目录:
- 初始化
- 发送命令和重试机制
- 总结
前言
前面说了 Jedis(2.9.0) 如何支持 Redis Sentinel 的,今天看看 Jedis 是如何支持 Redis Cluster 的。
1 初始化
Jedis Cluster 构造方法:
public JedisCluster(Set jedisClusterNode, int connectionTimeout, int soTimeout,
int maxAttempts, final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig) {
super(jedisClusterNode, connectionTimeout, soTimeout, maxAttempts, poolConfig);
}
注意: Set 中包含所有主从节点。
通过层层跟踪,我们来到了 initializeSlotsCache 方法。
private void initializeSlotsCache(Set startNodes, GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, String password) {
for (HostAndPort hostAndPort : startNodes) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis(hostAndPort.getHost(), hostAndPort.getPort());
if (password != null) {
jedis.auth(password);
}
try {
//
cache.discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(jedis);
break;
} catch (JedisConnectionException e) {
// try next nodes
} finally {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}
}
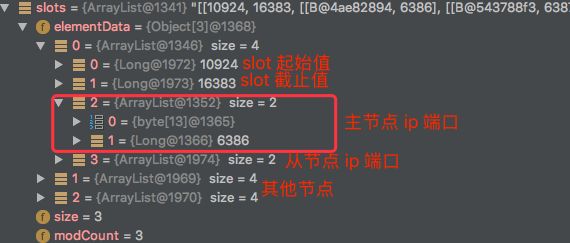
这个 cache 设计上就是 Redis Cluster slot 的缓存,每个 slot 都指向一个连接池。看看这个 cache 的内部结构:
public class JedisClusterInfoCache {
private final Map nodes = new HashMap();// ip:port 对应的连接池
private final Map slots = new HashMap();// slot 对应的连接池
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private final Lock r = rwl.readLock();
private final Lock w = rwl.writeLock();
private volatile boolean rediscovering;
private final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig;
private int connectionTimeout;
private int soTimeout;
private String password;
private static final int MASTER_NODE_INDEX = 2;// 主节点下标
其中,在 initializeSlotsCache方法中,会遍历所有的节点信息,但是,只会执行一次 cache.discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(jedis),如果失败了,就继续执行这个方法。为什么只需要执行一次呢?
来看看 cache.discoverClusterNodesAndSlots 方法:
public void discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(Jedis jedis) {
w.lock();
try {
reset();
List该方法作用如下:通过任意一个节点,得到所有主节点的信息。数据格式为:
得到这些信息后,根据 ip + port 创建连接池,并缓存所有的连接池,key 为 “ip:port”,value 则是对应的连接池,如果是主节点,则更进一步,将 solt 和连接池也全部缓存,便于查询。
该方法涉及的几个方法如下:
private List getAssignedSlotArray(List slotInfo) {
List slotNums = new ArrayList();
// 0位是起始 slot, 1 位是截止 slot, 这里是得到所有的 slot
for (int slot = ((Long) slotInfo.get(0)).intValue(); slot <= ((Long) slotInfo.get(1)).intValue(); slot++) {// 初始是第一个, slot 不能大于第二个 slot
slotNums.add(slot);
}
return slotNums;
}
public JedisPool setupNodeIfNotExist(HostAndPort node) {
w.lock();
try {
String nodeKey = getNodeKey(node); // ip:port
JedisPool existingPool = nodes.get(nodeKey);// 从 map 里获取缓存
if (existingPool != null) return existingPool;// 如果有,就不再初始化
// 创建连接池
JedisPool nodePool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, node.getHost(), node.getPort(),
connectionTimeout, soTimeout, password, 0, null, false, null, null, null);
nodes.put(nodeKey, nodePool);// 缓存
return nodePool;
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
public void assignSlotsToNode(List targetSlots, HostAndPort targetNode) {
w.lock();
try {
JedisPool targetPool = setupNodeIfNotExist(targetNode);// 获取该节点的连接池
for (Integer slot : targetSlots) {// 将所有槽位指向该连接池
slots.put(slot, targetPool);
}
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
所以,当这个步骤成功以后,所有的 slot 和对应的连接池都初始化好了,后面就直接 break 了。如果途中失败了,则继续尝试。
2 发送命令和重试机制
好了,我们已经知道,slot 和连接池是保存在 JedisClusterInfoCache 类中的,那么,我们使用 API 的时候又是怎么操作的呢?
