注: 本文首发于 博客 CodeSheep · 程序羊,欢迎光临 小站!本文共 851字,阅读大约需要 3分钟 !
概述
在如今高并发的互联网应用中,缓存的地位举足轻重,对提升程序性能帮助不小。而3.x开始的 Spring也引入了对 Cache的支持,那对于如今发展得如火如荼的 Spring Boot来说自然也是支持缓存特性的。当然 Spring Boot默认使用的是 SimpleCacheConfiguration,即使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager 来实现的缓存。但本文将讲述如何将 Ehcache缓存应用到Spring Boot应用中。
「Ehcache」 是一个基于Java实现的开源缓存管理库,提供了用内存、磁盘文件存储、以及分布式存储等多种灵活的管理方案。使用方式和原理都有点类似于 Spring事务管理,配合各项注解可以很容易的上手。
下文就上手来摸一摸它,结合对数据库的操作,我们让 Ehcache作为本地缓存来看一下效果!
准备工作
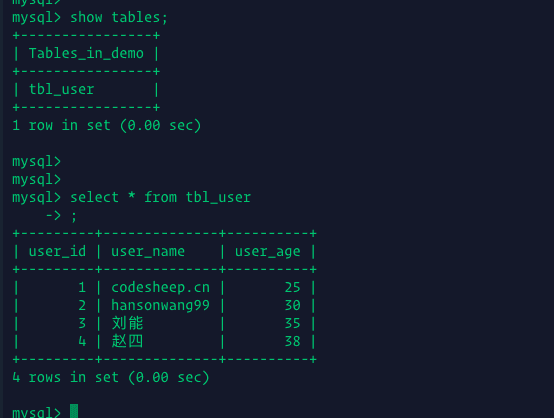
- 准备好数据库和数据表并插入相应的数据(MySQL)
比如我这里准备了一张用户表,包含几条记录:
我们将通过模拟数据库的存取操作来看看 Ehcache缓存加入后的效果。
搭建工程:Springboot + MyBatis + MySQL + Ehcache
pom.xml 中添加如下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
net.sf.ehcache
ehcache
建立 Ehcache配置文件
创建Ehcache的配置文件 ehcache.xml并置于项目 classpath下:
配置 application.properties
server.port=80
# Mysql 数据源配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://121.196.213.251:3306/demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=xxxxxx
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# mybatis 配置
mybatis.type-aliases-package=cn.codesheep.springbt_ehcache.entity
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
# ehcache 配置
spring.cache.ehcache.config=classpath:ehcache.xml编写操作数据库和 Ehcache缓存的业务代码
- 编写entity
public class User {
private Long userId;
private String userName;
private Integer userAge;
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public Integer getUserAge() {
return userAge;
}
public void setUserAge(Integer userAge) {
this.userAge = userAge;
}
}- 编写mapper
public interface UserMapper {
List getUsers();
int addUser(User user);
List getUsersByName( String userName );
} - 编写service
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public List getUsers() {
return userMapper.getUsers();
}
public int addUser( User user ) {
return userMapper.addUser(user);
}
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#userName")
