iOS 蓝牙开发主要有以下几种方法:
1. GameKit.framework
是最基本的蓝牙通讯框架,通过蓝牙可以实现文件的共享(仅限设备沙盒中的文件), 只能存在于iOS设备之间,同一个应用内连接.多用于游戏开发,比如五子棋对战.从 iOS7 开始过期了.
2. CoreBlueTooth.framework
必须要支持蓝牙4.0,且iPhone4以上,即至少4s手机。可与第三方设备交互数据,蓝牙4.0以低功耗著称,所以一般被称为BLE(bluetooth low energy).
3. ExternalAccessory.framework
可于第三方蓝牙设备交互,但是它有个不好的地方,External Accessory 需要拿到苹果公司的MFI认证。官方demo是 EADemo 和 BTLE .
4. Multipeer Connectivity.framework
只能用于iOS设备之间,且iOS7才引入。主要是为了共享文件,但是文件是在 Sandbox 内.
一般推荐使用第二种.
CoreBluetooth 介绍
CoreBluetooth框架的核心其实是两个东西,peripheral 和 central, 可以理解成外设和中心。对应他们分别有一组相关的API和类,如下图所示:
每个蓝牙4.0的设备都是通过服务和特征来展示自己的,一个设备必然包含一个或多个服务,每个服务下面又包含若干个特征。特征是与外界交互的最小单位。比如说,一台蓝牙4.0设备,用特征A来描述自己的出厂信息,用特征B来与收发数据等。
服务和特征都是用UUID来唯一标识的,UUID的概念如果不清楚请自行google,国际蓝牙组织为一些很典型的设备(比如测量心跳和血压的设备)规定了标准的service UUID.
特征的UUID比较多,这里就不列举了, 如下:
#define BLE_UUID_ALERT_NOTIFICATION_SERVICE 0x1811
#define BLE_UUID_BATTERY_SERVICE 0x180F
#define BLE_UUID_BLOOD_PRESSURE_SERVICE 0x1810
#define BLE_UUID_CURRENT_TIME_SERVICE 0x1805
#define BLE_UUID_CYCLING_SPEED_AND_CADENCE 0x1816
#define BLE_UUID_DEVICE_INFORMATION_SERVICE 0x180A
#define BLE_UUID_GLUCOSE_SERVICE 0x1808
#define BLE_UUID_HEALTH_THERMOMETER_SERVICE 0x1809
#define BLE_UUID_HEART_RATE_SERVICE 0x180D
#define BLE_UUID_HUMAN_INTERFACE_DEVICE_SERVICE 0x1812
#define BLE_UUID_IMMEDIATE_ALERT_SERVICE 0x1802
#define BLE_UUID_LINK_LOSS_SERVICE 0x1803
#define BLE_UUID_NEXT_DST_CHANGE_SERVICE 0x1807
#define BLE_UUID_PHONE_ALERT_STATUS_SERVICE 0x180E
#define BLE_UUID_REFERENCE_TIME_UPDATE_SERVICE 0x1806
#define BLE_UUID_RUNNING_SPEED_AND_CADENCE 0x1814
#define BLE_UUID_SCAN_PARAMETERS_SERVICE 0x1813
#define BLE_UUID_TX_POWER_SERVICE 0x1804
#define BLE_UUID_CGM_SERVICE 0x181A
作为一个中心要实现完整的通讯,一般要经过这样几个步骤:
建立中心角色 — 扫描外设(discover)— 连接外设(connect) — 扫描外设中的服务和特征(discover) — 与外设做数据交互(explore and interact) — 断开连接(disconnect)。
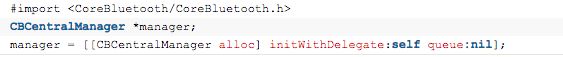
1. 建立中心角色
首先在我自己类的头文件中要包含CoreBluetooth的头文件,并继承两个协议,代码如下:
2. 扫描外设(discover)
在代理方法中扫描外部设备, 代码如下:
/**
* scanForPeripheralsWithServices :如果传入指定的数组,那么就只会扫描数组中对应ID的设备
* 如果传入nil,那么就是扫描所有可以发现的设备
* 扫描完外部设备就会通知CBCentralManager的代理 */
- (void)centralManagerDidUpdateState:(CBCentralManager *)central {
if ([central state] ==CBCentralManagerStatePoweredOn) {
[manager scanForPeripheralsWithServices:nil options:options];
}}
/**
* 发现外部设备,每发现一个就会调用这个方法
* 所以可以使用一个数组来存储每次扫描完成的数组 */
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager *)central didDiscoverPeripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral advertisementData:(NSDictionary *)advertisementData RSSI:(NSNumber *)RSSI {
//有可能会导致重复添加扫描到的外设
//所以需要先判断数组中是否包含这个外设
