Java数据结构与算法 day09 树结构实际应用(二)
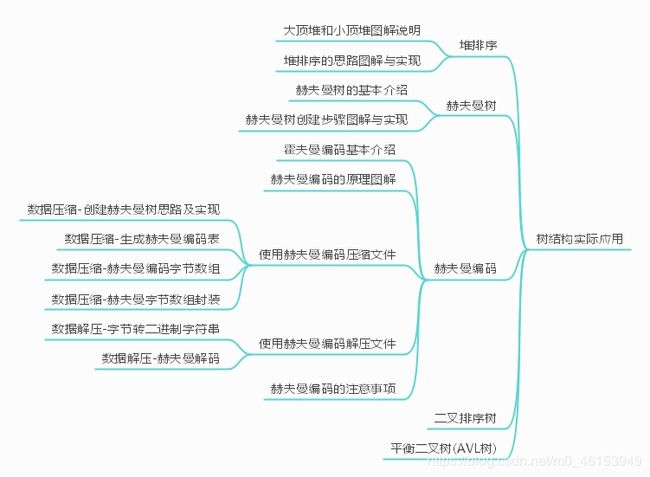
文章目录
- 第10章 树结构的实际应用
- 赫夫曼编码
- 霍夫曼编码基本介绍
- 赫夫曼编码的原理图解
- 数据压缩-创建赫夫曼树思路及实现
- 数据压缩-生成赫夫曼编码表
- 数据压缩-赫夫曼编码字节数组
- 数据压缩-赫夫曼字节数组封装
- 数据解压-字节转二进制字符串
- 数据解压-赫夫曼解码
- 使用赫夫曼编码压缩文件
- 使用赫夫曼编码解压文件
- 赫夫曼编码的注意事项
- 本章部分导图
第10章 树结构的实际应用
本章源码:https://github.com/name365/Java-Data-structure
赫夫曼编码
霍夫曼编码基本介绍
基本介绍:
1.赫夫曼编码也翻译为 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式, 属于一种程序算法 2.赫夫曼编码是赫哈夫曼树在电讯通信中的经典的应用之一。 3.赫夫曼编码广泛地用于数据文件压缩。其压缩率通常在20%~90%之间 4.赫夫曼码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,称之为最佳编码
赫夫曼编码的原理图解
- 变长编码的举例说明
- 通信领域中信息的处理方式1-定长编码
i like like like java do you like a java // 共40个字符(包括空格)
105 32 108 105 107 101 32 108 105 107 101 32 108 105 107 101 32 106 97 118 97 32 100 111 32 121 111 117 32 108 105 107 101 32 97 32 106 97 118 97 //对应Ascii码
01101001 00100000 01101100 01101001 01101011 01100101 00100000 01101100 01101001 01101011 01100101 00100000 01101100 01101001 01101011 01100101 00100000 01101010 01100001 01110110 01100001 00100000 01100100 01101111 00100000 01111001 01101111 01110101 00100000 01101100 01101001 01101011 01100101 00100000 01100001 00100000 01101010 01100001 01110110 01100001 //对应的二进制
按照二进制来传递信息,总的长度是 359 (包括空格)
在线转码 工具 :https://www.mokuge.com/tool/asciito16/
- 通信领域中信息的处理方式2-变长编码
i like like like java do you like a java // 共40个字符(包括空格)
d:1 y:1 u:1 j:2 v:2 o:2 l:4 k:4 e:4 i:5 a:5 :9 // 各个字符对应的个数
0= , 1=a, 10=i, 11=e, 100=k, 101=l, 110=o, 111=v, 1000=j, 1001=u, 1010=y, 1011=d
说明:按照各个字符出现的次数进行编码,原则是出现次数越多的,则编码越小,比如 空格出现了9 次, 编码为0 ,其它依次类推.
按照上面给各个字符规定的编码,则我们在传输 "i like like like java do you like a java" 数据时,编码就是
10010110100...
