【实验环境】
系统:Centos6.4
IP: 192.168.56.120
设置服务器的文件描述符
如果后面配置nginx的时候,需要调大worker_connections 这个参数,则需要对系统的文件描述符进行设置,否则可能会出现下面的报错:
worker_connections exceed open file resource limit: 1024
(1) 修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件,在文件中添加如下行:
* soft noproc 65535
* hard noproc 65535
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
就是限制了任意用户的最大线程数和文件数为65535。
其中*为所有用户的打开文件数限制,可用"*"号表示修改所有用户的限制;soft或hard指定要修改软限制还是硬限制;65535则指定了想要修改的新的限制值,即最大打开文件数(请注意软限制值要小于或等于硬限制)。修改完后保存文件。
(2) 修改/etc/pam.d/login文件,在文件中添加如下行:
session required /lib/security/pam_limits.so
这是告诉Linux在用户完成系统登录后,应该调用pam_limits.so模块来设置系统对该用户可使用的各种资源数量的最大限制(包括用户可打开的最大文件数限制),而pam_limits.so模块就会从/etc/security/limits.conf文件中读取配置来设置这些限制值。修改完后保存此文件。
(3) 修改/etc/rc.local脚本,在脚本中添加如下行:
echo “65535"> /proc/sys/fs/file-max
完成上面3步之后重启服务器,重启完,通过ulimit -n 命令确认系统最大文件描述符是否为刚刚设置的值:
[root@localhost ~]# ulimit -n
65535
【实验配置】
一、安装Nginx
[root@localhost ~]# yum install pcre-devel openssl-devel perl-ExtUtils-Embed gcc gcc-c++ make wget
[root@localhost src]# wget http://labs.frickle.com/files/ngx_cache_purge-1.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-0.8.32.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# tar xf ngx_cache_purge-1.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# tar xf nginx-0.8.32.tar.gz
[root@localhost src]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M www
[root@localhost nginx-0.8.32]# ./configure --user=www --group=www --add-module=../ngx_cache_purge-1.0 --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module
[root@localhost nginx-0.8.32]# make && make install
注意:这里nginx可能要使用较低的版本,我用新版本1.5.x 编译安装的时候会报错:
make[1]: *** [objs/addon/ngx_cache_purge-1.0/ngx_cache_purge_module.o] Error 1
make[1]: Leaving directory `/usr/src/nginx-1.5.3'
make: *** [build] Error 2
二、配置Nginx
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /data/proxy_temp_dir
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /data/web/www
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /data/proxy_cache_dir
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user www www;
worker_processes 8;
error_log logs/error.log crit;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 300m;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
client_body_buffer_size 512k;
proxy_connect_timeout 5;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_send_timeout 5;
proxy_buffer_size 16k;
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 128k;
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
gzip_vary on;
#注:proxy_temp_path和proxy_cache_path指定的路径必须在同一分区
proxy_temp_path /data/proxy_temp_dir;
proxy_cache_path /data/proxy_cache_dir levels=1:2 keys_zone=cache_one:200m inactive=1d max_size=30g;
#设置Web缓存区名称为cache_one,内存缓存空间大小为200MB,1天清理一次缓存,硬盘缓存空间大小为30G
upstream web_proxy_cache {
server 192.168.56.113:80 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server 192.168.56.114:80 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
}
server {
listen 80;
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.56.120;
root /data/web/www;
index index.html index.htm;
location / {
proxy_next_upstream http_502 http_504 error timeout invalid_header;
# 如果后端的服务器返回502、504、执行超时等错误,自动将请求转发到upstream负载均衡池中的另一台服务器,实现故障转移
proxy_cache cache_one;
proxy_cache_valid 200 304 12h; #对不同的HTTP状态码设置不同的缓存时间
# 以域名、URI、参数组合成Web缓存的Key值,Nginx根据Key值哈希,存储缓存内容到二级缓存目录内
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://web_proxy_cache;
expires 1d;
}
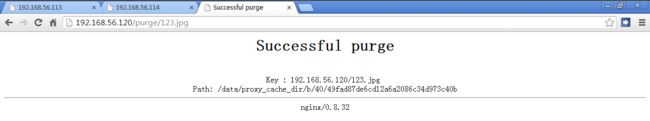
# 用于清除缓存,假设一个URL为http://192.168.56.120/test.txt,通过访问http://192.168.56.120/purge/test.txt就可以清除该URL的缓存。
location ~ /purge(/.*) { # 设置只允许指定的IP或IP段才可以清除URL缓存
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 192.168.56.0/24;
deny all;
proxy_cache_purge cache_one $host$1$is_args$args;
}
location ~ .*\.(php|jsp|cgii)?$ { # 扩展名以.php、.jsp、.cgi结尾的动态应用程序不缓存
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://web_proxy_cache;
}
access_log off;
}
}
检查配置是否有误
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
启动nginx
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
三、测试
在web1和web2 两个web服务器上创建不同页面
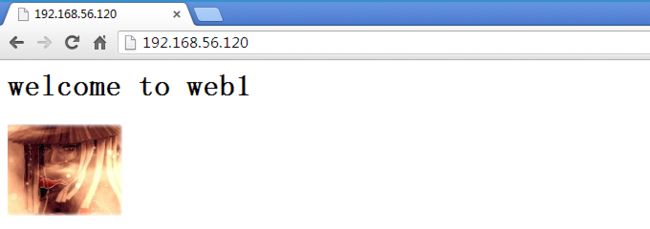
[root@web1 ~]# vim /data/web/www/index.html
welcome to web1

在/data/web/www/ 目录下上传一个图片,命名为123.jpg
[root@web1 ~]# service httpd start
[root@web2 ~]# service httpd start
测试能否正常代理以及作为web缓存
[root@localhost ~]# curl -dump http://192.168.56.120
welcome to web1
[root@localhost ~]# curl -dump http://192.168.56.120
welcome to web2
四、通过日志查看HIT 情况
1、开启日志
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" ' '"$upstream_cache_status"'; access_log logs/access.log main;
2、添加
$upstream_cache_status
这个变量用来显示缓存的状态,我们可以在配置中添加一个http头来显示这一状态
location / {
proxy_next_upstream http_502 http_504 error timeout invalid_header;
proxy_cache cache_one;
proxy_cache_valid 200 304 12h;
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://web_proxy_cache;
expires 1d;
}
3、通过日志查看是否hits中缓存
可以看到,第一次访问的时候是没有通过缓存的,状态为-MISS
192.168.56.1 - - [09/Aug/2013:12:18:02 +0800] "GET /123.jpg HTTP/1.1" 200 4496 "http://192.168.56.120/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/27.0.1453.93 Safari/537.36" "-""
MISS"
第二次访问的时候则是通过缓存,状态为HITS
192.168.56.1 - - [09/Aug/2013:12:18:02 +0800] "GET /123.jpg HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "http://192.168.56.120/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/27.0.1453.93 Safari/537.36" "-""
HIT"
4、计算HIT命中概率
[root@localhost logs]#
awk '{if($NF=="\"HIT\"") hit++} END{printf "%.2f%\n",hit/NR*100}' access.log
51.85%