
JSR-303是一个数据验证的规范,但是spring并没有对其进行实现,Hibernate Validator是实现了这一规范的,通过此这个实现来讲SpringMVC对JSR-303的支持。
JSR-303的校验是基于注解的,首先要把这些注解标记在需要验证的实体类的属性上或是其对应的get方法上。
登录需要验证类
public class Login {
@NotEmpty
log4j
香水浓
log4j
log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG, STDOUT, DAILYFILE, HTML, DATABASE
#log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG, STDOUT, DAILYFILE, ROLLINGFILE, HTML
#console
log4j.appender.STDOUT=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4
使用ajax和history.pushState无刷新改变页面URL
agevs
jquery框架Ajaxhtml5chrome
表现
如果你使用chrome或者firefox等浏览器访问本博客、github.com、plus.google.com等网站时,细心的你会发现页面之间的点击是通过ajax异步请求的,同时页面的URL发生了了改变。并且能够很好的支持浏览器前进和后退。
是什么有这么强大的功能呢?
HTML5里引用了新的API,history.pushState和history.replaceState,就是通过
centos中文乱码
AILIKES
centosOSssh
一、CentOS系统访问 g.cn ,发现中文乱码。
于是用以前的方式:yum -y install fonts-chinese
CentOS系统安装后,还是不能显示中文字体。我使用 gedit 编辑源码,其中文注释也为乱码。
后来,终于找到以下方法可以解决,需要两个中文支持的包:
fonts-chinese-3.02-12.
触发器
baalwolf
触发器
触发器(trigger):监视某种情况,并触发某种操作。
触发器创建语法四要素:1.监视地点(table) 2.监视事件(insert/update/delete) 3.触发时间(after/before) 4.触发事件(insert/update/delete)
语法:
create trigger triggerName
after/before
JS正则表达式的i m g
bijian1013
JavaScript正则表达式
g:表示全局(global)模式,即模式将被应用于所有字符串,而非在发现第一个匹配项时立即停止。 i:表示不区分大小写(case-insensitive)模式,即在确定匹配项时忽略模式与字符串的大小写。 m:表示
HTML5模式和Hashbang模式
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSHashbang模式HTML5模式
我们可以用$locationProvider来配置$location服务(可以采用注入的方式,就像AngularJS中其他所有东西一样)。这里provider的两个参数很有意思,介绍如下。
html5Mode
一个布尔值,标识$location服务是否运行在HTML5模式下。
ha
[Maven学习笔记六]Maven生命周期
bit1129
maven
从mvn test的输出开始说起
当我们在user-core中执行mvn test时,执行的输出如下:
/software/devsoftware/jdk1.7.0_55/bin/java -Dmaven.home=/software/devsoftware/apache-maven-3.2.1 -Dclassworlds.conf=/software/devs
【Hadoop七】基于Yarn的Hadoop Map Reduce容错
bit1129
hadoop
运行于Yarn的Map Reduce作业,可能发生失败的点包括
Task Failure
Application Master Failure
Node Manager Failure
Resource Manager Failure
1. Task Failure
任务执行过程中产生的异常和JVM的意外终止会汇报给Application Master。僵死的任务也会被A
记一次数据推送的异常解决端口解决
ronin47
记一次数据推送的异常解决
需求:从db获取数据然后推送到B
程序开发完成,上jboss,刚开始报了很多错,逐一解决,可最后显示连接不到数据库。机房的同事说可以ping 通。
自已画了个图,逐一排除,把linux 防火墙 和 setenforce 设置最低。
service iptables stop
巧用视错觉-UI更有趣
brotherlamp
UIui视频ui教程ui自学ui资料
我们每个人在生活中都曾感受过视错觉(optical illusion)的魅力。
视错觉现象是双眼跟我们开的一个玩笑,而我们往往还心甘情愿地接受我们看到的假象。其实不止如此,视觉错现象的背后还有一个重要的科学原理——格式塔原理。
格式塔原理解释了人们如何以视觉方式感觉物体,以及图像的结构,视角,大小等要素是如何影响我们的视觉的。
在下面这篇文章中,我们首先会简单介绍一下格式塔原理中的基本概念,
线段树-poj1177-N个矩形求边长(离散化+扫描线)
bylijinnan
数据结构算法线段树
package com.ljn.base;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* POJ 1177 (线段树+离散化+扫描线),题目链接为http://poj.org/problem?id=1177