以 set 方法为例:
public String set(final String key, final String value) {
return new JedisClusterCommand(connectionHandler, maxAttempts) {
@Override
public String execute(Jedis connection) {
return connection.set(key, value);
}
}.run(key);
}
这里会创建一个 Redis 命令对象,然后执行 run 方法,run 方法里会回调命令对象的 execute 方法。run 方法内部调用的是 runWithRetries 方法,看名字,这是一个带有重试机制的方法. 该方法有个参数就是 int attempts,用户自己设置的重试次数。
看看 runWithRetries 方法实现(因为包含了失败重试逻辑,所以很长):
private T runWithRetries(byte[] key, int attempts, boolean tryRandomNode, boolean asking) {
if (attempts <= 0) {// 重试次数
throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?");
}
Jedis connection = null;
try {
if (asking) {// 第一次 false,如果节点 A 正在迁移槽 i 至节点 B , 那么当节点 A 没能在自己的数据库中找到命令指定的数据库键时, 节点 A 会向客户端返回一个 ASK 错误, 指引客户端到节点 B 继续查找指定的数据库键
connection = askConnection.get();
connection.asking();// 到目标节点打开客户端连接标识
// if asking success, reset asking flag
asking = false;
} else {
if (tryRandomNode) {// 如果是随机的
connection = connectionHandler.getConnection();
} else {// 默认不是随机的,通过 CRC16 算法获取 slot 对应的节点的连接池中的连接
connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key));
}
}
// 执行
return execute(connection);
} catch (JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException jnrcne) {// 集群不存在
throw jnrcne;
} catch (JedisConnectionException jce) {// 连接异常
// release current connection before recursion
releaseConnection(connection);//归还连接
connection = null;
if (attempts <= 1) {// 如果重试次数只有一次,那就更新连接池,并抛出异常
this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache();
throw jce;
}
return runWithRetries(key, attempts - 1, tryRandomNode, asking);// 否则递归重试,重试次数减一
} catch (JedisRedirectionException jre) {// 如果是重定向异常,例如 moved ,ASK
// if MOVED redirection occurred,
if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) {// 节点在接到一个命令请求时, 会先检查这个命令请求要处理的键所在的槽是否由自己负责, 如果不是的话, 节点将向客户端返回一个 MOVED 错误, MOVED 错误携带的信息可以指引客户端转向至正在负责相关槽的节点
// 如果是 moved 错误,就更新连接池, ASK 就不必更新缓存,只需要临时访问就行
this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(connection);
}
// 归还旧的连接
releaseConnection(connection);
connection = null;
// 如果是 ASK
if (jre instanceof JedisAskDataException) {
asking = true;
// 设置 ThreadLocal,新的连接是 ASK 指定的节点
askConnection.set(this.connectionHandler.getConnectionFromNode(jre.getTargetNode()));
} else if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) {// 如果是 moved 错误,不处理错误,重试。
} else {
throw new JedisClusterException(jre);
}
// 重试