public List getUsersByName( String userName ) {
List users = userMapper.getUsersByName( userName );
System.out.println( "从数据库读取,而非读取缓存!" );
return users;
}
} 看得很明白了,我们在 getUsersByName接口上添加了注解:@Cacheable。这是 Ehcache的使用注解之一,除此之外常用的还有 @CachePut和 @CacheEvit,分别简单介绍一下:
-
@Cacheable:配置在getUsersByName方法上表示其返回值将被加入缓存。同时在查询时,会先从缓存中获取,若不存在才再发起对数据库的访问 -
@CachePut:配置于方法上时,能够根据参数定义条件来进行缓存,其与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中,所以主要用于数据新增和修改操作上 -
@CacheEvict:配置于方法上时,表示从缓存中移除相应数据。
- 编写controller
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
CacheManager cacheManager;
@GetMapping("/users")
public List getUsers() {
return userService.getUsers();
}
@GetMapping("/adduser")
public int addSser() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(4l);
user.setUserName("赵四");
user.setUserAge(38);
return userService.addUser(user);
}
@RequestMapping( value = "/getusersbyname", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public List geUsersByName( @RequestBody User user ) {
System.out.println( "-------------------------------------------" );
System.out.println("call /getusersbyname");
System.out.println(cacheManager.toString());
List users = userService.getUsersByName( user.getUserName() );
return users;
}
} 改造SpringBoot应用主类
主要是在启动类上通过 @EnableCaching注解来显式地开启 Ehcache缓存
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("cn.codesheep.springbt_ehcache")
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbtEhcacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbtEhcacheApplication.class, args);
}
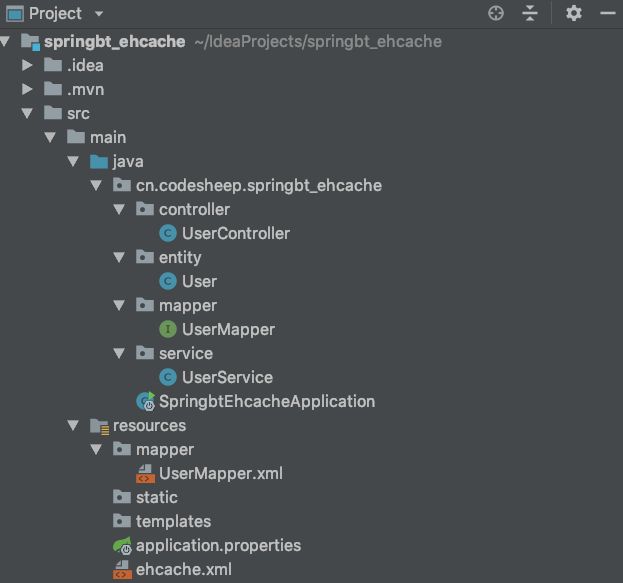
}最终完工的整个工程的结构如下:
实际实验
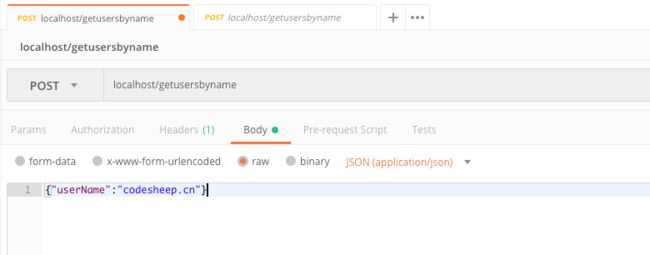
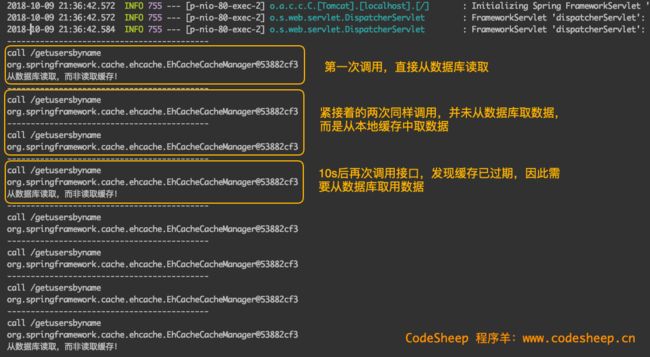
通过多次向接口 localhost/getusersbynamePOST数据来观察效果:
可以看到缓存的启用和失效时的效果(上文ehcache的配置文件中设置了缓存user的实效时间为10s):
后 记
由于能力有限,若有错误或者不当之处,还请大家批评指正,一起学习交流!
- My Personal Blog:CodeSheep 程序羊
- 我的半年技术博客之路
本文实验代码在此
可 长按 或 扫描 下面的 小心心 来订阅作者公众号 CodeSheep,获取更多 务实、能看懂、可复现的 原创文 ↓↓↓