一.理论知识部分
1.Java的抽象口工具箱( Abstract WindowToolkit, AWT)包含在java.awt包中,它提供了许多用来设计GUI的组件类和容器类。
2.AWT库处理用户界面元素的方法:把图形元素的创建和行为委托给本地GUI工具箱进行处理。
3.Swing用户界面库是非基于对等体的GUI工具箱。Swing具有更丰富并且更方便的用户界面元素集合。Swing对底层平台的依赖很少,因此与平台相关的bug很少。Swing会带来交叉平台上的统一视觉体验。Swing类库被放在 javax.swing 包里。
4.大部分AWT组件都有其 Swing的等价组件。Swing组件的名字一般是在AWT组件名前面添加一个字母“J”,如:JButton,JFrame,JPanel等。
5.通常把由Component类的子类或间接子类创建的对象称为一个组件。
6.组件类的常用API
java.awt.Component 1.0
– boolean isVisible() 检查组件是否可见
– void setVisible(boolean b) 设置组件可见
– void setSize(int width,int height) 把组件缩放到指定宽度和高度
– void setBounds(int x,int y,intwidth,int height) 移动并缩放组件
– Dimension getSize() 得到组件的大小
– void setSize(Dimension d) 把组件缩放到指定的大小
– void setLocation(int x,int y)
7.容器是Java中能容纳和排列组件的组件。常用的容器是框架(Frame,JFrame)
8.java.awt.Frame 类的常用API
void setResizable(boolean b) 缩放框架
void setTitle(String s) 设置框架标题
void setIconImage(Image image) 将Image用作框架图标
9.Container类提供了一个方法add(),用来在容器类组件对象中添加其他组件。容器本身也是一个组件,可以把一个容器添加到另一个容器里,实现容器嵌套。
10.定位:常用Component类的setLocation和setBounds方法
11.创建框架时的常用类及API
java.awt.Component 1.0
– boolean isVisible() 检查组件是否可见
– void setVisible(boolean b) 设置组件可见
– void setSize(int width,int height) 把组件缩放到指定宽度和高度
– void setBounds(int x,int y,intwidth,int height) 移动并缩放组件
– Dimension getSize() 得到组件的大小
– void setSize(Dimension d) 把组件缩放到指定的大小
12.Java SE了包含一个Java 2D库,该库提供了一个非常强大的图形操作集。
13.Graphics 2D类是Graphics类的子类,Graphics。2D类对象通常可用Graphics对象转换而来。
14.Java 2D图形类使用浮点数坐标系,这样可为坐标指定单位。
15.图像:(1)在Java应用程序中,一旦图像保存在本地或因特网的某个位置上,就可以将它们直接读入到java应用程序中。(2)完成将一个图像文件加载到程序中,再调用Graphics类提供的DrawImage()显示它。
二.实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API;
(2) 掌握Java GUI中2D图形绘制常用类的API;
(3) 了解Java GUI中2D图形中字体与颜色的设置方法;
(4) 了解Java GUI中2D图像的载入方法。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第10章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 运行下列程序,观察程序运行结果。
| import javax.swing.*; public class SimpleFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,300, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); } } |
import javax.swing.*; public class SimpleFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,300, 200);//移动组件并调整其大小 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//设置默认关闭窗口操作 frame.setVisible(true); } }
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材407页程序10-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;与上面程序对比,思考异同;
l 掌握空框架创建方法;
l 了解主线程与事件分派线程概念;
l 掌握GUI顶层窗口创建技术。
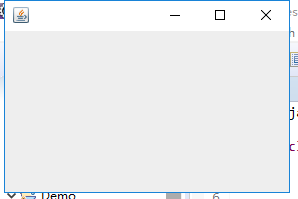
package simpleFrame; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.33 2015-05-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SimpleFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> //Lambda表达式 { SimpleFrame frame = new SimpleFrame(); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } class SimpleFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;//设置静态常量宽和高 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public SimpleFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
测试程序2:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材412页程序10-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握确定框架常用属性的设置方法。
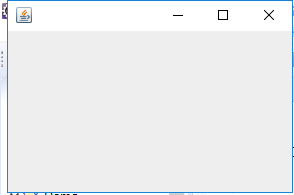
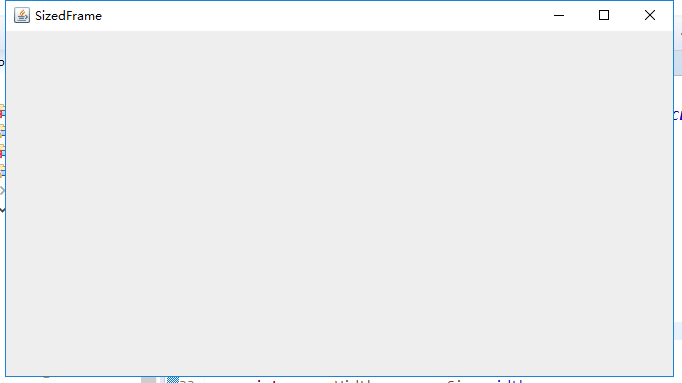
