一、字符串String详解
1、实例化
实例化String对象:直接赋值、使用关键字new来进行开辟空间
代码
public class Test41 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello"; //直接赋值
System.out.println(str);
//使用new关键字
String str1 = new String("Hello1");
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
结果:
Hello
Hello1
由上图可以看出,使用new关键字实例化对象,在内存中开辟了两个空间用来存储他们,其中一个是无用的,所以使用第一种直接赋值方式更合理一些,可以更省略一些空间。
2、String的内容比较
由以下代码进行说明
代码
public class Test42 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
System.out.println(a==b);
String str = "Hello";
String str1 = new String("Hello"); //开辟了两个空间地址
System.out.println(str==str1); //"==" 比较的是地址
System.out.println(str.equals(str1)); //"equals"比较的是内容
}
}
结果:
true
false
true
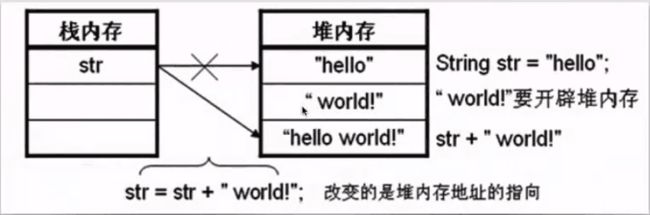
3、字符串内容不可更改
代码
public class Test43 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello";
String str1 = str + " world!";
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
结果:
hello world!
二、String字符串常用方法
1、字符串长度
length()方法
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
System.out.println("str字符串的长度:"+str.length());
}
}
结果:
str字符串的长度:10
2、字符串转换数组
toCharArray()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
// 字符串转换成数组
char data[] = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]+" ");
}
}
}
结果:
h e l l o w o r l d
3、从字符串中取出指定位置的字符
charAt()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
// 从字符串中取出指定位置的字符
System.out.println(str.charAt(7));
}
}
结果:
r
4、字符串与byte数组的转换
getBytes()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
//字符串与byte数组的转换
byte bytes[] = str.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes)+"\t");
}
}
}
结果:
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
helloworld
5、过滤字符串中存在的字符
indexOf()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "[email protected]";
System.out.println("@字符所在的位置:"+str.indexOf("@"));
}
}
结果:
@字符所在的位置:10
6、去掉字符串的前后空格
trim()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello world";
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str.trim());
}
}
结果:
hello world
hello world
7、从字符串中取出子字符串
subString()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
System.out.println(str.substring(4));
System.out.println( str.substring(5));
}
}
结果:
oworld
world
8、大小写转换
toLowerCase()、toUpperCase()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world";
String str1 = "SEC";
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str1.toLowerCase());
}
}
结果:
HELLO WORLD
sec
9、判断字符串的开头结尾字符
endsWith()、startWith()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String email = "[email protected]";
System.out.println(email.startsWith("sec"));
System.out.println(email.endsWith("com"));
System.out.println(email.endsWith("163.com"));
}
}
结果:
true
true
false
10、替换String字符串中的一个字符
replace()
代码
public class Test44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String email = "[email protected]";
System.out.println("将字符串中的e替换成m:"+email.replace('e', 'm'));
}
}
结果:
将字符串中的e替换成m:[email protected]
三、StringBuffer方法
1、认识StringBuffer
缓冲区,本身也是操作字符串,但是与String不同,StringBuffer是可以更改的。
StringBuffer是一个操作类,所以必须通过实例化进行操作。
代码
public class Test45 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello");
System.out.println("StringBuffer更改前:"+sBuffer.toString());
tell(sBuffer);
System.out.println("StringBuffer更改后:"+sBuffer.toString());
String string = "android";
System.out.println("String更改前:"+string);
tell1(string);
System.out.println("String更改后:"+string);
}
public static void tell(StringBuffer s) {
s.append(" I love sec");
}
public static void tell1(String str) {
str = "java";
}
}
结果:
StringBuffer更改前:hello
StringBuffer更改后:hello I love sec
String更改前:android
String更改后:android
2、StringBuffer常用方法
append() 追加
示例
public class Test46 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello ");
sBuffer.append("world");
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
}
}
结果:
hello world
insert() 插入
示例
public class Test46 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello ");
sBuffer.append("world");
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
sBuffer.insert(6, "love "); //从第7个位置开始插入字符love
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
}
}
结果:
hello world
hello love world
replace() 替换
示例
public class Test46 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello ");
sBuffer.append("world");
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
sBuffer.replace(1, 4, "wwtcom");//从第2个位置到第4个位置替换成"wwtcom"
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
}
}
结果:
hello world
hwwtcomo world
indexOf() 字符串存在的位置
示例
public class Test46 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello@");
sBuffer.append("world");
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());
System.out.println("@字符存在的位置:"+sBuffer.indexOf("@"));
}
}
结果:
hello@world
@字符存在的位置:5
3、StringBuffer类的应用
代码
public class Test47 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
str = str + i;
}
System.out.println(str); //使用String需要开辟101个空间,很耗资源
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
sBuffer.append("hello");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sBuffer.append(i);
}
System.out.println(sBuffer.toString());//使用StringBuffer运行很快,不需要重新开辟空间
}
}
结果:
hello0123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
hello0123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
四、StringBuider用法
- 一个可变的字符序列,该类被设计作用StringBuffer的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候。建议优先考虑该类,速度比StringBuffer要快。
- 但是如果设计到线程安全,建议使用StringBuffer。
- 常用方法:
append()、insert()使用方式与StringBuffer是一样的。
代码
public class Test48 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sBuilder = new StringBuilder();
sBuilder.append("Hello ");
sBuilder.append("world");
System.out.println("sBuilder更改前:"+sBuilder.toString());
sBuilder.insert(6, "love "); //从第7个位置开始插入字符love
System.out.println("sBuilder更改后:"+sBuilder.toString());
}
}
结果:
sBuilder更改前:Hello world
sBuilder更改后:Hello love world