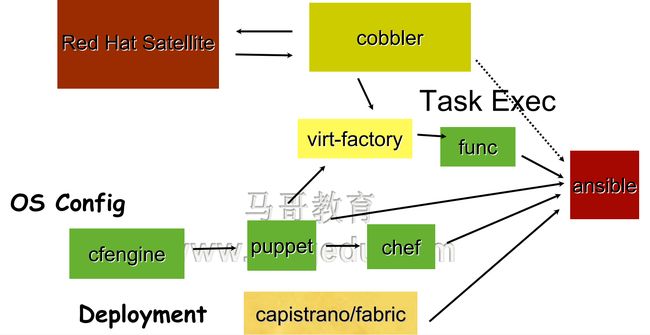
一、常见的自动化运维工具:
OS Provisioning:PXE, Cobbler
OS Config:puppet, saltstack, chef, func
Task Exec:fabric, saltstack, func
Program Deployment:fabric
管理主机控制被管理节点的方式:
agent:被管理节点上需要安装代理程序以接受管理主机的操作;如puppet, func
agentless:被管理节点不需安装代理程序,管理主机借助ssh传递操作指令,如ansible, fabric;
二、ansible介绍
ansible是一款基于python开发,揉合了众多自动化运维工具功能的轻量级自动化运维工具,目前实现了除系统安装以外的批量系统配置、批量任务执行及批量程序部署等功能。
1、ansibler的架构
⑴ansible核心程序
⑵connection plugins:连接插件,负责和被控制端通信;
⑶host inventory:主机库,定义可控制的主机;
⑷modules:core modules、custom modules
⑸playbook:剧本,使用YAML编写的声明性的配置文件
⑹plugins:各种插件,完成日志记录、邮件等功能;
ansible从host inventory中获取被控制的主机信息,通过connection plugins连接主机,调用指指定模块向被控制端发送操作指令。
2、ansible的特性
⑴高度模块化,借助模块完成各种任务
⑵agentless,即无需在被控制端安装agent
⑶默认基于ssh协议向被控制端发送操作指令
①基于密钥认证
②在inventory文件中指定账号和密码
⑷一系列任务执行可写成剧本(playbook)
⑸具有幂等性:不会重复执行相同操作,比如不会重复安装软件
三、ansible安装配置
以下node1为ansible主机,node2、node3、node4为被控主机
1、rpm安装(epel源)
yum -y install ansible #只需要在控制端安装
主配置文件:/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
inventory:/etc/ansible/hosts
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install ansible Installed: ansible.noarch 0:1.9.4-1.el6 Dependency Installed: PyYAML.x86_64 0:3.10-3.1.el6 libyaml.x86_64 0:0.1.3-4.el6_6 python-babel.noarch 0:0.9.4-5.1.el6 python-crypto2.6.x86_64 0:2.6.1-2.el6 python-httplib2.noarch 0:0.7.7-1.el6 python-jinja2.x86_64 0:2.2.1-2.el6_5 python-keyczar.noarch 0:0.71c-1.el6 python-pyasn1.noarch 0:0.0.12a-1.el6 python-setuptools.noarch 0:0.6.10-3.el6 python-simplejson.x86_64 0:2.0.9-3.1.el6 sshpass.x86_64 0:1.05-1.el6 Complete! [root@node1 ~]# rpm -ql ansible | less /etc/ansible /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg #主配置文件 /etc/ansible/hosts #host inventory /etc/ansible/roles /usr/bin/ansible #主程序 /usr/bin/ansible-doc #获取帮助信息 /usr/bin/ansible-galaxy /usr/bin/ansible-playbook #运行“剧本”的命令 /usr/bin/ansible-pull /usr/bin/ansible-vault #可把playbook加密存放 /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/ansible ... [root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg ... [defaults] # some basic default values... inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #inventory文件路径 #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ remote_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp pattern = * forks = 5 #执行任务时启动的并发线程数 poll_interval = 15 sudo_user = root #ask_sudo_pass = True #ask_pass = True transport = smart #remote_port = 22 #远程被控节点的ssh端口 module_lang = C ... ...