字符的编码都不能是其他字符编码的前缀,符合此要求的编码叫做前缀编码, 即不能匹配到重复的编码(这个在赫夫曼编码中,还要进行举例说明,看不懂,不捉急)
- 赫夫曼编码的原理图解
要传输的字符串
i like like like java do you like a java
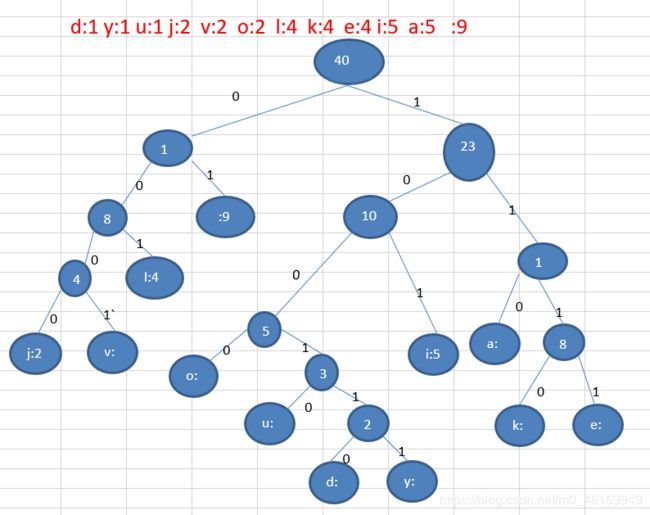
统计各个字符:d:1 y:1 u:1 j:2 v:2 o:2 l:4 k:4 e:4 i:5 a:5 :9 // 各个字符对应的个数
按照上面字符出现的次数构建一颗赫夫曼树, 次数作为权值
构成赫夫曼树的步骤:
1) 从小到大进行排序, 将每一个数据,每个数据都是一个节点 , 每个节点可以看成是一颗最简单的二叉树
2) 取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树
3) 组成一颗新的二叉树, 该新的二叉树的根节点的权值是前面两颗二叉树根节点权值的和
4) 再将这颗新的二叉树,以根节点的权值大小 再次排序, 不断重复 1-2-3-4 的步骤,直到数列中,所有的数据都被处理,就得到一颗赫夫曼树
4) 根据赫夫曼树,给各个字符,规定编码 (前缀编码), 向左的路径为0 向右的路径为1 , 编码如下: o: 1000 u: 10010 d: 100110 y: 100111 i: 101 a : 110 k: 1110 e: 1111 j: 0000 v: 0001 l: 001 : 01 5) 按照上面的赫夫曼编码,我们的"i like like like java do you like a java" 字符串对应的编码为 (注意这里我们使用的无损压缩) 1010100110111101111010011011110111101001101111011110100001100001110011001111000011001111000100100100110111101111011100100001100001110 通过赫夫曼编码处理 长度为 133 6) 长度为 : 133 说明: 原来长度是 359 , 压缩了 (359-133) / 359 = 62.9% 此编码满足前缀编码, 即字符的编码都不能是其他字符编码的前缀。不会造成匹配的多义性 赫夫曼编码是无损处理方案
- 注意事项
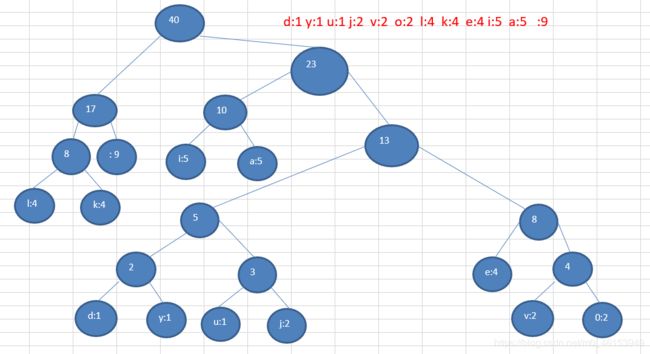
注意, 这个赫夫曼树根据排序方法不同,也可能不太一样,这样对应的赫夫曼编码也不完全一样,但是wpl 是一样的,都是最小的, 比如: 如果我们让每次生成的新的二叉树总是排在权值相同的二叉树的最后一个,则生成的二叉树为:
数据压缩-创建赫夫曼树思路及实现
将给出的一段文本,比如 "i like like like java do you like a java" , 根据前面叙述的赫夫曼编码原理,对其进行数据压缩处理 ,形式如 "1010100110111101111010011011110111101001101111011110100001100001110011001111000011001111000100100100110111101111011100100001100001110
"
步骤1:根据赫夫曼编码压缩数据的原理,需要创建 "i like like like java do you like a java" 对应的赫夫曼树.
