简介
CoreData是一个框架,可以将咱们的OC对象和存储在SQLite文件中的数据进行互相转换。并且做这些操作,你不需要写任何SQLite语句。
和ORM的区别
ORM-对象关系映射
CoreData-它具备ORM的某些功能
必备知识
NSManagedObject
从CoreData中取出来对象,默认都是NSManagedObject对象,通过键值对来存取所有的实体属性,相当于数据库中的表格记录NSManagedObjectContext
负责应用与数据库之间的交互,增删改查基本操作都要用到NSManagedObjectModel
被管理的数据模型,可以添加实体及实体的属性,若新建的项目带CoreData,即为XXX.xcdatamodeldNSPersistentStoreCoordinator
数据库的连接器,设置数据存储的名字,位置,存储方式等NSFetchRequest
获取数据时的请求NSEntityDescription
用来描述实体
简单使用(创建工程时带CoreData)
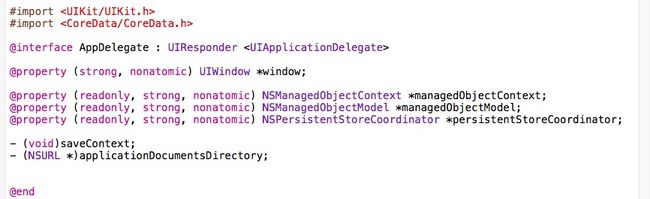
- 新建工程时勾选Use Core Data,则AppDelegate.h中
在AppDelegate.m(项目名称BBB,自带的Model为BBB.xcdatamodeld)中
#pragma mark - Core Data stack
@synthesize managedObjectContext = _managedObjectContext;
@synthesize managedObjectModel = _managedObjectModel;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator = _persistentStoreCoordinator;
- (NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory {
// The directory the application uses to store the Core Data store file. This code uses a directory named "iii.BBB" in the application's documents directory.
return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
}
- (NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"BBB" withExtension:@"momd"];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}
- (NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and returns a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"BBB.sqlite"];
NSError *error = nil;
NSString *failureReason = @"There was an error creating or loading the application's saved data.";
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @"Failed to initialize the application's saved data";
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@"YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN" code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
- (NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext {
// Returns the managed object context for the application (which is already bound to the persistent store coordinator for the application.)
if (_managedObjectContext != nil) {
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *coordinator = [self persistentStoreCoordinator];
if (!coordinator) {
return nil;
}
_managedObjectContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] initWithConcurrencyType:NSMainQueueConcurrencyType];
[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];
return _managedObjectContext;
}
#pragma mark - Core Data Saving support
- (void)saveContext {
NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = self.managedObjectContext;
if (managedObjectContext != nil) {
NSError *error = nil;
if ([managedObjectContext hasChanges] && ![managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
}
}
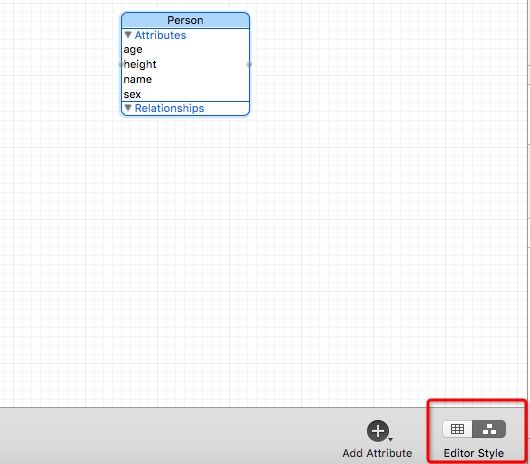
- 建好后你会发现工程中多了XXX.xcdatamodeld,我们需要在这里添加实体(首字母大写)和实体的属性。
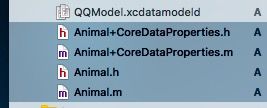
- 因为利用Core Data取出的实体都是NSManagedObject类型,可以通过键值对来存取对象,但如果还要做其他操作,则需要创建NSManagedObject的子类,建时勾选工程和实体,建好后会发现工程中多了四个文件
导入CoreData.framework和头文件
代码实现
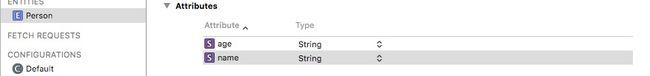
0-创建实体Person,有两个属性name和age
1-因为创建工程时带Core Data,AppDelegate中含了我们需要用的,所以在要操作的控制器中
#import
#import "AppDelegate.h"
#import "Person.h"
@interface ViewController ()
{
AppDelegate *app;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
app =[UIApplication sharedApplication].delegate;
