1.解压到本地
2.创建测试文件(接收控制台数据输出给控制台)
vim local.yml
filebeat.inputs:
#接收数据,捕获数据
- type: stdin
#类型为,标准输入,就是控制台输入
enabled: true
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
#输出数据,到控制台
pretty: true
enable: true./filebeat -e -c local.yml #启动filebeat
holle
#键入 "holle"
输出结果
{
"@timestamp": "2020-03-26T08:44:32.621Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.0.0"
},
"input": {
"type": "stdin"
},
"agent": {
"type": "filebeat",
"ephemeral_id": "5c55d697-d706-4f10-9ba4-294e2faf741e",
"hostname": "cs25",
"id": "d11ef6a4-735c-4077-976f-3de48d442ef5",
"version": "7.0.0"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"host": {
"name": "cs25"
},
"message": "holle",
"log": {
"offset": 0,
"file": {
"path": ""
}
}
}#看见反馈能看到 "holle" 被捕获到了
3.测试读取文件(捕获文件输出到控制台)
vim flie.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /root/*.log
#捕获数据的路径,*表示该目录下的所有log文件
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
pretty: true
enable: true./filebeat -e -c file.yml #以file.yml 配置文件启动 fliebeat
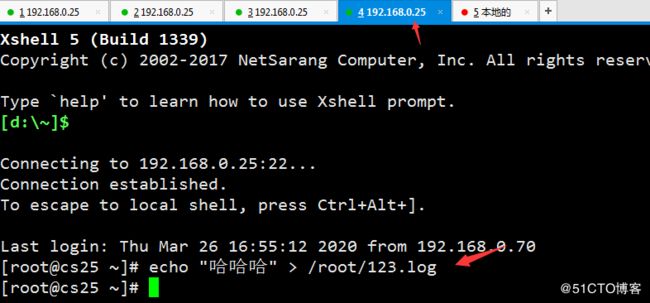
#再启动一个xshell 连接 'echo "哈哈哈" > /root/123.log' 输入几个字符到 123.log
输出结果
{
"@timestamp": "2020-03-26T08:52:36.664Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.0.0"
},
"agent": {
"type": "filebeat",
"ephemeral_id": "d58a676c-13de-4f7c-a1d7-0974d89e06d9",
"hostname": "cs25",
"id": "d11ef6a4-735c-4077-976f-3de48d442ef5",
"version": "7.0.0"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"log": {
"offset": 0,
"file": {
"path": "/root/123.log"
}
},
"message": "哈哈哈",
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"host": {
"name": "cs25"
}
}#看结果反馈,我们输入到文件里的信息,被filebeat 捕获了。
4.自定义字段,tag
vim file_zdy.yml #修改之前的配置文件
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /root/*.log
tags: ["web"]
#添加自定义tag,便于后续的处理
fields:
from: cs
#添加自定义字段
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
output.console:
pretty: true
enable: true再次启动一个xshell 输入数据到"/root/123.log"文件
输出结果
{
"@timestamp": "2020-03-26T09:01:08.561Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "filebeat",
"type": "_doc",
"version": "7.0.0"
},
"message": "666",
"tags": [
"web"
],
"input": {
"type": "log"
},
"fields": {
