如何在sql中选取每一组的第一行/最后行/前几行
转载请注明: TheViper http://www.cnblogs.com/TheViper
部分翻译自How to select the first/least/max row per group in SQL
一些常见的sql问题有着类似的解决方法,比如:查找每个程序最近的日志,查找每个商品分类中最受欢迎的商品,查找每个玩家的玩出的前5高分。。。这些问题可以被归纳为从各组中选出Top N.
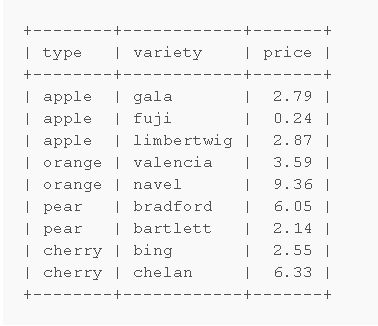
选取每个分类中价格最低的行
步骤:1.找到要求的所需的值price。2.填充其他字段
方法1.自连接
按type分组并选取价格最低的行
select type, min(price) as minprice from fruits group by type;
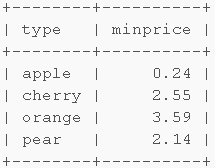
用自连接把剩下的行与上面的行合并,由于上面的查询已经分好组了,这里用子查询把剩下的字段连接到没分组的表中。
select f.type, f.variety, f.price from ( select type, min(price) as minprice from fruits group by type ) as x inner join fruits as f on f.type = x.type and f.price = x.minprice;

事实上此方法直接用group分组就可以了,不知道作者怎么想的。
SELECT TYPE,variety, MIN(price) AS minprice FROM fruits GROUP BY TYPE;
方法2 相关子查询
这种方法效率低点,但是很清晰。
select type, variety, price from fruits where price = (select min(price) from fruits as f where f.type = fruits.type);
选取每组的Top N行
select type, variety, price from fruits where price = (select min(price) from fruits as f where f.type = fruits.type) or price = (select min(price) from fruits as f where f.type = fruits.type and price > (select min(price) from fruits as f2 where f2.type = fruits.type));
可以看到,先选出价格最低的行,然后选出价格第二低的行,两个用or连接。
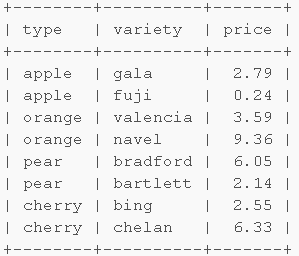
这个也可以用自连接写,不过要复杂点。可以看到,如果需要选出top3,top4,...的时候,这种方法就会变得糟糕。
这里有个更好的方法
select type, variety, price from fruits where ( select count(*) from fruits as f where f.type = fruits.type and f.price <= fruits.price ) <= 2;
这个可以理解成,遍历外面的fruits各行,如果同一分类中,还有其他行<=该行且这样的行的个数<=2,那该行符合要求,取出。
可以看到这种方法很优雅,因为改变n为其他值时都不需要重写。但是这个方法和上个方法本质上是一样的,都用到了子查询。而一些查询优化器在子查询上做的不够好。
使用union
如果(type, price)上有索引,并且索引可以过滤很多行,这时就可以对各个分类用limit.然后union把它们合并。
(select * from fruits where type = 'apple' order by price limit 2) union all (select * from fruits where type = 'orange' order by price limit 2) union all (select * from fruits where type = 'pear' order by price limit 2) union all (select * from fruits where type = 'cherry' order by price limit 2)
注意,这里是UNION ALL,不是UNION。这样做可以防止在返回结果前,对结果排序以去除重复的行。在该情景中不会出现重复的行,所以这里要告诉数据库不要排序去重。
关于union可以参见Using UNION to implement loose index scan in MySQL
使用用户变量(user variables) 仅限mysql
上面union这种方法在行数较少且有索引可以用来排序时,是个好办法。下面介绍的方法仅对mysql有效。介绍这种方法前请看我的另外一篇文章 how to number rows in MySQL。
文章简单说来,就是为同一分类的行依次递增编号

而下面介绍的方法正是基于此。
set @num := 0, @type := ''; select type, variety, price from ( select type, variety, price, @num := if(@type = type, @num + 1, 1) as row_number, @type := type as dummy from fruits order by type, price ) as x where x.row_number <= 2;
子查询创建临时表,并向里面填充row_number,dummy,这是一次操作。然后从中选出row_number<=2的行,这又是一次操作。尽管有两次操作,但其复杂度仍然是O(n),只和表的大小相关,这比相关子查询的复杂度O(n2)好很多。相关子查询的n是分类个数,如果有很多分类的话,性能会很糟糕。
(完)