return runWithRetries(key, attempts - 1, false, asking);
} finally {
releaseConnection(connection);
}
}
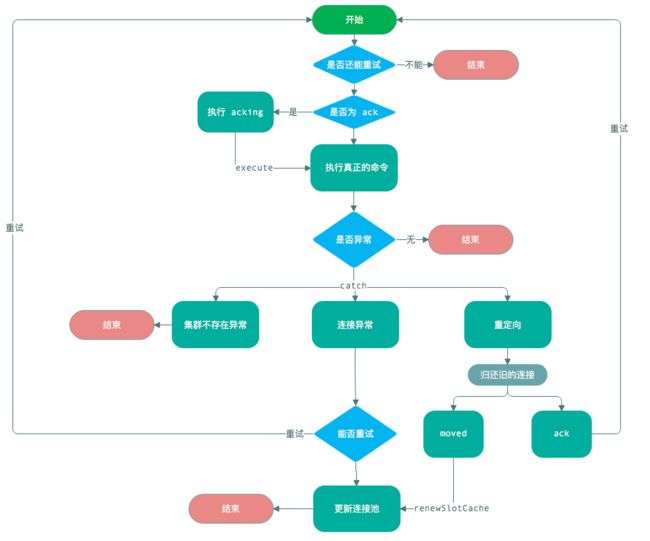
该方法主要步骤如下:
- 默认是使用 CRC16 算法通过 key 得到 slot ,然后,根据 slot 得到 Jedis 连接,也就是从我们刚刚说的缓存里获取连接。
- 得到连接后,回调命令对象的 execute 方法。
- 如果发生了 JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException 异常,表明集群不存在,则直接抛出异常,结束方法。
- 如果发生了 JedisConnectionException 连接异常,则进行递归重试,如果重试次数只剩一次,则刷新连接池缓存。
- 如果发生了 JedisRedirectionException 重定向异常,如果返回的是 moved,则刷新连接池。如果是 ASK,则不刷新连接池,在下次递归中直接使用 ASK 返回的信息进行调用。下次递归时,先执行 asking 命令打开新的客户端连接,如果成功,则执行真正的命令。
- 最终,归还连接。
大致的流程图如下:
这里说一下 ASK 和 MOVED:
ASK:如果节点 A 正在迁移槽 i 至节点 B , 那么当节点 A 没能在自己的数据库中找到命令指定的数据库键时, 节点 A 会向客户端返回一个 ASK 错误, 指引客户端到节点 B 继续查找指定的数据库键。
MOVED:节点在接到一个命令请求时, 会先检查这个命令请求要处理的键所在的槽是否由自己负责, 如果不是的话, 节点将向客户端返回一个 MOVED 错误, MOVED 错误携带的信息可以指引客户端转向至正在负责相关槽的节点。
两者的共同点都是重定向,不同点是:ASK 是迁移过程中返回的,MOVED 是迁移结束后返回的。如返回 ASK ,那么就不必更新客户端缓存,因为客户端无法知道什么时候迁移完成,因此只能是临时性的重定向。但是 MOVED 重定向说明键对应的 slot 已经成功的转移到了新的节点,那么就可以换成这些连接。
注意:当重试次数不够时,会抛出 throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?") 异常,原因是节点宕机或请求超时触发了重试,而重试次数耗尽就会触发这个异常。
当 Cluster 进行故障发现到完成故障转移,需要一定的时间,节点宕机期间,所有指向这个节点的命令都会触发重试,当收到 moved 命令则会进行连接刷新 —— 也就是 renewSlotCache 方法。
注意:更新连接池的过程是串行加锁的!!
代码如下:
public void renewClusterSlots(Jedis jedis) {
//If rediscovering is already in process - no need to start one more same rediscovering, just return
if (!rediscovering) {
try {
w.lock();
rediscovering = true;
if (jedis != null) {
try {
discoverClusterSlots(jedis);
return;
} catch (JedisException e) {
//try nodes from all pools
}
}
for (JedisPool jp : getShuffledNodesPool()) {
try {
jedis = jp.getResource();
discoverClusterSlots(jedis);
return;
} catch (JedisConnectionException e) {
// try next nodes
} finally {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}
} finally {
rediscovering = false;
w.unlock();
}
}
}
注意:代码中使用了写锁,而获取连接池时则使用了读锁,读写锁是互斥的,这时将导致所有访问集群的线程阻塞!!!
当然,只有出现 MOVED 错误或者 JedisConnectionException 异常且无法继续重试时,才会进行刷新连接池操作。
3 总结
本文旨在分析 Jedis 如何支持 Redis Cluster,因为 Redis Cluster 需要客户端来支持分片。Jedis 内部使用了一个 JedisClusterInfoCache 保存 slot 和 pool,ip:port 和 pool 的映射关系,ip:port 的缓存更多是服务于 ask 时寻找节点。
在使用客户端是时候,Jedis 会有重试机制,用户可以设置重试次数,如果发生了 ask,客户端会自动根据返回值重定向,如果发生了 moved,则会刷新连接池中的 slot,因为集群发生了迁移。
需要注意的是,当集群进行迁移的时候,如果有客户端访问迁移的节点,那么将会导致刷新连接池,而这个连接池是有锁,当刷新的时候,使用的是写锁,将导致所有的读都会阻塞,所以,迁移尽量在业务低谷进行。
了解客户端的原理,有助于我们理解 Redis Cluster 的运行原理,也有助于我们平时编写代码,运维缓存,排查故障。