"from": "cs"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"host": {
"name": "cs25"
},
"agent": {
"ephemeral_id": "5615f0e9-2000-486d-a918-6288d0d431ee",
"hostname": "cs25",
"id": "d11ef6a4-735c-4077-976f-3de48d442ef5",
"version": "7.0.0",
"type": "filebeat"
},
"log": {
"offset": 0,
"file": {
"path": "/root/123.log"
}
}
}#看结果反馈,tag和字段都加上去了
5.输出到Elasticsearch
vim file_el.yml #修改配置文件
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /root/*.log
tags: ["web"]
fields:
from: cs
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
#指定索引的分片数
output.elasticsearch:
#指定输出到elasticsearch,下面hosts是elasticsearch的服务监听地址
hosts: ["192.168.0.25:9200","192.168.0.27:9200","192.168.0.69:9200"]./filebeat -e -c file_el.yml #启动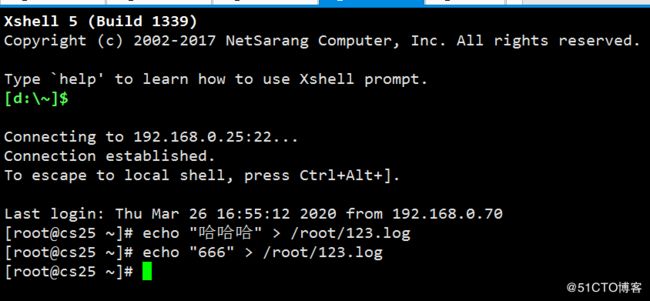
#在另一个xshell 里输入数据到日志里
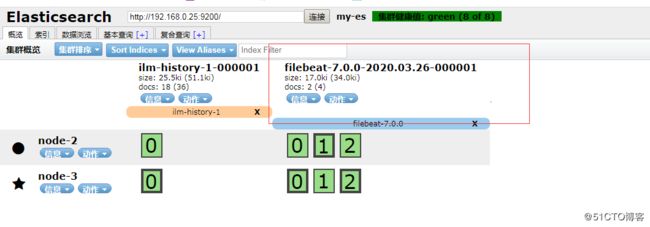
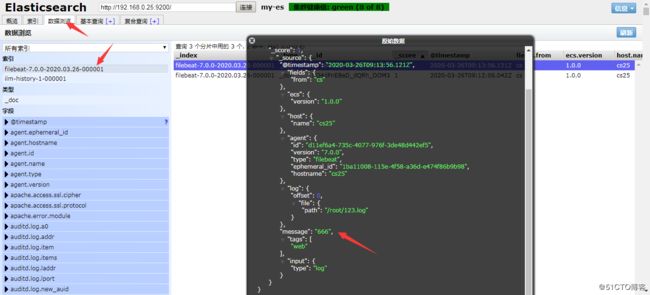
#登录到elasticsearch 上,能看到新创建了一个索引,查看数据也能看到刚刚输入的数据。
Filebeat由两个主要组件组成:prospector 和 harvester。harvester:
负责读取单个文件的内容。
如果文件在读取时被删除或重命名,Filebeat将继续读取文件。prospector
prospector 负责管理harvester并找到所有要读取的文件来源。
如果输入类型为日志,则查找器将查找路径匹配的所有文件,并为每个文件启动一个harvester。
Filebeat目前支持两种prospector类型:log和stdin。
Filebeat如何保持文件的状态
Filebeat 保存每个文件的状态并经常将状态刷新到磁盘上的注册文件中。
该状态用于记住harvester正在读取的最后偏移量,并确保发送所有日志行。
如果输出(例如Elasticsearch或Logstash)无法访问,Filebeat会跟踪最后发送的行,并在输出再次可用时继续读取文件。
在Filebeat运行时,每个prospector内存中也会保存的文件状态信息,当重新启动Filebeat时,将使用注册文件的数据来重建文件状态,Filebeat将每个harvester在从保存的最后偏移量继续读取。文件状态记录在data/registry文件中。
#参数说明
-e: 输出到标准输出,默认输出到syslog和logs下
-c: 指定配置文件
-d: 输出debug信息
6.收集httpd 的日志
vim file_httpd.yml #编辑httpd的filebeat的配置文件
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/httpd/error_log
tags: ["httpd_access"]
#收集访问日志
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/httpd/access_log
tags: ["httpd_error"]
#收集错误日志
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
#指定索引的分片数
output.elasticsearch:
#指定输出到elasticsearch,下面hosts是elasticsearch的服务监听地址
hosts: ["192.168.0.25:9200","192.168.0.27:9200","192.168.0.69:9200"]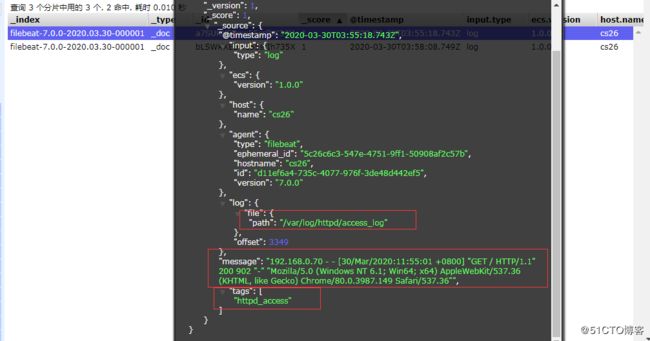
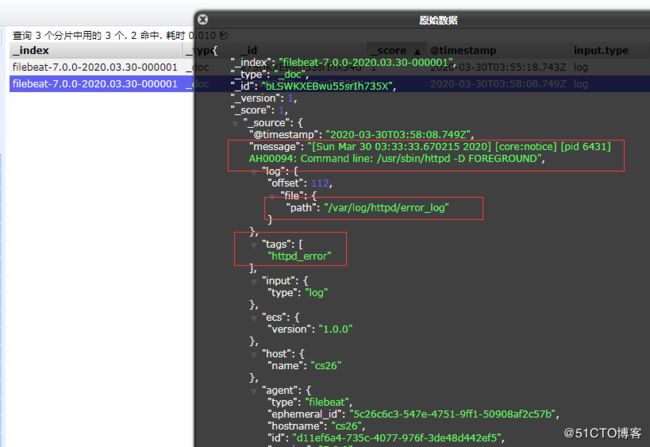
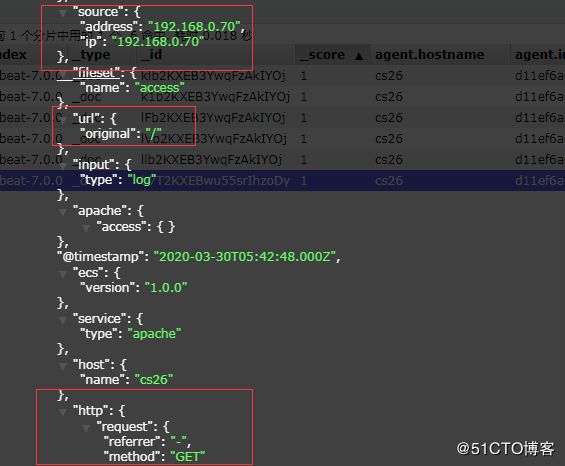
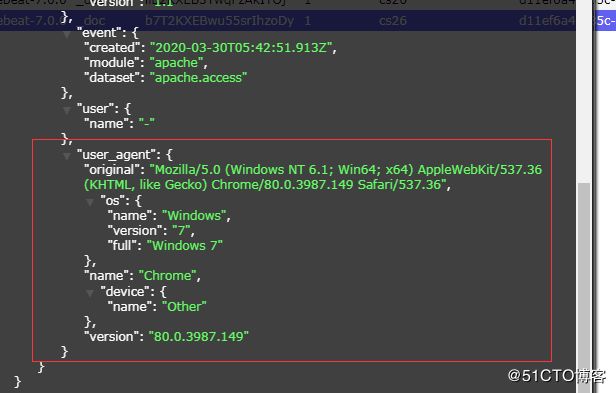
可以看到,在message中已经获取到了httpd的日志,但是,内容并没有经过处理,只是读取到原数据,那么对于我们后期的操作是不利的,有办法解决吗?
