基于opencv的车道线检测(c++)
基于opencv的车道线检测
原理:
算法基本思想说明:
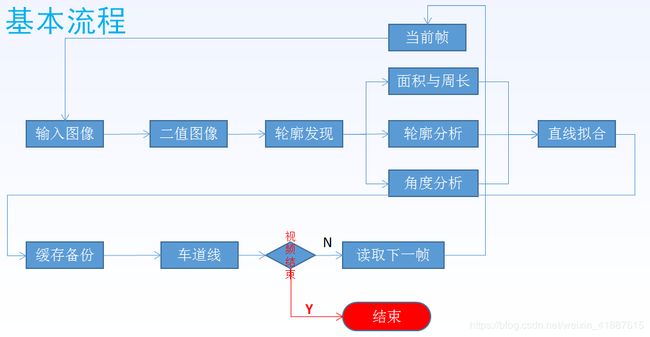
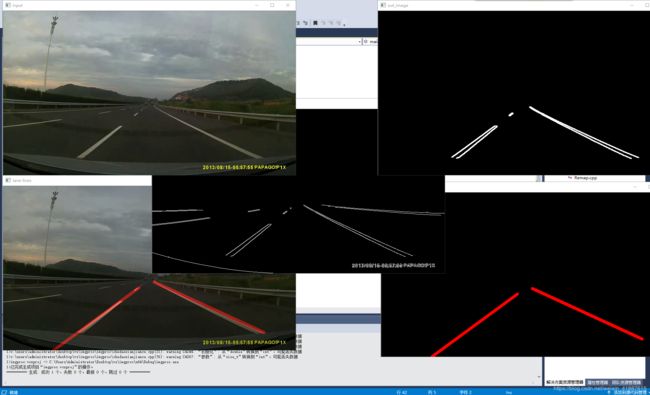
传统的车道线检测,多数是基于霍夫直线检测,其实这个里面有个很大的误区,霍夫直线拟合容易受到各种噪声干扰,直接运用有时候效果不好,更多的时候通过霍夫直线检测进行初步的筛选,然后再有针对性的进行直线拟合,根据拟合的直线四个点坐标,绘制出车道线,这种方式可以有效避免霍夫直线拟合不良后果,是一种更加稳定的车道线检测方法,在实际项目中,可以选择两种方法并行,在计算出结果后进行叠加或者对比提取,今天分享的案例主要是绕开了霍夫直线检测,通过对二值图像进行轮廓分析与几何分析,提取到相关的车道线信息、然后进行特定区域的像素扫描,拟合生成直线方程,确定四个点绘制出车道线,对连续的视频来说,如果某一帧无法正常检测,就可以通过缓存来替代绘制,从而实现在视频车道线检测中实时可靠。
原理图:
代码:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/**
**1、读取视频
**2、二值化
**3、轮廓发现
**4、轮廓分析、面积就算,角度分析
**5、直线拟合
**6、画出直线
**
*/
Point left_line[2];
Point right_line[2];
void process(Mat &frame, Point *left_line, Point *right_line);
Mat fitLines(Mat &image, Point *left_line, Point *right_line);
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
//读取视频
VideoCapture capture("E:/opencv/road_line.mp4");
int height = capture.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT);
int width = capture.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH);
int count = capture.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT);
int fps = capture.get(CAP_PROP_FPS);
//初始化
left_line[0] = Point(0,0);
left_line[1] = Point(0, 0);
right_line[0] = Point(0, 0);
right_line[1] = Point(0, 0);
cout << height<<" "<< width<< " " <(i, j) = 0;
}
}
imshow("binary", binary);
//寻找轮廓
vector> contours;
findContours(binary, contours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
Mat out_image = Mat::zeros(gray.size(), gray.type());
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
//计算面积与周长
double length = arcLength(contours[i], true);
double area = contourArea(contours[i]);
//cout << "周长 length:" << length << endl;
//cout << "面积 area:" << area << endl;
//外部矩形边界
Rect rect = boundingRect(contours[i]);
int h = gray.rows - 50;
//轮廓分析:
if (length < 5.0 || area < 10.0) {
continue;
}
if (rect.y > h) {
continue;
}
//最小包围矩形
RotatedRect rrt = minAreaRect(contours[i]);
//关于角度问题:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41887615/article/details/91411086
//cout << "最小包围矩形 angle:" << rrt.angle << endl;
double angle = abs(rrt.angle);
//angle < 50.0 || angle>89.0
if (angle < 20.0 || angle>84.0) {
continue;
}
if (contours[i].size() > 5) {
//用椭圆拟合
RotatedRect errt = fitEllipse(contours[i]);
//cout << "用椭圆拟合err.angle:" << errt.angle << endl;
if ((errt.angle<5.0) || (errt.angle>160.0))
{
if (80.0 < errt.angle && errt.angle < 100.0) {
continue;
}
}
}
//cout << "开始绘制:" << endl;
drawContours(out_image, contours, i, Scalar(255), 2, 8);
imshow("out_image", out_image);
}
Mat result = fitLines(out_image, left_line, right_line);
imshow("result", result);
Mat dst;
addWeighted(frame, 0.8, result, 0.5,0, dst);
imshow("lane-lines", dst);
}
//直线拟合
Mat fitLines(Mat &image, Point *left_line, Point *right_line) {
int height = image.rows;
int width = image.cols;
Mat out = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_8UC3);
int cx = width / 2;
int cy = height / 2;
vector left_pts;
vector right_pts;
Vec4f left;
for (int i = 100; i < (cx-10); i++)
{
for (int j = cy; j < height; j++)
{
int pv = image.at(j, i);
if (pv == 255)
{
left_pts.push_back(Point(i, j));
}
}
}
for (int i = cx; i < (width-20); i++)
{
for (int j = cy; j < height; j++)
{
int pv = image.at(j, i);
if (pv == 255)
{
right_pts.push_back(Point(i, j));
}
}
}
if (left_pts.size() > 2)
{
fitLine(left_pts, left, DIST_L1, 0, 0.01, 0.01);
double k1 = left[1] / left[0];
double step = left[3] - k1 * left[2];
int x1 = int((height - step) / k1);
int y2 = int((cx - 25)*k1 + step);
Point left_spot_1 = Point(x1, height);
Point left_spot_end = Point((cx - 25), y2);
line(out, left_spot_1, left_spot_end, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 8, 0);
left_line[0] = left_spot_1;
left_line[1] = left_spot_end;
}
else
{
line(out, left_line[0], left_line[1], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 8, 0);
}
if (right_pts.size()>2)
{
Point spot_1 = right_pts[0];
Point spot_end = right_pts[right_pts.size()-1];
int x1 = spot_1.x;
int y1 = spot_1.y;
int x2 = spot_end.x;
int y2 = spot_end.y;
line(out, spot_1, spot_end, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 8, 0);
right_line[0] = spot_1;
right_line[1] = spot_end;
}
else
{
line(out, right_line[0], right_line[1], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 8, 0);
}
return out;
}