2、添加被控主机
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
ntp.magedu.com #不属于任何组的主机直接定义在文件中最上端
[websrvs] #可将一批主机归于一个组
www1.magedu.com:2222 #若被控节点的ssh使用了非默认端口,可以在被控节点后标明
www2.magedu.com
www[01:50].example.com #可使用通配
172.16.100.7
[dbsrvs]
db-[a:f].example.com
◆默认以root用户身份执行,如果是口令认证,则需要在任务执行时输入密码或在inventory中的被控制主机旁以参数的形式指明,例如:
192.168.30.20 ansible_connection=ssh ansible_user=fedora ansible_port=2222 ansible_pass=magedu ansible_become=true ansible_become_user=root ansible_become_method=sudo ansible_become_pass=magedu
ansible_user、ansible_port、ansible_pass分别取代了2.0以前版本中的ansible_ssh_user、ansible_ssh_port、ansible_ssh_pass
基于口令认证当然比较麻烦,故通常配置ssh基于密钥认证
inventory中还有一些可配置的参数,具体见官方文档
◆主机变量
可以在inventory中定义主机时为其添加主机变量。例如:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808
www2.magedu.com http_port=8080 maxRequestsPerChild=909
◆组变量
组变量是指赋予给指定组内所有主机上的变量。例如:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com
www2.magedu.com
[websrvs:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.magedu.com
nfs_server=nfs.magedu.com
◆组嵌套
inventory中,组还可以包含其它的组,并且也可以向组中的主机指定变量。例如:
[apache]
httpd1.magedu.com
httpd2.magedu.com
[nginx]
ngx1.magedu.com
ngx2.magedu.com
[websrvs:children]
apache
nginx
[websrvs:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.magedu.com
注意:在inventory文件中定义的变量只能在playbook中使用,而ansible命令不支持
[root@node1 ~]# cd /etc/ansible/ [root@node1 ansible]# vim hosts #inventory文件中有些配置示例,可参考 .... # Ex 1: Ungrouped hosts, specify before any group headers. ## green.example.com #可以是主机名 ## blue.example.com ## 192.168.100.1 #也可是ip地址 ## 192.168.100.10 # Ex 2: A collection of hosts belonging to the 'webservers' group ## [webservers] ## alpha.example.org ## beta.example.org ## 192.168.1.100 ## 192.168.1.110 # If you have multiple hosts following a pattern you can specify # them like this: ## www[001:006].example.com # Ex 3: A collection of database servers in the 'dbservers' group ## [dbservers] ## ## db01.intranet.mydomain.net ## db02.intranet.mydomain.net ## 10.25.1.56 ## 10.25.1.57 ... [root@node1 ansible]# cp hosts hosts.bac [root@node1 ansible]# vim hosts [websrvs] 192.168.30.20 192.168.30.13 [dbsrvs] 192.168.30.14
3、配置ssh基于密钥认证
ssh-keygen -t rsa
ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa ... Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 49:87:45:68:24:2d:a1:23:6f:e3:8d:ec:88:a8:43:f9 root@node1 The key's randomart p_w_picpath is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ | o+.oo | | ...+o | | . o oo . | | o . . o | | . + S | | o + + | |. . + . | |o. E | |=.. . | +-----------------+ [root@node1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected] ... [root@node1 ~]# ssh [email protected] 'hostname' node2 #以同样的方式将公钥文件复制到其它被控节点
4、ansible的几个命令:
⑴ansible-doc
ansible-doc -l:列出所有模块
ansible-doc [-s] MODULE_NAME:查看指定模块的用法
-s:生成可以复制到playbook中以作修改的摘要;简而言之就是以简要形式显示模块用法
⑵ansible:执行任务
ansible
-m module_name:指定调用的模块
-a args:指定向模块传递的参数
-f #:指定并发数
-k:默认基于密钥认证,使用该选项指定基于口令认证
◆host-pattern:
all #所有主机
192.168.30.20, 192.168.30.*
www.example.com, www.example.com:ftp.test.com
websrvs #组中的所有主机
websrvs:dbsrvs #两个组中的所有主机
websrvs:!dbsrvs #在websrvs不在dbsrvs的主机
websrvs:&dbsrvs #同时在websrvs和dbsrvs中的主机
5、ansible常用模块及其使用示例
①command:命令模块,默认模块,用于在远程执行命令;command模块并不支持shell变量和管道等,若想使用shell来执行,应调用shell模块
例:ansible [-m command] all -a 'date'
[root@node1 ~]# ansible all -a 'date' 192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Sat Apr 9 01:21:18 CST 2016 192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Tue May 3 16:18:06 CST 2016 192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> Tue May 3 16:18:06 CST 2016 [root@node1 ~]# ansible 192.168.30.20:192.168.30.14 -a 'hostname' 192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> node4 192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> node2
②cron:周期性任务计划模块
state:
present:生成
absent:移除
例:ansible websrvs -m cron -a 'name="sync time" minute="*/3" job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate 172.16.100.1 &> /dev/null"'
[root@node1 ~]# ansible all -m cron -a 'name="sync time" minute="*/10" job="/usr/sbin/ntpdate 0.centos.pool.ntp.org &> /dev/null"'
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"jobs": [
"sync time"
]
}
192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"jobs": [
"sync time"
]
}
192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"jobs": [
"sync time"
]
}
[root@node2 ~]# crontab -l #Ansible: sync time */10 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate 0.centos.pool.ntp.org &> /dev/null
③user:管理用户
例:ansible websrvs -m user -a 'name=fedora password=加密串'
[root@node1 ~]# openssl passwd -1 -salt `openssl rand -hex 4`
Password:
$1$56ff09e3$xedL2L61OEqnX0I7uVCiV.