7.filebeat——Module
前面要想实现日志数据的读取以及处理都是自己手动配置的,其实,在Filebeat中,有大量的Module,可以简化我们的配置,直接就可以使用,如下:
./filebeat modules enable apache #开启httpd 的mod
./filebeat modules list #查看已开启的modules
vim ${path.config}/modules.d/apache.yml #修改httpd modules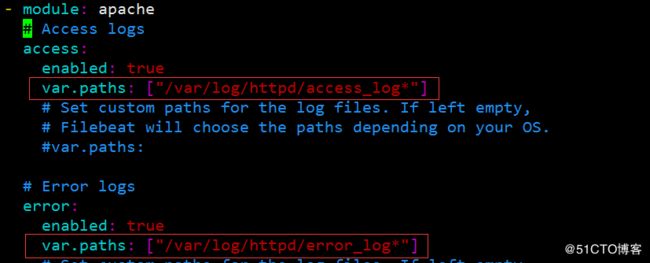
#加入httpd 的日志路径
vim file_httpd.yml #修改httpd的fliebeat配置文件
filebeat.inputs:
#- type: log
# enabled: true
# paths:
# - /var/log/httpd/access_log
# tags: ["httpd_access"]
#- type: log
# enabled: true
# paths:
# - /var/log/httpd/error_log
# tags: ["httpd_error"]
#输入不需要了,由下面的modules 输入
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
#指定索引的分片数
output.elasticsearch:
#指定输出到elasticsearch,下面hosts是elasticsearch的服务监听地址
hosts: ["192.168.0.25:9200","192.168.0.27:9200","192.168.0.69:9200"]
filebeat.config.modules:
path: modules.d/*.yml
#读取这个路径的所有 modules的配置文件,由于只有httpd软件开启了mod,所有只有httpd的生效
reload.enabled: false8.Metricbeat
Metricbeat有2部分组成,一部分是Module,另一部分为Metricset。
Module
收集的对象,如:mysql、redis、nginx、操作系统等;
Metricset
收集指标的集合,如:cpu、memory、network等;
部署与收集系统指标
vim metricbeat.yml #修改默认的配置文件
metricbeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
index.codec: best_compression
setup.kibana:
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.0.25:9200","192.168.0.27:9200","192.168.0.69:9200"]
processors:
- add_host_metadata: ~
- add_cloud_metadata: ~./metricbeat -e #启动即可
#到elasticsearch上查看,多了很多的系统信息
9.收集nginx 状态
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #配置nginx选项,开启nginx状态信息,注意这个需要"--
with-http_stub_status_module" 模块
location /nginx-status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}#最加一个location,开启nginx状态信息
./metricbeat modules enable nginx #开启nginx 的modules
vim modules.d/nginx.yml #修改nginx 的 metricbeat的modules 配置文件
- module: nginx
period: 10s
hosts: ["http://192.168.0.25"]
server_status_path: "nginx-status"./metricbeat modules disable system #关闭收集系统的modules
./metricbeat -e #开启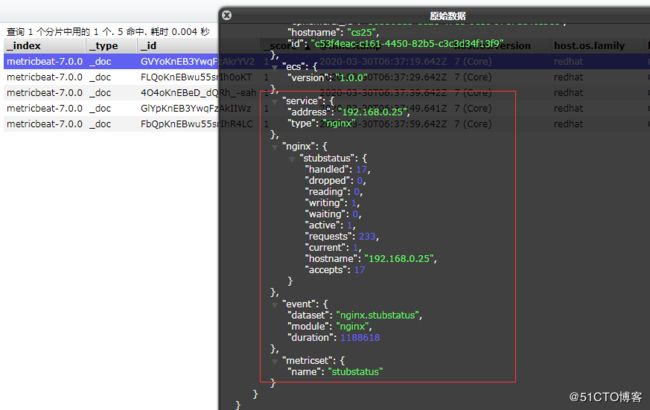
#如图,nginx的指标数据已经被收集了