talk is cheap show me the code —— Linus Torvalds
本章将结合开源项目IMBRA讲解如何解析一个DCM文件
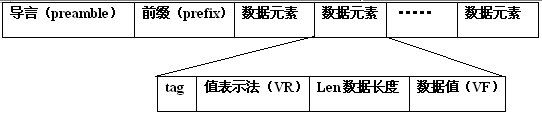
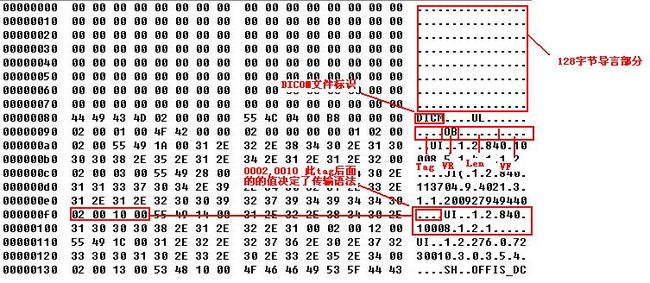
文件开头会有128字节的导言,这部分数据没有内容。接着是4字节DICOM文件标识,存储这"DICM"。然后紧接着就是dicom数据数据元素了
try
{
pStream->read(oldDicomSignature, 8);
}
catch(StreamEOFError&)
{
IMEBRA_THROW(CodecWrongFormatError, "detected a wrong format");
}
// Skip the first 128 bytes (8 already skipped)
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
pStream->seekForward(120);
// Read the DICOM signature (DICM)
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
std::uint8_t dicomSignature[4];
pStream->read(dicomSignature, 4);
// Check the DICM signature
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const char* checkSignature="DICM";
if(::memcmp(dicomSignature, checkSignature, 4) != 0)
{
bFailed=true;
}
旧版本的DCM文件会在开头8个字节验证签名,在读完128字节后,读取4个字节验证DICOM标识。
pStream->read((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId));
//将转化成大端格式 或者小端格式
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId), endianType);
(*pReadSubItemLength) += (std::uint32_t)sizeof(tagId);
// Check for EOF
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if(pStream->endReached())
{
break;
}
// Check the byte order
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if(bFirstTag && tagId==0x0200)
{
// Reverse the last adjust
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId), endianType);
// Fix the byte adjustment
endianType=streamController::highByteEndian;
// Redo the byte adjustment
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId), endianType);
}
接下来开始读取数据元素了,现读取两个字节的tagId,并且验证大小端。
if(tagId!=0x0002 && bCheckTransferSyntax)
{
// Reverse the last adjust
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId), endianType);
std::string transferSyntax = pDataSet->getString(
0x0002,
0x0,
0x0010,
0,
0,
endianType == streamController::lowByteEndian ? "1.2.840.10008.1.2.1" : "1.2.840.10008.1.2.2");
if(transferSyntax == "1.2.840.10008.1.2.2")
endianType = streamController::highByteEndian;
if(transferSyntax == "1.2.840.10008.1.2")
bExplicitDataType=false;
bCheckTransferSyntax=false;
// Redo the byte adjustment
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagId, sizeof(tagId), endianType);
}
dicom的数据元素的tagId是从大到小的读取的,而最小的tagId就是从0x0002,当tagId不是0x0002说明已经读取完所以关于0x0002的tagId。从中找出(0002,0010)的tag,这个tag设置当前数据是否大端格式,显示VR编码还是隐式VR编码。"1.2.840.10008.1.2.2"表示大端格式,1.2.840.10008.1.2表示隐式编码。
if(bExplicitDataType && tagId!=0xfffe)
{
// Get the tag's type
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
std::string tagTypeString((size_t)2, ' ');
pStream->read((std::uint8_t*)&(tagTypeString[0]), 2);
(*pReadSubItemLength) += 2;
// Get the tag's length
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
pStream->read((std::uint8_t*)&tagLengthWord, sizeof(tagLengthWord));
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagLengthWord, sizeof(tagLengthWord), endianType);
(*pReadSubItemLength) += (std::uint32_t)sizeof(tagLengthWord);
// The data type is valid
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
try
{
tagType = dicomDictionary::getDicomDictionary()->stringDataTypeToEnum(tagTypeString);
tagLengthDWord=(std::uint32_t)tagLengthWord;
wordSize = dicomDictionary::getDicomDictionary()->getWordSize(tagType);
if(dicomDictionary::getDicomDictionary()->getLongLength(tagType))
{
pStream->read((std::uint8_t*)&tagLengthDWord, sizeof(tagLengthDWord));
pStream->adjustEndian((std::uint8_t*)&tagLengthDWord, sizeof(tagLengthDWord), endianType);
(*pReadSubItemLength) += (std::uint32_t)sizeof(tagLengthDWord);
}
}
catch(const DictionaryUnknownDataTypeError&)
{
// The data type is not valid. Switch to implicit data type
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
bExplicitDataType = false;
if(endianType == streamController::lowByteEndian)
tagLengthDWord=(((std::uint32_t)tagLengthWord)<<16) | ((std::uint32_t)tagTypeString[0]) | (((std::uint32_t)tagTypeString[1])<<8);
else
tagLengthDWord=(std::uint32_t)tagLengthWord | (((std::uint32_t)tagTypeString[0])<<24) | (((std::uint32_t)tagTypeString[1])<<16);
}
} // End of the explicit data type read block
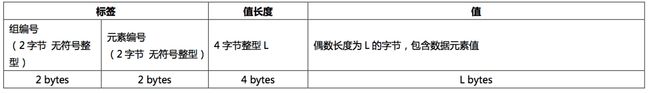
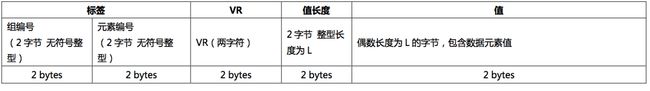
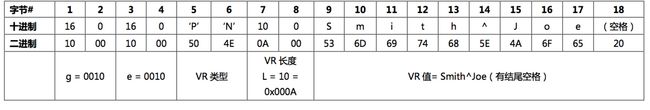
显示编码解析 取先获取VR 再获取长度 最后获取值
if((!bExplicitDataType || tagId==0xfffe))
{
// Group length. Data type is always UL
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if(tagSubId == 0)
{
tagType = tagVR_t::UL;
}
else
{
try
{
tagType = dicomDictionary::getDicomDictionary()->getTagType(tagId, tagSubId);
}
catch(const DictionaryUnknownTagError&)
{
tagType = tagVR_t::UN;
}
wordSize = dicomDictionary::getDicomDictionary()->getWordSize(tagType);
}
}
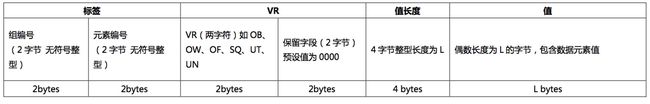
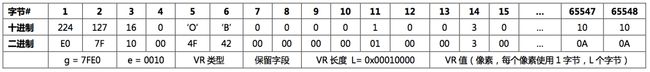
隐式编码解析