1. What is a group:
Two or more individuals, interacting and interdependent, who come together to achieve particular objectives
Formal – defined by the organization’s structure
Informal – neither formally structured nor organizationally determined
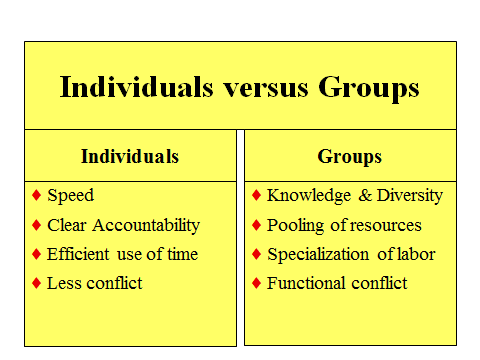
2. Individual vs. group
3. When Are Groups Superior to Individuals:
-Group members are heterogeneous
-Members have complementary skills
-Ideas may be freely communicated
-Good ideas are accepted
4. Tuckman’s 5-stage Model of Group Development
Forming: Awkward, polite early stage of a group’s life
Storming: Open conflict establishes the pecking order
Norming: Group establishes norms of performance and behavior
Performing: Energy devoted to accomplishing goals
Adjourning: Final stage as group prepares to disband
5. Group cohesiveness:
Degree to which group members desire to remain as part of the group – can positively or negatively influence performance!
Influenced by:
+ Severity of initiation into the group
+ Conditions of external threat
+ Amount of time that members spend together
- Size of group (i.e., smaller tends to be more cohesive)
+ History of success
Cautions:
- Cohesiveness can be problematic if group’s goals are
contrary to the parent organization’s goals
- Cohesiveness can blind a group to outside influences
6. Potential Pitfalls
a. Groupthink - Tendency for members of highly cohesive groups to conform so strongly to group pressures regarding a certain decision that they fail to think critically and reject the potentially correcting influences of outsiders.
Strategies for avoiding groupthink
- Promote open inquiry
- Use subgroups
- Appoint “deviant” member
b. Group polarization (Groupshift) - Tendency for members to emerge from group discussion more extreme than they went in.
c. Social Loafing - Tendency for group members to exert less individual effort on cooperative tasks as group size increases
overcome social loafing:
-Make each performer identifiable
--- Public posting
--- Reward individual achievement
- Make work tasks more important and interesting
- Make individuals feel that their contributions are important
7. 6 Common Misperceptions about Teams
#1: Harmony = Better Performance
Actually: Opposite is true when conflict is functional.
#2: Mix it up = Good to bring in new members
Actually: Longer team members together = Better performance.
#3: Bigger the better
Actually: Size biggest impediment to effective collaboration.
#4: Face to face = Passé.
Actually: Teams working remotely at disadvantage.
#5: All depends on team leader.
Actually: Leaders matter, but mostly for team launch and to create effective conditions.
#6: Teamwork is magical = Gather talented people and let them work it out.
Actually: Need careful thought and preparation to facilitate effective teams.