前言
在开发编程中,我们经常会遇到功能非常相似的功能模块,只是他们的处理的数据不一样,所以我们会分别采用多个方法来处理不同的数据类型。但是这个时候,我们就会想一个问题,有没有办法实现利用同一个方法来传递不同种类型的参数呢?
这个时候,泛型也就因运而生,专门来解决这个问题的。
泛型是在C#2.0就推出的一个新语法,由框架升级提供的功能。
说明
泛型通过参数化类型实现在同一份代码上操作多种数据类型。例如使用泛型的类型参数T,定义一个类Stack ,
可以用Stack 、Stack 或者Stack 实例化它,从而使类Stack可以处理int、string、Person类型数据。这样可以避免运行时类型转换或封箱操作的代价和风险。泛型提醒的是将具体的东西模糊化。
同时使用泛型类型可以最大限度地重用代码、保护类型安全以及提高性能。
可以创建:泛型接口、泛型类、泛型方法、泛型事件和泛型委托
开始
泛型类
泛型类封装不特定于特定数据类型的操作。 泛型类最常见用法是用于链接列表、哈希表、堆栈、队列和树等集合。 无论存储数据的类型如何,添加项和从集合删除项等操作的执行方式基本相同。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// T是int类型
GenericClass genericInt = new GenericClass();
genericInt._T = 123;
// T是string类型
GenericClass genericString = new GenericClass();
genericString._T = "123";
}
新建一个GenericClass类
///
/// 泛型类
///
///
{
public T _T;
}
泛型方法
泛型方法是通过类型参数声明的方法, 解决用一个方法,满足不同参数类型
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 泛型方法
Console.WriteLine("************Generic**************");
int iValue = 123;
string sValue = "456";
DateTime dtValue = DateTime.Now;
object oValue = "MrValue";
GenericMethod.Show(iValue);//需要指定类型参数
//GenericMethod.Show(iValue);//必须吻合
GenericMethod.Show(iValue);//能省略,自动推算
GenericMethod.Show(sValue);
GenericMethod.Show(dtValue);
GenericMethod.Show 新建一个GenericMethod
///
/// 泛型方法
///
public class GenericMethod
{
///
/// 2.0推出的新语法
/// 泛型方法解决用一个方法,满足不同参数类型;做相同的事儿
/// 没有写死参数类型,调用的时候才指定的类型
/// 延迟声明:把参数类型的声明推迟到调用
/// 推迟一切可以推迟的~~ 延迟思想
/// 不是语法糖,而是2.0由框架升级提供的功能
/// 需要编译器支持+JIT支持
///
/// T/S 不要用关键字 也不要跟别的类型冲突
///
public static void Show(T tParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(GenericMethod), tParameter.GetType().Name, tParameter.ToString());
}
}
泛型接口
为泛型集合类或表示集合中的项的泛型类定义接口通常很有用处。在c#中,通过尖括号“<>”将类型参数括起来,表示泛型。声明泛型接口时,与声明一般接口的唯一区别是增加了一个 。一般来说,声明泛型接口与声明非泛型接口遵循相同的规则。
泛型接口定义完成之后,就要定义此接口的子类。定义泛型接口的子类有以下两种方法。
(1)直接在子类后声明泛型。
(2)在子类实现的接口中明确的给出泛型类型。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 泛型接口
CommonInterface commonInterface = new CommonInterface();
commonInterface.GetT("123");
#endregion
}
新建GenericInterface.cs类文件
///
/// 泛型类
///
///
{
public T _T;
}
///
/// 泛型接口
///
public interface IGenericInterface
{
//泛型类型的返回值
T GetT(T t);
}
///
/// 使用泛型的时候必须指定具体类型,
/// 这里的具体类型是int
///
public class CommonClass : GenericClass
{
}
///
/// 必须指定具体类型
///
public class CommonInterface : IGenericInterface
{
public string GetT(string t)
{
return t;
}
}
///
/// 子类也是泛型的,继承的时候可以不指定具体类型
///
/// : GenericClass
{
}
泛型委托
泛型委托主要是想讲一下Action 和Func 两个委托,因为这两个在Linq中是经常见到的。
Action 只能委托必须是无返回值的方法
Fun 只是委托必须有返回值的方法
不管是不是泛型委托,只要是委托委托那能用Lamdba表达式,因为不管Lamdba表达式还是匿名函数其实都是将函数变量化。
下面简单的来做的demo说下两个的用法,这个会了基本linq会了一半了。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 泛型委托
Action action = s => {
Console.WriteLine(s);
};
action("i3yuan");
Func func = (int a, int b) => {
return a + b;
};
Console.WriteLine("sum:{0}", func(1,1));
Console.ReadLine();
#endregion
}
上面其实都是将函数做为变量,这也是委托的思想。action是实例化了一个只有一个字符串参数没有返回值得函数变量。func是实例化了一个有两个int类型的参数返回值为int的函数变量。
可以看到通过Lamdba表达式和泛型的结合,算是又方便了开发者们,更加方便实用。
引入委托常用的另一方式
无论是在类定义内还是类定义外,委托可以定义自己的类型参数。引用泛型委托的代码可以指定类型参数来创建一个封闭构造类型,这和实例化泛型类或调用泛型方法一样,如下例所示:
public delegate void MyDelegate(T item);
public void Notify(int i){}
//...