-
具体思路:
- 创建Node { data (存放数据), weight (权值), left 和 right }
- 得到 “i like like like java do you like a java” 对应的 byte[] 数组
- 编写一个方法,将准备构建赫夫曼树的Node 节点放到 List , 形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]…], 体现 d:1 y:1 u:1 j:2 v:2 o:2 l:4 k:4 e:4 i:5 a:5 :9
- 可以通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
-
代码实现如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
System.out.println("nodes = " + nodes);
//创建的二叉树
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
System.out.println("前序遍历赫夫曼树:");
hfTree.preOrder();
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
数据压缩-生成赫夫曼编码表
我们已经生成了赫夫曼树, 下面将继续完成任务: 1.生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码, 如下表: =01 a=100 d=11000 u=11001 e=1110 v=11011 i=101 y=11010 j=0010 k=1111 l=000 o=0011
具体代码如下(相关思路看注释!!!):
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
System.out.println("nodes = " + nodes);
//创建的二叉树
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
System.out.println("前序遍历赫夫曼树:");
hfTree.preOrder();
//验证是否生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表:" + hfCodes);
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
数据压缩-赫夫曼编码字节数组
2.使用赫夫曼编码来生成赫夫曼编码数据 ,即按照上面的赫夫曼编码,将"i like like like java do you like a java" 字符串生成对应的编码数据, 形式如下. 1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100
- 此处运用到原码反码补码相关知识点,对此知识有所遗忘的读者,可以先了解一下相关知识,再进行阅读!!!当然,笔者也对此处知识也做了总结,可以参考:《Java基础》一文中的《进制与进制间的转换》
具体代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
//如何将 数据进行解压(解码)
//分步过程
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
System.out.println("nodes = " + nodes);
//创建的二叉树
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
System.out.println("前序遍历赫夫曼树:");
hfTree.preOrder();
//验证是否生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表:" + hfCodes);
//测试
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
System.out.println("hfCodeBytes=" + Arrays.toString(hfCodeBytes));//17
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
数据压缩-赫夫曼字节数组封装
使用赫夫曼编码来解码数据,具体要求是 1.前面我们得到了赫夫曼编码和对应的编码 byte[] , 即:[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28] 现在要求使用赫夫曼编码, 进行解码,又重新得到原来的字符串"i like like like java do you like a java"
即对上述的方法进行封装
具体代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
byte[] hfCoBytes = hfZip(bytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的结果=" + Arrays.toString(hfCoBytes) + "长度是:" + hfCoBytes.length);
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用.
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午6:50:14
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(即压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] hfZip(byte[] bytes){
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据 nodes 创建的赫夫曼树
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
//对应的赫夫曼编码(根据 赫夫曼树)
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
至此,赫夫曼编码的字节压缩方法过程的叙述就结束了,它的解压方法叙述如下:
数据解压-字节转二进制字符串
使用赫夫曼编码来解码数据,具体要求是 1.前面我们得到了赫夫曼编码和对应的编码 byte[] , 即:[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28] 现在要求使用赫夫曼编码, 进行解码,又重新得到原来的字符串"i like like like java do you like a java"
//完成数据的解压
//思路
//1.将hfCoBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..."
//2.赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..." =》 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》 "i like like like java do you like a java"
具体代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
byte[] hfCoBytes = hfZip(bytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的结果=" + Arrays.toString(hfCoBytes) + "长度是:" + hfCoBytes.length);
//测试byToBitString方法
System.out.println(byToBitString(false, (byte)-1));
}
//完成数据的解压
//思路
//1.将hfCoBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..."
//2.赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..." =》 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》 "i like like like
java do you like a java"
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串, 如果看不懂,可以参考我的笔记:Java基础二进制的原码,反码,补码
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午8:31:31
* @param b 传入的 byte
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位如果是true ,表示需要补高位,如果是false表示不补, 如果是最后一个字节,无需补高位
* @return 是该b 对应的二进制的字符串(注意是按补码返回)
*/
private static String byToBitString(boolean flag,byte b){
//使用变量保存
int temp = b; //将b转成int
//如果是正数我们还存在补高位
if(flag){
temp |= 256; //按位与256 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 ==》 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回temp对应的二进制补码
if(flag){
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
}else{
return str;
}
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用.
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午6:50:14
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(即压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] hfZip(byte[] bytes){
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据 nodes 创建的赫夫曼树
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
//对应的赫夫曼编码(根据 赫夫曼树)
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
数据解压-赫夫曼解码
通过上述原理,它的解码具体代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + bytes.length); //40
byte[] hfCoBytes = hfZip(bytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的结果=" + Arrays.toString(hfCoBytes) + "长度是:" + hfCoBytes.length);
//测试byToBitString方法
// System.out.println(byToBitString(false, (byte)-1));
byte[] decode = decode(huffCodes, hfCoBytes);
System.out.println("原来的字符串=" + new String(decode));
}
//编写一个方法,完成对压缩数据的解码
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午8:54:55
* @param hfCodes 赫夫曼编码表 map
* @param hfBytes 赫夫曼编码得到的字节数组
* @return 就是原来的字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte,String> hfCodes, byte[] hfBytes) {
//1.先得到 hfCoBytes对应的 二进制的字符串 , 形式 1010100010111...