HTTP协议详解
chicony
http协议
引言
Scala设计模式
chenchao051
设计模式scala
Scala设计模式
我的话: 在国外网站上看到一篇文章,里面详细描述了很多设计模式,并且用Java及Scala两种语言描述,清晰的让我们看到各种常规的设计模式,在Scala中是如何在语言特性层面直接支持的。基于文章很nice,我利用今天的空闲时间将其翻译,希望大家能一起学习,讨论。翻译
安装mysql
daizj
mysql安装
安装mysql
(1)删除linux上已经安装的mysql相关库信息。rpm -e xxxxxxx --nodeps (强制删除)
执行命令rpm -qa |grep mysql 检查是否删除干净
(2)执行命令 rpm -i MySQL-server-5.5.31-2.el
HTTP状态码大全
dcj3sjt126com
http状态码
完整的 HTTP 1.1规范说明书来自于RFC 2616,你可以在http://www.talentdigger.cn/home/link.php?url=d3d3LnJmYy1lZGl0b3Iub3JnLw%3D%3D在线查阅。HTTP 1.1的状态码被标记为新特性,因为许多浏览器只支持 HTTP 1.0。你应只把状态码发送给支持 HTTP 1.1的客户端,支持协议版本可以通过调用request
asihttprequest上传图片
dcj3sjt126com
ASIHTTPRequest
NSURL *url =@"yourURL";
ASIFormDataRequest*currentRequest =[ASIFormDataRequest requestWithURL:url];
[currentRequest setPostFormat:ASIMultipartFormDataPostFormat];[currentRequest se
C语言中,关键字static的作用
e200702084
C++cC#
在C语言中,关键字static有三个明显的作用:
1)在函数体,局部的static变量。生存期为程序的整个生命周期,(它存活多长时间);作用域却在函数体内(它在什么地方能被访问(空间))。
一个被声明为静态的变量在这一函数被调用过程中维持其值不变。因为它分配在静态存储区,函数调用结束后并不释放单元,但是在其它的作用域的无法访问。当再次调用这个函数时,这个局部的静态变量还存活,而且用在它的访
win7/8使用curl
geeksun
win7
1. WIN7/8下要使用curl,需要下载curl-7.20.0-win64-ssl-sspi.zip和Win64OpenSSL_Light-1_0_2d.exe。 下载地址:
http://curl.haxx.se/download.html 请选择不带SSL的版本,否则还需要安装SSL的支持包 2. 可以给Windows增加c
Creating a Shared Repository; Users Sharing The Repository
hongtoushizi
git
转载自:
http://www.gitguys.com/topics/creating-a-shared-repository-users-sharing-the-repository/ Commands discussed in this section:
git init –bare
git clone
git remote
git pull
git p
Java实现字符串反转的8种或9种方法
Josh_Persistence
异或反转递归反转二分交换反转java字符串反转栈反转
注:对于第7种使用异或的方式来实现字符串的反转,如果不太看得明白的,可以参照另一篇博客:
http://josh-persistence.iteye.com/blog/2205768
/**
*
*/
package com.wsheng.aggregator.algorithm.string;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
代码实现任意容量倒水问题
home198979
PHP算法倒水
形象化设计模式实战 HELLO!架构 redis命令源码解析
倒水问题:有两个杯子,一个A升,一个B升,水有无限多,现要求利用这两杯子装C
Druid datasource
zhb8015
druid
推荐大家使用数据库连接池 DruidDataSource. http://code.alibabatech.com/wiki/display/Druid/DruidDataSource DruidDataSource经过阿里巴巴数百个应用一年多生产环境运行验证,稳定可靠。 它最重要的特点是:监控、扩展和性能。 下载和Maven配置看这里: http
两种启动监听器ApplicationListener和ServletContextListener
spjich
javaspring框架
引言:有时候需要在项目初始化的时候进行一系列工作,比如初始化一个线程池,初始化配置文件,初始化缓存等等,这时候就需要用到启动监听器,下面分别介绍一下两种常用的项目启动监听器
ServletContextListener
特点: 依赖于sevlet容器,需要配置web.xml
使用方法:
public class StartListener implements
JavaScript Rounding Methods of the Math object
何不笑
JavaScriptMath
The next group of methods has to do with rounding decimal values into integers. Three methods — Math.ceil(), Math.floor(), and Math.round() — handle rounding in differen