[root@node1 ~]# ansible dbsrvs -m user -a 'name=federa password=$1$56ff09e3$xedL2L61OEqnX0I7uVCiV'
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"createhome": true,
"group": 503,
"home": "/home/federa",
"name": "federa",
"password": "NOT_LOGGING_PASSWORD",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 503
}
[root@node1 ~]# ansible dbsrvs -m user -a 'name=federa state=absent'
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "federa",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
④copy:复制文件
src=:指定本地源文件路径
content=:取代src=,表示直接用此处指定的内容生成为目标文件内容
dest:指定远程目标文件路径
force: 当设置为yes时,如果目标主机存在该文件,但内容不同,会强制覆盖。默认为yes
backup: 在覆盖之前备份源文件,yes/no
例:ansible websrvs -m copy -a 'src=/mine/ntp.conf dest=/etc/ntp.conf[ owner=root group=root mode=644 backup=yes]'
ansible websrvs -m copy -a 'content="hello" dest=/tmp/test.ansible'
[root@node1 ~]# ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/root/test.ansible dest=/tmp/'
192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "5c074e046394da951a17e8baa97fb67833f20733",
"dest": "/tmp/test.ansible",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "c4c6374c8a58aadfda80777e13f17e9f",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 14,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1462272045.11-211394086056695/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
...
⑤file:设定文件属性
path=:指明目标文件路径,等同 dest 或 name
src=:被链接的源文件路径,只应用于 state=link 的情况
force=:强制创建软链接
state=:后面接文件的各种状态,如directory, link, hard, file及absent(删除)
directory: 如果目录不存在,则创建目录
file: 即使文件不存在,也不会被创建
absent: 删除目录、文件或链接文件
touch: 如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新文件,如果存在,则更新其时间戳
link: 创建软链接
hard
其它选项:owner, group, mode, recurse
例:ansible websrvs -m file -a 'src=/tmp/test.ansible path=/tmp/test.link state=link'
ansible websrvs -m file -a 'owner=fedra group=fedra mode=644 path=/tmp/test.ansible'
⑥service:控制服务的运行状态
enabled=:是否开机自动启动,取值为true或false
state=:状态,取值有started, stopped, restarted
例:ansible websrvs -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=true'
[root@node3 ~]# service httpd status httpd is stopped
[root@node1 ~]# ansible 192.168.30.13 -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started'
192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started"
}
[root@node3 ~]# service httpd status httpd (pid 30552) is running...
⑦shell:
ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'echo $TERM'
[root@node1 ~]# ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'echo $TERM' 192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> xterm 192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >> xterm
⑧script:将本地脚本复制到远程主机并执行
例:ansible websrvs -m script -a '/root/adduser.sh'
⑨ping:测试指定主机是否能连接
[root@node1 ~]# ansible all -m ping
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
⑩yum:管理程序包
name=:指明要安装或卸载的程序包,可带上版本号
state:present,latest表示安装;absent表示卸载
例:ansible all -m yum -a 'name=zsh'
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=zsh state=absent'
[root@node1 ~]# ansible dbsrvs -m yum -a 'name=zsh state=latest'
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
...
⑾setup:收集远程主机的facs
playbook运行时,会自动调用setup模块收集远程主机的相关信息(称为facts,如操作系统版本、ip地址、cpu数量等),这些信息保存于变量中,可在playbook中引用。
我们也可直接使用ansible命令直接获取这些变量信息:
ansible all -m setup [-a 'filter=ansible_eth[0-2]']
filter:过滤器,表示只返回与指定shell风格通配符匹配的变量信息
ansible all -m setup --tree /tmp/facts
--tree:表示将收集的facs以树状的结构输入到指定文件中
[root@node1 ~]# ansible websrvs -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_fqdn'
192.168.30.20 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_fqdn": "node2"
},
"changed": false
}
192.168.30.13 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_fqdn": "node3"
},
"changed": false
}
[root@node1 ~]# ansible dbsrvs -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_processor*'
192.168.30.14 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_processor": [
"GenuineIntel",
"Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4510U CPU @ 2.00GHz",
"GenuineIntel",
"Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4510U CPU @ 2.00GHz"
],
"ansible_processor_cores": 2,
"ansible_processor_count": 1,
"ansible_processor_threads_per_core": 1,
"ansible_processor_vcpus": 2
},
"changed": false
}
⑿template
template是使用了Jinjia2格式作为文件模版,进行文档内变量的替换的模块。它的每次使用都会被ansible标记为”changed”状态。
举个例子:
vim /root/httpd.conf
...
ServerName ` ansible_fqdn `
ansible websrvs -m template -a 'src=/root/httpd.conf desc=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
当/root/httpd.conf文件被复制到第一个主机时,ServerName的值被替换成第一个主机的ansible_fqdn的值node2,而被复制到第二个主机时,ServerName的值会被替换成node3
⒀synchronize
该模块会调用rsync命令,用于将ansible机器的指定目录推送到客户机器 的指定目录下
示例:ansible 192.168.30.20 -m synchronize -a 'src=/usr/local/src/ dest=/usr/local/src/ delete=yes compress=yes'
⒁get_url
常用模块,可以实现在远程主机上下载url到本地
示例:ansible 192.168.30.20 -m get_url -a 'url=http://ftp.linux.ncsu.edu/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm dest=/tmp'
⒂其它模块:filesystem, group, hostname等