demo地址
Android组件化专题,详细讲解组件化的使用及配置,以及实现的原理。
本文章讲解了组件化的由来及配置,下期讲解页面路由跳转及路由原理与apt
1. 组件化的由来
模块化、组件化和插件化的关系?
(摘自百度百科)模块化是指解决一个复杂的问题时自顶向下逐层把系统划分为若干个模块的过程,各个模块可独立工作。
在技术开发领域,模块化是指拆分代码,当代码特别臃肿的时候,用模块化将代码分而治之、解耦分层。
在Android的领域模块化具体的实施方法为:组件化和插件化。
更加详细的讲解
组件化和插件化的区别
一套完整的插件化或组件化都必须能够实现单独调试、集成编译、数据传输、UI 跳转、生命周期和代码边界这六大功能。插件化和组件化最重要而且是唯一的区别的就是:插件化可以动态增加和修改线上的模块,组件化的动态能力相对较弱,只能对线上已有模块进行动态的加载和卸载,不能新增和修改。
2. 怎样实现组件化
要实现组件化需要考虑的问题主要包括下面几个:
- 代码解耦。将一个庞大的工程拆分解耦,这是非常耗时耗力的工作,但这也是最基础最重要的一步
- 数据传递。每个组件都有可能提供给其他组件使用,主项目与组件、组件与组件之间的数据传递
- UI跳转。
- 组件的生命周期。组件加载、卸载和降维的生命周期
- 集成调试。在开发阶段如何做到按需的编译组件?一次调试中可能只有一两个组件参与集成,这样编译的时间就会大大降低,提高开发效率。
- 代码隔离。如何杜绝耦合的产生。
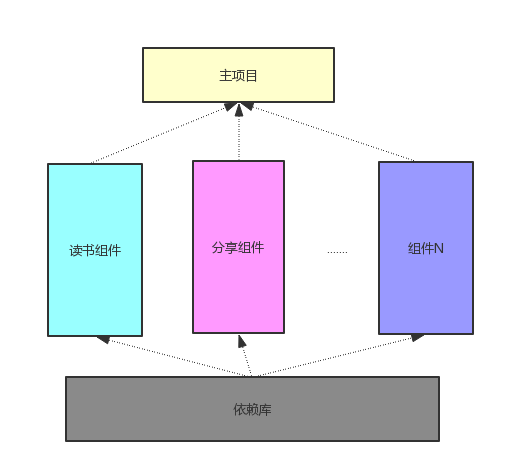
实现组件化的第一步 整理代码拆分结构
实现组件化的第一步首先是,整理项目工程结构,明确哪些功能是可以作为组件。
建议画图整理项目结构,如下图:
实现组件化的第二步 在拆分代码之前进行基础配置
统一整理builde配置以及组件/集成模式的切换,实现组件的单独调试
- 在项目根部新建 config.build
ext {
// false 集成模式
// true 组件模式
isComponent = false
androidConfig = [
compileSdkVersion: 27,
minSdkVersion : 19,
targetSdkVersion : 27,
versionCode : 1,
versionName : "1.0"
]
appIdConfig = [
app : "com.prim.component.demo",
moudle1: "demo.prim.com.moudle1"
]
supportLibrary = "27.1.1"
dependencies = [
appcompatv7: "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:${supportLibrary}"
]
}
- 主build中加入配置
apply from: "config.gradle"
- moudle 配置,调用config.gradle 中的配置
//配置apply
if (isComponent) {
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
} else {
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
}
//获取config文件中的配置 rootProject 项目的主对象
def config = rootProject.ext.androidConfig
def appIdConfig = rootProject.ext.appIdConfig
def dependenciesConfig = rootProject.ext.dependencies
android {
compileSdkVersion config.compileSdkVersion
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion config.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion config.targetSdkVersion
versionCode config.versionCode
versionName config.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
//如果moudle为组件 配置组件的app ID
if (isComponent) {
applicationId appIdConfig.app
}
//配置BuildConfig 代码中可以调用判断moudle是否为组件
buildConfigField("boolean","isComponent",String.valueOf(isComponent))
//配置资源文件
sourceSets {
main {
if (isComponent) {//如果moudle为组件则配置 AndroidManifest
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/moudle/AndroidManifest.xml'
// 配置组件模式下的java代码主文件
java.srcDirs 'src/main/java','src/main/moudle/java'
} else {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/AndroidManifest.xml'
}
}
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation dependenciesConfig.appcompatv7
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:+'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:+'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.2'
}
- app 配置,调用组件
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
def config = rootProject.ext.androidConfig
def appIdConfig = rootProject.ext.appIdConfig
def dependenciesConfig = rootProject.ext.dependencies
android {
compileSdkVersion config.compileSdkVersion
defaultConfig {
applicationId appIdConfig.app
minSdkVersion config.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion config.targetSdkVersion
versionCode config.versionCode
versionName config.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
//配置BuildConfig 代码中可以调用判断moudle是否为组件
buildConfigField("boolean","isComponent",String.valueOf(isComponent))
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation dependenciesConfig.appcompatv7
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:+'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.2'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.2'
if (!isComponent){//当moudle1 不为组件时才允许导入
implementation project(':moudle1')
}
}
下期讲解页面路由跳转及路由原理与apt。
Android的组件化专题:
组件化配置
APT实战
路由框架原理
模块间的业务通信