NSManagedObjectContext *context = app.managedObjectContext;
}
2-增
1.创建实体,并为实体属性赋值
Person *p = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Person" inManagedObjectContext:context];
p.name = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"大倩倩%d",arc4random()%10];
p.age = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",arc4random()%60];
2.保存数据
[context save:nil];
***************************************************************
3.查询
建立请求
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init] ;
读取实体
NSEntityDescription *entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Person" inManagedObjectContext:context];
请求连接实体
request.entity = entity;
遍历所有实体,将每个实体的信息存放在数组中
NSArray *arr = [context executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
打印
for (Person *p in arr)
{
NSLog(@"name=%@,age=%@", p.name,p.age);
}
因为是写在viewDidLoad中,每运行一次增加一条数据
3-删
1.建立请求,连接实体
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init] ;
request.entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Person" inManagedObjectContext:context];
2.设置条件过滤(搜索age属性中包含”12“的那条记录,注意等号必须加,可以有空格,也可以是==)
NSPredicate *predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"age=%@", @"12"];
request.predicate = predicate;
3.遍历所有实体,将每个实体的信息存放在数组中
NSArray *arr = [context executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
4.删除并保存
if(arr.count)
{
for (Person *p in arr)
{
[context deleteObject:p];
}
//保存
[context save:nil];
}
4-改
1.建立请求,连接实体
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init] ;
request.entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Person" inManagedObjectContext:context];
2.设置条件过滤(搜索所有name属性不为“大倩倩1”的数据)
NSPredicate *predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name!=%@", @"大倩倩1"];
request.predicate = predicate;
3.遍历所有实体,将每个实体的信息存放在数组中
NSArray *arr = [app.managedObjectContext executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
4.更改并保存
if(arr.count)
{
for (Person *p in arr)
{
p.name = @"更改";
}
//保存
[context save:nil];
}
else
{
NSLog(@"无检索");
}
简单使用(创建工程时不带Core Data)
- 新建Data Model
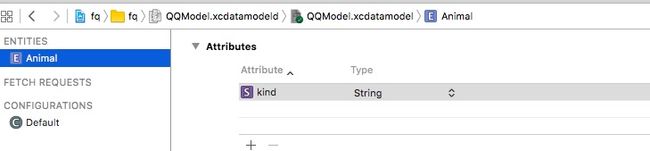
- 我建了QQModel(QQModel.xcdatamodeld),并建了一个Animal实体和kind属性
- 为QQModel建立NSManagedObject的子类
- 写代码
1-导入CoreData.framework
2-新建类CoreDataBase,继承自NSObject,将创建工程时使用CoreData中,AppDelegate自带的代码粘贴过来
1. CoreDataBase.h
#import
#import
@interface CoreDataBase : NSObject
@property (readonly, strong, nonatomic) NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext;
@property (readonly, strong, nonatomic) NSManagedObjectModel *managedObjectModel;
@property (readonly, strong, nonatomic) NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *persistentStoreCoordinator;
- (void)saveContext;
- (NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory;
- (void)insertCoreData:(NSString *)str;
- (void)queryCoreData;
@end
2. CoreDataBase.m
#import "CoreDataBase.h"
@implementation CoreDataBase
#pragma mark - Core Data stack
@synthesize managedObjectContext = _managedObjectContext;
@synthesize managedObjectModel = _managedObjectModel;
@synthesize persistentStoreCoordinator = _persistentStoreCoordinator;
- (NSURL *)applicationDocumentsDirectory {
// The directory the application uses to store the Core Data store file. This code uses a directory named "iii.BBB" in the application's documents directory.
