github地址:https://github.com/Iamdreaming/WC
题目描述
-
Word Count
- 实现一个简单而完整的软件工具(源程序特征统计程序)。
- 进行单元测试、回归测试、效能测试,在实现上述程序的过程中使用相关的工具。
- 进行个人软件过程(PSP)的实践,逐步记录自己在每个软件工程环节花费的时间。
WC 项目要求
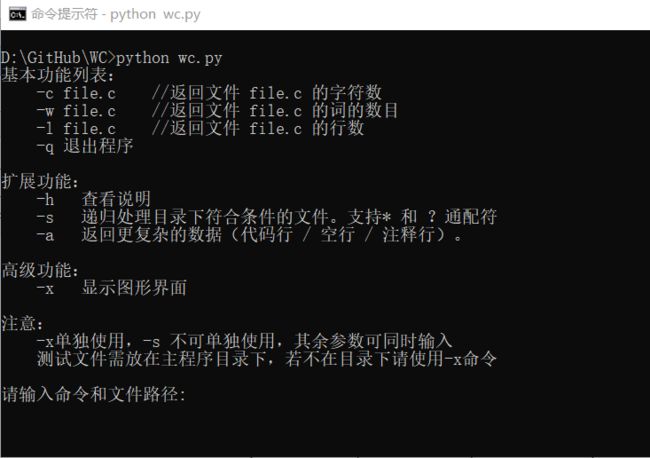
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
-
遇到的困难及解决方法
-
困难描述
1.仅仅了解正则表达式,以及未接触过re库,
2.对python标准库tkinter库,os库的学习 -
做过哪些尝试
查看正则表达式相关文档,并学习re库,tkinter,os相关文档及csdn博客,期间了解了python三大gui库wxpython,tkinter,pygt,
由于wxpython相关文档较少以及pyqt上手难度较高,最终选择了python标准库tkinter -
是否解决
使用正则表达式解决通配符?,*问题,以及单词匹配问题(汉字无法解决,并用空格+正则表达式解决单词识别)以及实现gui界面(虽然好丑) -
有何收获
学会了一边查文档一边编程
很多时候觉得实现这个功能很麻烦,但开始写代码其实很简单
学习到tkinter,re的使用
-
代码
代码有三个类:text_count()处理文本统计,infor_windows() gui界面,Order()对命令处理调用text_count(),以及handle_file()获得-s命令操作符合的文件路径
调用相关的库:
import os
import re
import time
import tkinter
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter import filedialog
class text_count():
def __init__(self, path):
self.path = path
def char_count(self):
# 统计字符数 -c
file_object = open(self.path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
context = file_object.read()
# 将空格和换行符去掉
context = context.replace(' ', '')
context = context.replace('\n', '')
string = "字符数为"+str(len(context))
return string
def words_count(self):
# 统计单词数 -w
reg = re.compile(r'\w+')
file_object = open(self.path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
context = file_object.read()
words = context.split()
for word in words:
if reg.search(word) == None:
words.remove(word)
string = '单词个数为' + str(len(words))
return string
def lines_count(self):
# 统计行数 -l
file_object = open(self.path, 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
count = 0
for line in file_object.readlines():
count += 1
string = '行数为' + str(count)
return string
def more_information(self):
# 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行) -a
file_object = open(self.path, 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
count = [0, 0, 0]
flag = False # 用于判断/*
for line in file_object.readlines():
if len(line) <= 1:
count[0] += 1
elif r'//' in line:
count[1] += 1
elif r'/*' in line:
flag = True
count[1] += 1
elif flag:
count[1] += 1
if r'*/' in line:
flag = False
else:
count[2] += 1
string1 = '空行数为' + str(count[0])
string2 = '注释行数为' + str(count[1])
string3 = '代码行数为' + str(count[2])
string_all = [string1, string2, string3]
return string_all
class infor_windows(tkinter.Frame):
def __init__(self, master):
# 将窗口分为三个部分,对应三个容器frame1,frame2,order_frame
frame1 = tkinter.Frame(master)
frame2 = tkinter.Frame(master)
order_frame = tkinter.Frame(master)
frame1.grid(row=0, column=5)
frame2.grid(row=4, column=5)
order_frame.grid(row=4, column=12)
# self.name获取文件名并显示在entry文本框
self.name = tkinter.Variable()
self.entry = tkinter.Entry(frame1, textvariable=self.name)
self.entry.pack(side='left')
# self.text显示文本内容
self.text = tkinter.Text(frame2, width=40, height=20)
# 文件选择按钮 self.select_button,调用open_fil()函数
self.select_button = tkinter.Button(
frame1, text='选择', command=self.open_file)
self.select_button.pack(side='right')
self.text.pack()
# c命令按钮以及结果显示
self.c_button = tkinter.Button(
order_frame, text='c命令', command=self.order_c)
self.get_c = tkinter.Variable()
self.show_c = tkinter.Entry(order_frame, textvariable=self.get_c)
self.c_button.pack()
self.show_c.pack()
#
self.w_button = tkinter.Button(
order_frame, text='w命令', command=self.order_w)
self.get_w = tkinter.Variable()
self.show_w = tkinter.Entry(order_frame, textvariable=self.get_w)
self.w_button.pack()
self.show_w.pack()
#
self.l_button = tkinter.Button(