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
//将byte数组转成二进制的字符串
for(int i = 0; i < hfBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = hfBytes[i];
//判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == hfBytes.length - 1);
builder.append(byToBitString(!flag, b));
}
// System.out.println("二进制字符串="+builder.toString());
//把字符串安装指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
//把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为反向查询 a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<String,Byte>();
for(Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry: hfCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
//创建要给集合,存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
//i 可以理解成就是索引,扫描 builder
for(int i = 0; i < builder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; //小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while(flag) {
//1010100010111... 递增的取出 key 1
String key = builder.substring(i, i+count); //i 不动,让count移动,指定匹配到一个字符
b = map.get(key);
if(b == null) { //说明没有匹配到
count++;
}else { //匹配到了
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count;//i 直接移动到 count
}
//当for循环结束后,我们list中就存放了所有的字符 "i like like like java do you like a java"
//把list 中的数据放入到byte[] 并返回
byte b[] = new byte[list.size()];
for(int i = 0;i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
// return null;
}
//完成数据的解压
//思路
//1.将hfCoBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..."
//2.赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..." =》 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》 "i like like like
java do you like a java"
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串, 如果看不懂,可以参考我的笔记:Java基础二进制的原码,反码,补码
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午8:31:31
* @param b 传入的 byte
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位如果是true ,表示需要补高位,如果是false表示不补, 如果是最后一个字节,无需补高位
* @return 是该b 对应的二进制的字符串(注意是按补码返回)
*/
private static String byToBitString(boolean flag,byte b){
//使用变量保存
int temp = b; //将b转成int
//如果是正数我们还存在补高位
if(flag){
temp |= 256; //按位与256 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 ==》 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回temp对应的二进制补码
if(flag){
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
}else{
return str;
}
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用.
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午6:50:14
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(即压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] hfZip(byte[] bytes){
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据 nodes 创建的赫夫曼树
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
//对应的赫夫曼编码(根据 赫夫曼树)
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
// System.out.println("测试 stringBuilder=" + stringBuilder.toString());
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
使用赫夫曼编码压缩文件
通过赫夫曼编码对一个字符串进行编码和解码, 下面我们来完成对文件的压缩和解压, 具体要求:给你一个图片文件,要求对其进行无损压缩, 看看压缩效果如何。
- 思路:读取文件-> 得到赫夫曼编码表 -> 完成压缩
代码实现如下:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试压缩文件
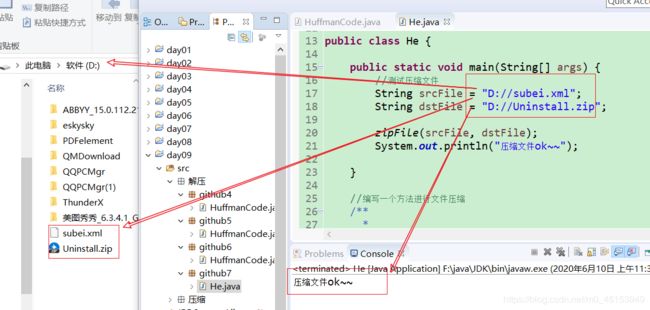
String srcFile = "D://subei.xml";
String dstFile = "D://Uninstall.zip";
zipFile(srcFile, dstFile);
System.out.println("压缩文件ok~~");
}
//编写一个方法进行文件压缩
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午9:44:35
* @param srcFile 传入需要压缩文件的路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后文件的保存路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile,String dstFile){
//创建输入流
FileInputStream is = null;
//创建输出流
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创建文件的输入流
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
//创建一个和源文件大小一样的byte[]
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
//读取文件
is.read(b);
//直接对源文件压缩
byte[] hfBytes = hfZip(b);
//创建文件的输出流
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
//创建一个和文件输出流关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
//把赫夫曼编码后的字节数组写入压缩文件
oos.writeObject(hfBytes);
//这里我们以对象流的方式写入赫夫曼编码,是为了以后我们恢复源文件时使用
//注意一定要把赫夫曼编码 写入压缩文件
oos.writeObject(huffCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally{
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用.