package sizedFrame; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-16 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SizedFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new SizedFrame(); frame.setTitle("SizedFrame"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } class SizedFrame extends JFrame { public SizedFrame() { // get screen dimensions Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize(); int screenHeight = screenSize.height; int screenWidth = screenSize.width; // set frame width, height and let platform pick screen location setSize(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);//相对大小 setLocationByPlatform(true);//由平台选择合适的位置 // set frame icon Image img = new ImageIcon("icon.gif").getImage(); setIconImage(img); } }
测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材418页程序10-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握在框架中添加组件;
l 掌握自定义组件的用法。
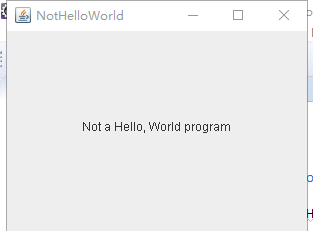
package notHelloWorld; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; /** * @version 1.33 2015-05-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class NotHelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new NotHelloWorldFrame(); frame.setTitle("NotHelloWorld"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * A frame that contains a message panel */ class NotHelloWorldFrame extends JFrame { public NotHelloWorldFrame() { add(new NotHelloWorldComponent()); pack(); } } /** * A component that displays a message. */ class NotHelloWorldComponent extends JComponent { public static final int MESSAGE_X = 75; public static final int MESSAGE_Y = 100; private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { g.drawString("Not a Hello, World program", MESSAGE_X, MESSAGE_Y); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
测试程序4:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材424 -425页程序10-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握2D图形的绘制方法。
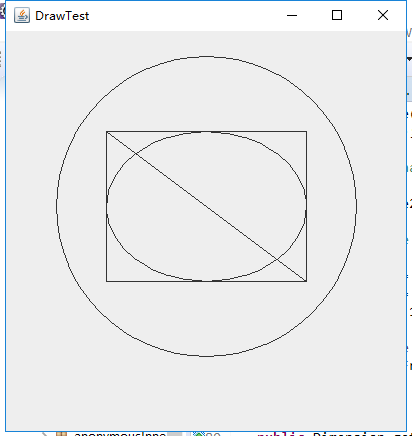
package draw; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.geom.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.33 2007-05-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class DrawTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new DrawFrame(); frame.setTitle("DrawTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * A frame that contains a panel with drawings */ class DrawFrame extends JFrame { public DrawFrame() { add(new DrawComponent()); pack(); } } /** * A component that displays rectangles and ellipses. */ class DrawComponent extends JComponent { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 400; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; // draw a rectangle double leftX = 100; double topY = 100; double width = 200; double height = 150; Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(leftX, topY, width, height); g2.draw(rect); // draw the enclosed ellipse Ellipse2D ellipse = new Ellipse2D.Double(); ellipse.setFrame(rect); g2.draw(ellipse); // draw a diagonal line g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(leftX, topY, leftX + width, topY + height)); // draw a circle with the same center double centerX = rect.getCenterX(); double centerY = rect.getCenterY(); double radius = 150; Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(); circle.setFrameFromCenter(centerX, centerY, centerX + radius, centerY + radius); g2.draw(circle); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