return [[[NSFileManager defaultManager] URLsForDirectory:NSDocumentDirectory inDomains:NSUserDomainMask] lastObject];
}
- (NSManagedObjectModel *)managedObjectModel {
// The managed object model for the application. It is a fatal error for the application not to be able to find and load its model.
if (_managedObjectModel != nil) {
return _managedObjectModel;
}
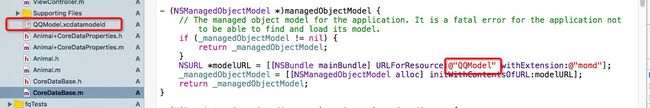
NSURL *modelURL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"QQModel" withExtension:@"momd"];
_managedObjectModel = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:modelURL];
return _managedObjectModel;
}
- (NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *)persistentStoreCoordinator {
// The persistent store coordinator for the application. This implementation creates and returns a coordinator, having added the store for the application to it.
if (_persistentStoreCoordinator != nil) {
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
// Create the coordinator and store
_persistentStoreCoordinator = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:[self managedObjectModel]];
NSURL *storeURL = [[self applicationDocumentsDirectory] URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"BBB.sqlite"];
NSError *error = nil;
NSString *failureReason = @"There was an error creating or loading the application's saved data.";
if (![_persistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:storeURL options:nil error:&error]) {
// Report any error we got.
NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[NSLocalizedDescriptionKey] = @"Failed to initialize the application's saved data";
dict[NSLocalizedFailureReasonErrorKey] = failureReason;
dict[NSUnderlyingErrorKey] = error;
error = [NSError errorWithDomain:@"YOUR_ERROR_DOMAIN" code:9999 userInfo:dict];
// Replace this with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
return _persistentStoreCoordinator;
}
- (NSManagedObjectContext *)managedObjectContext {
// Returns the managed object context for the application (which is already bound to the persistent store coordinator for the application.)
if (_managedObjectContext != nil) {
return _managedObjectContext;
}
NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *coordinator = [self persistentStoreCoordinator];
if (!coordinator) {
return nil;
}
_managedObjectContext = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] initWithConcurrencyType:NSMainQueueConcurrencyType];
[_managedObjectContext setPersistentStoreCoordinator:coordinator];
return _managedObjectContext;
}
#pragma mark - Core Data Saving support
- (void)saveContext {
NSManagedObjectContext *managedObjectContext = self.managedObjectContext;
if (managedObjectContext != nil) {
NSError *error = nil;
if ([managedObjectContext hasChanges] && ![managedObjectContext save:&error]) {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// abort() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
NSLog(@"Unresolved error %@, %@", error, [error userInfo]);
abort();
}
}
}
@end
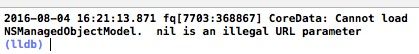
注意,这两个名字必须一致
不然会报如下错误
3-在CoreDataBase中封装增加和查询方法
1. CoreDataBase.h
#import "Animal.h"
- (void)insertCoreData:(NSString *)str;//增加
- (void)queryCoreData; //查询
2. CoreDataBase.m
//增减
- (void)insertCoreData:(NSString *)str
{
NSManagedObjectContext *context = [self managedObjectContext];
Animal *a = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Animal" inManagedObjectContext:context];
a.kind = str;
[context save:nil];
}
//查询
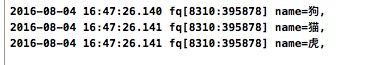
- (void)queryCoreData
{
NSManagedObjectContext *context = [self managedObjectContext];
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init] ;
//设置要查询的实体
NSEntityDescription *entity = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Animal" inManagedObjectContext:context];
request.entity = entity;
NSArray *arr = [context executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
for (Animal *a in arr)
{
NSLog(@"name=%@,", a.kind);
}
}
4-在ViewController中调用
#import "CoreDataBase.h"
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
CoreDataBase *base = [[CoreDataBase alloc] init];
[base insertCoreData:@"虎"];
[base queryCoreData];
}