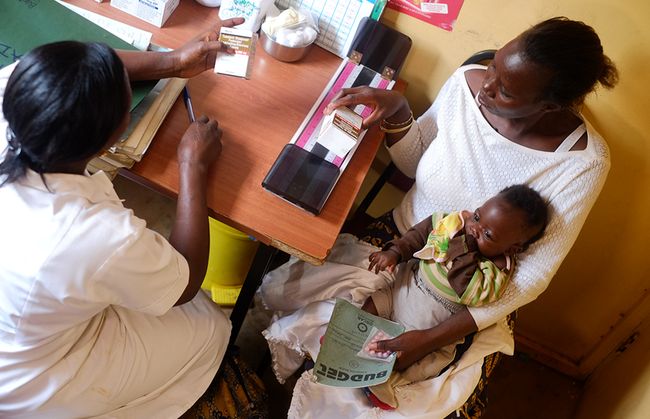
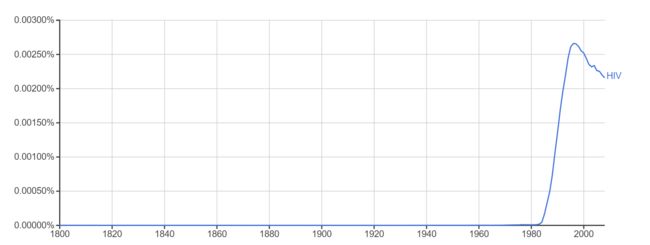Fight Against HIV
AIDS is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). According to the data from UNAIDS (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS), today there are more than 36.7 million people living with HIV. As an infectious disease, it can cause great harm to human body and bring people to death.
The history of HIV
HIV/AIDS was first observed in 1981 in the United States. The initial cases were a cluster of injecting drug users and homosexual men with no known cause of impaired immunity who showed symptoms of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. In 1982, the disease was named " AIDS". Soon after, AIDS spread rapidly across continents. In March 2015, a multinational scientific study found that the four known HIV strains are all from chimpanzees and gorillas in Cameroon, and this was the first time that human-being fully identified sources of HIV.
The following curve chart based on the data from Google Ngram shows the word frequency of “HIV” from 1800 to 2008. (The data from Google Ngram is from the word frequency statistics for Google 's 5.2 million digital books.) We can see that after 1981 the word frequency of “HIV” presents an exponential growth.
The current global AIDS situation
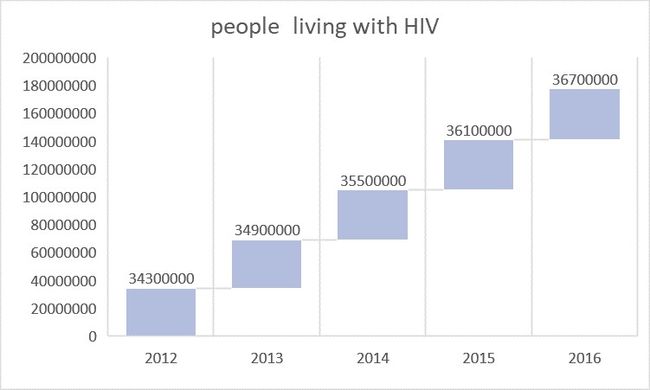
We collected the number of people living with HIV in the past five years globally and made a waterfall chart. As the chart shows, the number of people living with HIV hasincreased steadily over the past five years. According to UNAIDS, People newly infected with HIV of 2016 reached 1.8 million.
The region that has the largest number of people who live with HIV is Eastern and Southern Africa, as we can see from the following chart. Africa is the continent that most affected, reaching 19.4 million.
In western countries, HIV infection rates has been beginning to slow as a result of education on sex. However, in some special groups of people, like public health workers along with illegal sex workers and drug injectors, there are signs of a resurgence in infection rates. In third world countries like Africa countries, due to the limitation of economic conditions and lack of sex education, the infection rate remains very high.
AIDS related deaths
Not only in Africa, AIDS is destroying many people and families in the world. Every year many people die due to infection with HIV.