if (![self.peripherals containsObject:peripheral]) {
[self.peripherals addObject:peripheral];
}}
3. 连接外设(connect)
当扫描到4.0的设备后,系统会通过回调函数告诉我们设备的信息,然后我们就可以连接相应的设备,代码如下:
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager *)central didDiscoverPeripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral advertisementData:(NSDictionary*)advertisementData RSSI:(NSNumber*)RSSI {
if ([peripheral.name isEqualToString:BLE_SERVICE_NAME]){
[self connect:peripheral];
}}
-(BOOL)connect:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral{
self.manager.delegate =self;
[self.manager connectPeripheral:peripheral options:[NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES] forKey:CBConnectPeripheralOptionNotifyOnDisconnectionKey]];
}
4. 扫描外设中的服务和特征(discover)
同样的,当连接成功后,系统会通过回调函数告诉我们,然后我们就在这个回调里去扫描设备下所有的服务和特征,代码如下:
- (void)centralManager:(CBCentralManager*)central didConnectPeripheral:(CBPeripheral*)peripheral {
NSLog(@"Did connect to peripheral: %@", peripheral);
_testPeripheral = peripheral;
[peripheral setDelegate:self];
[peripheral discoverServices:nil];
}
一个设备里的服务和特征往往比较多,大部分情况下我们只是关心其中几个,所以一般会在发现服务和特征的回调里去匹配我们关心那些,比如下面的代码:
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral didDiscoverServices:(NSError*)error {
NSLog(@"didDiscoverServices");
if(error) {
NSLog(@"Discovered services for %@ with error: %@", peripheral.name, [error localizedDescription]);
if([self.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(DidNotifyFailConnectService:withPeripheral:error:)])
[self.delegate DidNotifyFailConnectService:nil withPeripheral:nil error:nil];
return;}
for(CBService *service in peripheral.services){
//发现服务
if([service.UUID isEqual:[CBUUID UUIDWithString:UUIDSTR_ISSC_PROPRIETARY_SERVICE]]) {
NSLog(@"Service found with UUID: %@", service.UUID);
//查找特征[peripheral discoverCharacteristics:nil forService:service];
break;}}}
//-----------------
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral *)peripheral didDiscoverCharacteristicsForService:(CBService *)service error:(NSError*)error {
if(error) {
NSLog(@"Discovered characteristics for %@ with error: %@", service.UUID, [error localizedDescription]);
[selferror];
return;}
NSLog(@"服务:%@",service.UUID);
for(CBCharacteristic *characteristic in service.characteristics){
//发现特征
if([characteristic.UUID isEqual:[CBUUID UUIDWithString:@"xxxxxxx"]]) {
NSLog(@"监听:%@",characteristic);
//监听特征[self.peripheral setNotifyValue:YES forCharacteristic:characteristic];}}}
相信你应该已经注意到了,回调函数都是以"did"开头的,这些函数不用你调用,达到条件后系统后自动调用。
5. 与外设做数据交互(explore and interact)
发送数据很简单,我们可以封装一个如下的函数:
//写数据
-(void)writeChar:(NSData*)data {
[_testPeripheral writeValue:data forCharacteristic:_writeCharacteristic type:CBCharacteristicWriteWithResponse];
}
_testPeripheral和_writeCharacteristic是前面我们保存的设备对象和可以读写的特征。
然后我们可以在外部调用它,比如当然我要触发刷卡时,先组好数据包,然后调用发送函数:
-(void)msrRead {
unsigned char command[512] = {0};
unsigned char char *pTmp;
int nSendLen =0;
unsigned char ucCrc[3] = {0};
_commandType = COMMAND_MSR_READ;
pTmp = command;
*pTmp =0x02;//start
pTmp++;
*pTmp =0xc1;//main cmd
pTmp++;
*pTmp =0x07;//sub cmd
pTmp++;
nSendLen =2;
*pTmp = nSendLen/256;
pTmp++;
*pTmp = nSendLen%256;
pTmp++;
*pTmp =0x00;//sub cmd
pTmp++;
*pTmp =0x00;//sub cmd
pTmp++;
Crc16CCITT(command+1,pTmp-command-1,ucCrc);
memcpy(pTmp,ucCrc,2);
NSData*data = [[NSData alloc]initWithBytes:&command length:9];
NSLog(@"send data:%@", data);
[g_BLEInstance.recvDatasetLength:0];
[g_BLEInstance writeChar:data];
}
数据的读分为两种,一种是直接读(reading directly),另外一种是订阅(subscribe)。从名字也能基本理解两者的不同。实际使用中具体用一种要看具体的应用场景以及特征本身的属性。前一个好理解,特征本身的属性是指什么呢?特征有个properties字段(characteristic.properties),它是一个整型值,有如下几个定义:
enum{
CBCharacteristicPropertyBroadcast =0x01,
CBCharacteristicPropertyRead =0x02,
CBCharacteristicPropertyWriteWithoutResponse =0x04,
CBCharacteristicPropertyWrite =0x08,
CBCharacteristicPropertyNotify =0x10,
CBCharacteristicPropertyIndicate =0x20,
CBCharacteristicPropertyAuthenticatedSignedWrites =0x40,
CBCharacteristicPropertyExtendedProperties =0x80,
};
比如说,你要交互的特征,它的properties的值是0x10,表示你只能用订阅的方式来接收数据。我这里是用订阅的方式,启动订阅的代码如下:
//监听设备
-(void)startSubscribe{
[_testPeripheral setNotifyValue:YES forCharacteristic:_readCharacteristic];
}
当设备有数据返回时,同样是通过一个系统回调通知我,如下所示:
- (void)peripheral:(CBPeripheral*)peripheral didUpdateValueForCharacteristic:(CBCharacteristic*)characteristic error:(NSError*)error{
if(error){
NSLog(@"Error updating value for characteristic %@ error: %@", characteristic.UUID, [error localizedDescription]);
if([_mainMenuDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(DidNotifyReadError:)])
[_mainMenuDelegateDidNotifyReadError:error];
return;}
[_recvData appendData:characteristic.value];
if([_recvData length] >=5){//已收到长度
unsigned char char* buffer = (unsigned char char*)[_recvData bytes];
int nLen = buffer[3]*256+ buffer[4];
if([_recvData length] == (nLen+3+2+2)){
//接收完毕,通知代理做事
if([_mainMenuDelegate respondsToSelector:@selector(DidNotifyReadData)])
[_mainMenuDelegateDidNotifyReadData];}}}
6. 断开连接(disconnect)
这个比较简单,只需要一个API就行了,代码如下:
//主动断开设备
-(void)disConnect {
if(_testPeripheral !=nil) {
NSLog(@"disConnect start");
[manager cancelPeripheralConnection:_testPeripheral]; }}