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午6:50:14
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(即压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] hfZip(byte[] bytes){
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据 nodes 创建的赫夫曼树
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
//对应的赫夫曼编码(根据 赫夫曼树)
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
// System.out.println("测试 stringBuilder=" + stringBuilder.toString());
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
使用赫夫曼编码解压文件
- 具体要求:将前面压缩的文件,重新恢复成原来的文件。
- 思路:读取压缩文件(数据和赫夫曼编码表)-> 完成解压(文件恢复)
代码实现如下:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试压缩文件
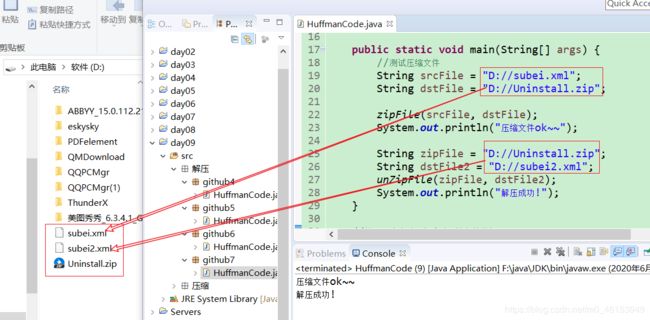
String srcFile = "D://subei.xml";
String dstFile = "D://Uninstall.zip";
zipFile(srcFile, dstFile);
System.out.println("压缩文件ok~~");
String zipFile = "D://Uninstall.zip";
String dstFile2 = "D://subei2.xml";
unZipFile(zipFile, dstFile2);
System.out.println("解压成功!");
}
//编写一个方法,完成对压缩文件的解压
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午11:41:42
* @param zipFile 准备解压的文件
* @param dstFile 将文件解压到哪个路径
*/
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile,String dstFile){
//定义文件输入流
InputStream is = null;
//定义一个对象输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
//定义文件的输出流
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//创建文件输入流
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
//创建一个和 is关联的对象输入流
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//读取byte数组 hfBytes
byte[] hfBytes = (byte[])ois.readObject();
//读取赫夫曼编码表
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<Byte,String> huffCodes = (Map<Byte,String>)ois.readObject();
//解码
byte[] bytes = decode(huffCodes, hfBytes);
//将bytes 数组写入到目标文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
//写数据到 dstFile 文件
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println(e2.getMessage());
}
}
}
//编写一个方法进行文件压缩
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午9:44:35
* @param srcFile 传入需要压缩文件的路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后文件的保存路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile,String dstFile){
//创建输入流
FileInputStream is = null;
//创建输出流
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创建文件的输入流
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
//创建一个和源文件大小一样的byte[]
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
//读取文件
is.read(b);
//直接对源文件压缩
byte[] hfBytes = hfZip(b);
//创建文件的输出流
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
//创建一个和文件输出流关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
//把赫夫曼编码后的字节数组写入压缩文件
oos.writeObject(hfBytes);
//这里我们以对象流的方式写入赫夫曼编码,是为了以后我们恢复源文件时使用
//注意一定要把赫夫曼编码 写入压缩文件
oos.writeObject(huffCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally{
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//编写一个方法,完成对压缩数据的解码
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午8:54:55
* @param hfCodes 赫夫曼编码表 map
* @param hfBytes 赫夫曼编码得到的字节数组
* @return 就是原来的字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte,String> hfCodes, byte[] hfBytes) {
//1.先得到 hfCoBytes对应的 二进制的字符串 , 形式 1010100010111...
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
//将byte数组转成二进制的字符串
for(int i = 0; i < hfBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = hfBytes[i];
//判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == hfBytes.length - 1);
builder.append(byToBitString(!flag, b));
}
// System.out.println("二进制字符串="+builder.toString());
//把字符串安装指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
//把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为反向查询 a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<String,Byte>();
for(Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry: hfCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
//创建要给集合,存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
//i 可以理解成就是索引,扫描 builder
for(int i = 0; i < builder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; //小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while(flag) {
//1010100010111... 递增的取出 key 1
String key = builder.substring(i, i+count); //i 不动,让count移动,指定匹配到一个字符
b = map.get(key);
if(b == null) { //说明没有匹配到
count++;
}else { //匹配到了
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count;//i 直接移动到 count
}
//当for循环结束后,我们list中就存放了所有的字符 "i like like like java do you like a java"
//把list 中的数据放入到byte[] 并返回
byte b[] = new byte[list.size()];
for(int i = 0;i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
// return null;
}
//完成数据的解压
//思路
//1.将hfCoBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..."
