Android HTTP实例 使用GET方法和POST方法发送请求
Android HTTP实例 使用GET方法和POST方法发送请求
Web程序:使用GET和POST方法发送请求
首先利用MyEclispe+Tomcat写好一个Web程序,实现的功能就是提交用户信息:用户名和年龄,使用GET和POST两种提交方式。
用浏览器打开:
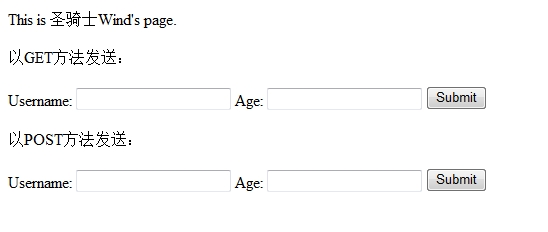
不管以哪一种方式,提交以后显示如下页面,将提交的信息再显示出来。

关键代码如下:

<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> This is 圣骑士Wind's page. <br> <p> 以GET方法发送:<br> <form action="servlet/WelcomeUserServlet" method="get"> Username: <input type="text" name="username" value=""> Age: <input type="text" name="age" value=""> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </p> <p> 以POST方法发送:<br> <form action="servlet/WelcomeUserServlet" method="post"> Username: <input type="text" name="username" value=""> Age: <input type="text" name="age" value=""> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> </form> </p> </body> </html>
第二个页面显示结果:

package com.shengqishiwind; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class WelcomeUserServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * The doGet method of the servlet. <br> * * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get. * * @param request the request send by the client to the server * @param response the response send by the server to the client * @throws ServletException if an error occurred * @throws IOException if an error occurred */ public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { process(request, response); } /** * The doPost method of the servlet. <br> * * This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to post. * * @param request the request send by the client to the server * @param response the response send by the server to the client * @throws ServletException if an error occurred * @throws IOException if an error occurred */ public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { process(request, response); } private void process(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String username = request.getParameter("username"); String age = request.getParameter("age"); response.setContentType("text/html"); PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); out.println("<html><head><title>Welcome!</title></head>"); out.println("<body> Welcome my dear friend!<br>"); out.println("Your name is: " + username + "<br>"); out.println("And your age is: " + age + "</body></html>"); out.flush(); out.close(); } }
Android程序:使用GET方法和POST方法发送请求
上面是用浏览器访问页面并提交数据,如果想在Android客户端提交,服务器端的代码是不用变的,只要写好客户端代码即可:
首先要在manifest中加上访问网络的权限:
<manifest ... >
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> ... </manifest>
布局文件:

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Username:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType="text" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="User Age:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/age" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType="number" /> <Button android:id="@+id/submit_get" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Submit using GET" /> <Button android:id="@+id/submit_post" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Submit using POST" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/result" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textColor="#0000FF" android:textSize="14sp"> </TextView> </LinearLayout>
主要Activity代码如下:
package com.example.httpdemo2; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.HttpResponse; import org.apache.http.NameValuePair; import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient; import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient; import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.TextView; public class HttpDemo2Activity extends Activity { private String TAG = "http"; private EditText mNameText = null; private EditText mAgeText = null; private Button getButton = null; private Button postButton = null; private TextView mResult = null; // 基本地址:服务器ip地址:端口号/Web项目逻辑地址+目标页面(Servlet)的url-pattern private String baseURL = "http://192.168.11.6:8080/HelloWeb/servlet/WelcomeUserServlet"; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { Log.i(TAG, "onCreate"); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_http_demo2); mNameText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.name); mAgeText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.age); mResult = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.result); getButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.submit_get); getButton.setOnClickListener(mGetClickListener); postButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.submit_post); postButton.setOnClickListener(mPostClickListener); } private OnClickListener mGetClickListener = new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Log.i(TAG, "GET request"); // 先获取用户名和年龄 String name = mNameText.getText().toString(); String age = mAgeText.getText().toString(); // 使用GET方法发送请求,需要把参数加在URL后面,用?连接,参数之间用&分隔 String url = baseURL + "?username=" + name + "&age=" + age; // 生成请求对象 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url); HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); // 发送请求 try { HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet); // 显示响应 showResponseResult(response);// 一个私有方法,将响应结果显示出来 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; private OnClickListener mPostClickListener = new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Log.i(TAG, "POST request"); // 先获取用户名和年龄 String name = mNameText.getText().toString(); String age = mAgeText.getText().toString(); NameValuePair pair1 = new BasicNameValuePair("username", name); NameValuePair pair2 = new BasicNameValuePair("age", age); List<NameValuePair> pairList = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(); pairList.add(pair1); pairList.add(pair2); try { HttpEntity requestHttpEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity( pairList); // URL使用基本URL即可,其中不需要加参数 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(baseURL); // 将请求体内容加入请求中 httpPost.setEntity(requestHttpEntity); // 需要客户端对象来发送请求 HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); // 发送请求 HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); // 显示响应 showResponseResult(response); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; /** * 显示响应结果到命令行和TextView * @param response */ private void showResponseResult(HttpResponse response) { if (null == response) { return; } HttpEntity httpEntity = response.getEntity(); try { InputStream inputStream = httpEntity.getContent(); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( inputStream)); String result = ""; String line = ""; while (null != (line = reader.readLine())) { result += line; } System.out.println(result); mResult.setText("Response Content from server: " + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
可以从中对比GET方法和POST方法的区别:
GET方法需要用?将参数连接在URL后面,各个参数之间用&连接。
POST方法发送请求时,仍然使用基本的URL,将参数信息放在请求实体中发送。
关于这点的讨论也可以查看本博客其他文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/05/26/3099776.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/06/12/3132702.html
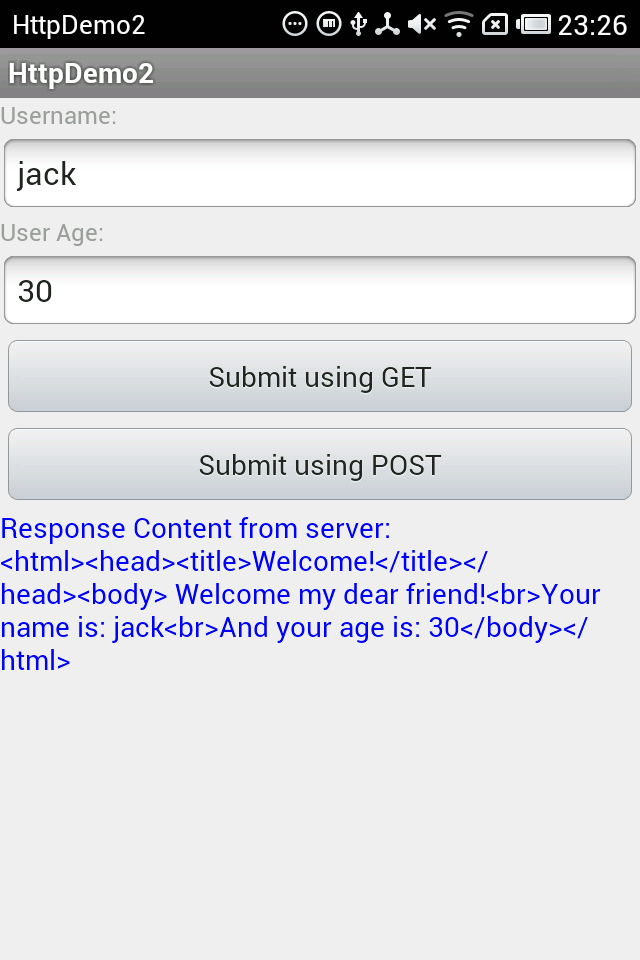
程序运行结果如下:
参考资料
Android开发视频教程HTTP操作。——http://www.marsdroid.org
Android Reference: package org.apache.http:
http://developer.android.com/reference/org/apache/http/package-summary.html
之前文章中,关于GET和POST的更多讨论:
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/05/26/3099776.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/06/12/3132702.html