UNAIDS divided all the infection countries into 8 regions—Eastern and Southern Africa, Western and Central Africa, Asia and the Pacific, Eastern Europe and Central Asia, Latin America, Middle East and North Africa, Western and Central Europe and North America, the Caribbean.
The tree chart shows the number of AIDS related deaths in 2016 of each region. The sizes of areas in the chart represent the amounts of deaths. Africa has the largest number of AIDS related deaths, exceeding 42,000 people dying from AIDS, while the Caribbean area owns the smallest.
In 2014, President Moga of Botswana, speaking at the 72nd OAU Council of ministers meeting, said that AIDS had spread like a plague on the African continent and that his country was now in danger of extinction. " We are in a state crisis. We are threatened by genocide as a whole. A large number of people are dying. We have lost the best young people, which is a tragedy. "
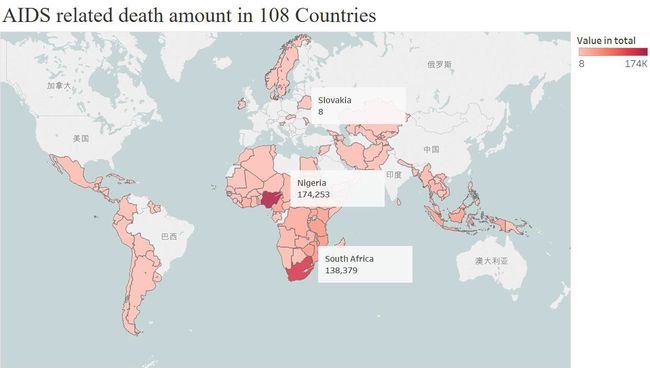
According to the data from UNDATA, in 2014 Nigeria had the largest number of death amount, followed by South Africa with the number of 138,379. The Europe country Slovakia had the smallest——8 people. And here are the map:
When people show AIDS symptoms, they will lose their ability to work and require medical protection. This is likely to cause social and national recession in their regions. Many governments in the regions have denied the existence of this problem for many years and have not been working on it until now. Lack of medical protection, ignorance of disease and its causes, and funding for education and treatment are among the main causes of death among AIDS patients in the third world.
Treatment and Hope
The World AIDS Dayis December 1st, which aims to raise public awareness of the globalspread of HIV. Lots of organizations and governments have been making everyendeavor to eliminate the discrimination towards HIV carriers and try to findthe way to cure it.
With the efforts in medical technology, now we have some treatment for AIDS patients. However, now there is no cure or effective HIV vaccine. Treatment consists of highly active antiretroviral therapy which slows progression of the disease. Treatment also includes preventive and active treatment of opportunistic infections.
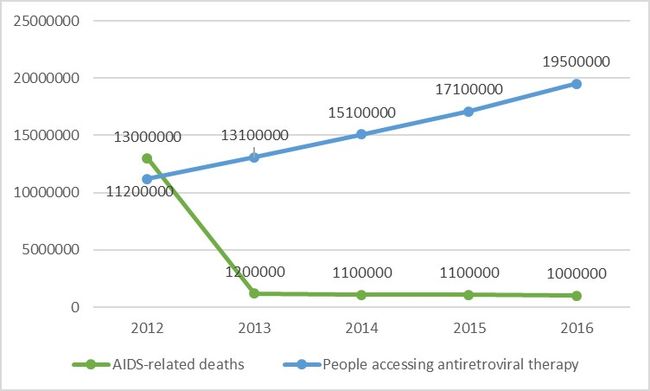
The following curve chart shows the relationship between global number of people accessing antiretroviral therapy and AIDS-related deaths in the past five years. And we can see that the world has made some achievement and progress in fighting against AIDS. The number of deaths decreased from 13,000,000 in 2012 to 1000,000 in 2016.
The world is stillworking towards stopping new HIV infections. And it’s essential for all of usto protect the human rights for HIV carriers. They also need the love and carefrom other people. UNAIDS set up a goal that ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030,and all of us needs to joint hands together to face the challenge to pursue a better future for the whole world.
Sources:
UNAIDS
http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf
UNDATA
http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?q=AIDS&d=UNAIDS&f=inID%3a33
My H5 version:http://u5794958.viewer.maka.im/k/445IA22C