//2.赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串 "1010100010111..." =》 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》 "i like like like java do you like a java"
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串, 如果看不懂,可以参考我的笔记:Java基础二进制的原码,反码,补码
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月10日上午8:31:31
* @param b 传入的 byte
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位如果是true ,表示需要补高位,如果是false表示不补, 如果是最后一个字节,无需补高位
* @return 是该b 对应的二进制的字符串(注意是按补码返回)
*/
private static String byToBitString(boolean flag,byte b){
//使用变量保存
int temp = b; //将b转成int
//如果是正数我们还存在补高位
if(flag){
temp |= 256; //按位与256 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 ==》 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回temp对应的二进制补码
if(flag){
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
}else{
return str;
}
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用.
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午6:50:14
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(即压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] hfZip(byte[] bytes){
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据 nodes 创建的赫夫曼树
Node hfTree = createHFTree(nodes);
//对应的赫夫曼编码(根据 赫夫曼树)
Map<Byte, String> hfCodes = getCodes(hfTree);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = zip(bytes, hfCodes);
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byte[]
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:55:21
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param hfCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的 byte[]
*
* 举例: String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
* =》 byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
*
* 返回的是字符串 "1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100101001101110001110000011011101000111100101000101111111100110001001010011011100"
* => 对应的 byte[] hfCodeBytes ,即 8位数字对应一个 byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
*
* hfCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补码)
* => byte [推导 10101000=> 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码)=> 11011000= -88 ]
* hfCodeBytes[1] = -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes,Map<Byte,String> hfCodes){
//1.利用 hfCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for(byte b : bytes){
stringBuilder.append(hfCodes.get(b));
}
// System.out.println("测试 stringBuilder=" + stringBuilder.toString());
//将 "1010100010111111110..." 转成 byte[]
//统计返回 byte[] hfCodeBytes 长度
//即 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;
int len;
if(stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0){
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
}else{
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的 byte数组
byte[] hfCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0;//记录是第几个byte
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) { //因为是每8位数字对应一个byte,所以步长 +8
String strByte;
if(i+8 > stringBuilder.length()) {//不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
}else{
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte 转成一个byte,放入到 hfCodeBytes
hfCodeBytes[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return hfCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在 Map 形式:
// 生成的赫夫曼编码表{32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffCodes = new HashMap<Byte,String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder 存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
*
* @Description 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffCodes集合
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午5:28:28
* @param nodes 传入结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是 0,右子结点 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node nodes,String code,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if(nodes != null){ //如果nodes == null不处理
//判断当前nodes是叶子结点,还是非叶子结点
if(nodes.date == null) { //非叶子结点
//递归处理,即先向左递归处理
getCodes(nodes.left,"0",stringBuilder2);
//再向右递归
getCodes(nodes.right,"1",stringBuilder2);
}else{ //否则,说明是一个叶子结点,就表示找到某个叶子结点的最后
huffCodes.put(nodes.date, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//为了调用方便,进行重载 getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffCodes;
}
/**
*
* @Description
* @author subei
* @date 2020年6月9日下午4:56:13
* @param bytes 接受字符数组
* @return 返回的就是List形式 [Node[date=97 ,weight = 5], Node[date=32,weight = 9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes){
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数,使用map[key,value]
Map<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for(byte b: bytes){
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if(count == null){ //Map中没有这个字符,初次检索
counts.put(b, 1);
}else{
counts.put(b, count+1);
}
}
//将每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for(Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()){
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List 创建对应的赫夫曼树
private static Node createHFTree(List<Node> nodes){
while(nodes.size() > 1){
//排序:从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理的两颗二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树,加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes 最后的结点,就是赫夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,存放数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
Byte date; //存放数据(字符)本身,比如‘a’ =》 97 ; ' ' =》 32
int weight; //权值,表示字符
Node left; //指向左子树
Node right; //指向右子树
public Node(Byte date, int weight) {
super();
this.date = date;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //按从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [date=" + date + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//前序遍历方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}
赫夫曼编码的注意事项
- 如果文件本身就是经过压缩处理的,那么使用赫夫曼编码再压缩效率不会有明显变化, 比如视频、pptx等等文件 [举例压一个.pptx]。
- 赫夫曼编码是按字节来处理的,因此可以处理所有的文件(二进制文件、文本文件) [举例压一个.xml文件]。
- 如果一个文件中的内容,重复的数据不多,压缩效果也不会很明显。