order_frame, text='l命令', command=self.order_l)
self.get_l = tkinter.Variable()
self.show_l = tkinter.Entry(order_frame, textvariable=self.get_l)
self.l_button.pack()
self.show_l.pack()
#
self.a_button = tkinter.Button(
order_frame, text='a命令', command=self.order_a)
self.show_a = tkinter.Text(order_frame, width=20, height=3)
self.a_button.pack()
self.show_a.pack()
# 使用text_count类并传递参数,调用相应函数返回结果
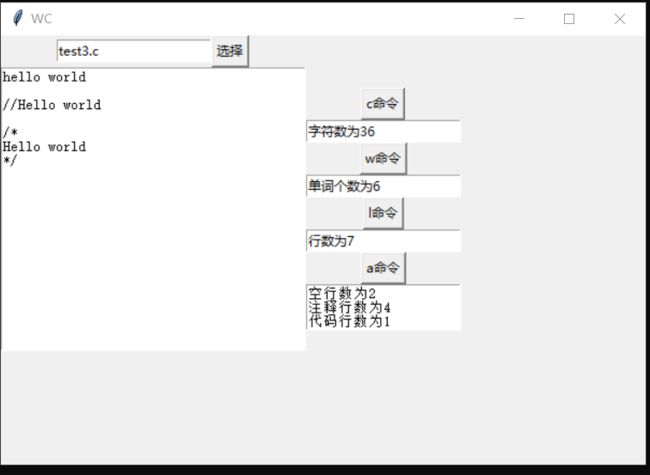
def order_c(self):
count_c = text_count(self.file_name)
self.get_c.set(count_c.char_count())
def order_w(self):
count_w = text_count(self.file_name)
self.get_w.set(count_w.words_count())
def order_l(self):
count_l = text_count(self.file_name)
count_l.char_count()
self.get_l.set(count_l.lines_count())
def order_a(self):
count_a = text_count(self.file_name)
strings = count_a.more_information()
for string in strings:
self.show_a.insert('insert', string + '\n')
def open_file(self):
# set()及delete()将所有文本清零
self.name.set('')
self.get_c.set('')
self.get_w.set('')
self.get_l.set('')
self.show_a.delete('1.0', 'end')
self.text.delete('1.0', 'end')
# 获取文件名
self.file_name = filedialog.askopenfilename()
self.name.set(self.file_name.split(r'/')[-1])
file = open(self.file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
for line in file.readlines():
self.text.insert('insert', line)
class Order():
def base_orders(self, w_c, words):
# 处理命令
if '-c' in words:
print(w_c.char_count())
if '-w' in words:
print(w_c.words_count())
if '-l' in words:
print(w_c.lines_count())
if '-a' in words:
for string in w_c.more_information():
print(string)
def senior_orders(self, words):
# 处理-s命令,当不存在-c命令时执行base_order
if os.path.exists(words[-1]) == False and '-s' not in words:
print('请正确输入\n')
elif '-s' in words:
i = 0
all_files = []
all_path = []
# word[-1]获取文件名并将通配符替换成正则表达式
word = words[-1]
word = word.replace('.', '\.')
word = word.replace('*', '.*')
word = word.replace('?', '.?')
# 获取当前文件的父目录
father_path = os.path.split(os.path.abspath('wc.py'))[0]
# 递归获取匹配文件名
handle_files(father_path, all_files, all_path, word)
for file in all_files:
print(file + ':')
w_c = text_count(all_path[i])
self.base_orders(w_c, words)
print()
i += 1
else:
w_c = text_count(words[-1])
self.base_orders(w_c, words)
print()
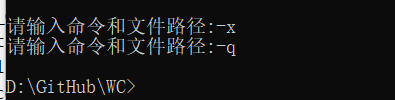
def gui_order(self, words):
# gui界面处理文件
if '-x' in words:
win = tkinter.Tk()
win.title('WC')
win.geometry('600x400')
inwindow = infor_windows(win)
win.mainloop()
else:
self.senior_orders(words)
def handle_files(father_path, all_files, all_path, word):
# 递归返回目录下符合条件的文件路径。-s
reg = re.compile(word)
file_list = os.listdir(father_path)
for file in file_list:
cur_path = os.path.join(father_path, file)
# 判断是否是文件夹
if os.path.isdir(cur_path):
handle_files(cur_path, all_files, all_path, word)
elif os.path.isfile(cur_path):
if reg.search(file):
all_path.append(cur_path)
all_files.append(file)
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 15 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 891 | 961 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 300 | 420 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 0 | 0 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 1 | 1 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 420 | 400 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 50 | 50 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 90 | 90 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 40 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 | 1011 | 1081 |