测试程序5:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材432页-433程序10-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形中字体的设置的方法;
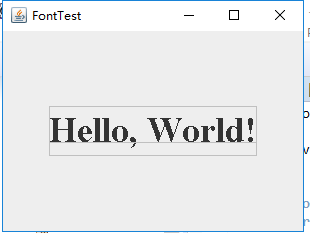
package font; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.font.*; import java.awt.geom.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-05-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class FontTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new FontFrame(); frame.setTitle("FontTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * A frame with a text message component */ class FontFrame extends JFrame { public FontFrame()//构造器 { add(new FontComponent());//添加窗口 pack();//调整窗口大小 } } /** * A component that shows a centered message in a box. */ class FontComponent extends JComponent { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; String message = "Hello, World!"; Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 36); g2.setFont(f);//设置字体 // measure the size of the message FontRenderContext context = g2.getFontRenderContext(); Rectangle2D bounds = f.getStringBounds(message, context); // set (x,y) = top left corner of text double x = (getWidth() - bounds.getWidth()) / 2; double y = (getHeight() - bounds.getHeight()) / 2; // add ascent to y to reach the baseline double ascent = -bounds.getY(); double baseY = y + ascent; // draw the message g2.drawString(message, (int) x, (int) baseY); g2.setPaint(Color.LIGHT_GRAY); // draw the baseline g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(x, baseY, x + bounds.getWidth(), baseY)); // draw the enclosing rectangle Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, bounds.getWidth(), bounds.getHeight()); g2.draw(rect); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
测试程序6:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材436页-437程序10-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解2D图形图像的显示方法。
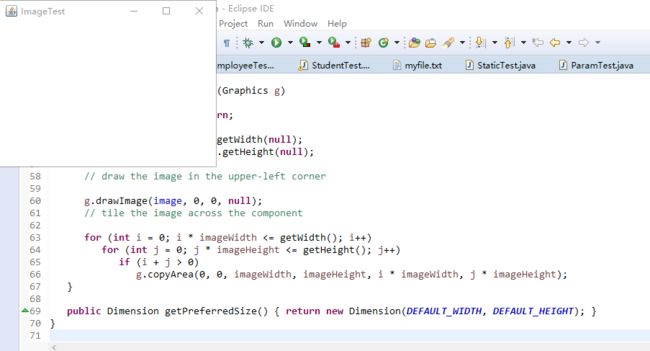
package image; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-05-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ImageTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ImageFrame(); frame.setTitle("ImageTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * A frame with an image component */ class ImageFrame extends JFrame { public ImageFrame() { add(new ImageComponent()); pack(); } } /** * A component that displays a tiled image */ class ImageComponent extends JComponent { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private Image image; public ImageComponent() { image = new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif").getImage(); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { if (image == null) return; int imageWidth = image.getWidth(null); int imageHeight = image.getHeight(null); // draw the image in the upper-left corner g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null); // tile the image across the component for (int i = 0; i * imageWidth <= getWidth(); i++) for (int j = 0; j * imageHeight <= getHeight(); j++) if (i + j > 0) g.copyArea(0, 0, imageWidth, imageHeight, i * imageWidth, j * imageHeight); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }
实验2:课后完成PTA平台题目集:2018秋季西北师范大学面向对象程序设计(Java)练习题集(ch6-ch9)
3.实验总结:
本周主要学习了与图形用户界面设计有关的知识,通过本章的学习,我对图形用户界面设计的相关知识有了一定的了解,了解了创建框架时的一些常用API。如何用一些组件去画字,图形等。但实际用这些知识自己去设计图形还是会有一定的难度。