MyDelegate m = new MyDelegate(Notify);
C#2.0版有个新特性称为方法组转换(method group conversion),具体代理和泛型代理类型都可以使用。用方法组转换可以把上面一行写做简化语法:
MyDelegate m = Notify;
在泛型类中定义的委托,可以与类的方法一样地使用泛型类的类型参数。
class Stack
{
T[] items;
int index
//...
public delegate void StackDelegate(T[] items);
}
引用委托的代码必须要指定所在类的类型参数,如下:
Stack s = new Stack();
Stack.StackDelegate myDelegate = StackNotify;
泛型委托在定义基于典型设计模式的事件时特别有用。因为sender[JX2] ,而再也不用与Object相互转换。
public void StackEventHandler(T sender, U eventArgs);
class Stack
{
//…
public class StackEventArgs : EventArgs{...}
public event StackEventHandler, StackEventArgs> stackEvent;
protected virtual void OnStackChanged(StackEventArgs a)
{
stackEvent(this, a);
}
}
class MyClass
{
public static void HandleStackChange(Stack stack, StackEventArgs args){...};
}
Stack s = new Stack();
MyClass mc = new MyClass();
s.StackEventHandler += mc.HandleStackChange;
泛型约束
所谓的泛型约束,实际上就是约束的类型T。使T必须遵循一定的规则。比如T必须继承自某个类,或者T必须实现某个接口等等。那么怎么给泛型指定约束?其实也很简单,只需要where关键字,加上约束的条件。
定义一个People类,里面有属性和方法:
public interface ISports
{
void Pingpang();
}
public interface IWork
{
void Work();
}
public class People
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Hi()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi");
}
}
public class Chinese : People, ISports, IWork
{
public void Tradition()
{
Console.WriteLine("仁义礼智信,温良恭俭让");
}
public void SayHi()
{
Console.WriteLine("吃了么?");
}
public void Pingpang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打乒乓球...");
}
public void Work()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
public class Hubei : Chinese
{
public Hubei(int version)
{ }
public string Changjiang { get; set; }
public void Majiang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打麻将啦。。");
}
}
public class Japanese : ISports
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public void Hi()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hi");
}
public void Pingpang()
{
Console.WriteLine("打乒乓球...");
}
}
打印方法
///
/// 打印个object值
/// 1 object类型是一切类型的父类
/// 2 通过继承,子类拥有父类的一切属性和行为;任何父类出现的地方,都可以用子类来代替
/// object引用类型 加入传个值类型int 会有装箱拆箱 性能损失
/// 类型不安全
///
///
public static void ShowObject(object oParameter)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is {0},parameter={1},type={2}",
typeof(Constraint), oParameter.GetType().Name, oParameter);
Console.WriteLine($"{((People)oParameter).Id}_{((People)oParameter).Name}");
}
在main方法中
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region Constraint 接口约束
Console.WriteLine("************Constraint*****************");
{
People people = new People()
{
Id = 123,
Name = "走自己的路"
};
Chinese chinese = new Chinese()
{
Id = 234,
Name = "晴天"
};
Hubei hubei = new Hubei(123)
{
Id = 345,
Name = "流年"
};
Japanese japanese = new Japanese()
{
Id = 7654,
Name = "i3yuan"//
};
CommonMethod.ShowObject(people);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(chinese);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(hubei);
CommonMethod.ShowObject(japanese);
Console.ReadLine();
}
#endregion
}
泛型约束总共有五种。
| 约束 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| T:结构 | 类型参数必须是值类型 |
| T:类 | 类型参数必须是引用类型;这一点也适用于任何类、接口、委托或数组类型。 |
| T:new() | 类型参数必须具有无参数的公共构造函数。 当与其他约束一起使用时,new() 约束必须最后指定。 |
| T:<基类名> | 类型参数必须是指定的基类或派生自指定的基类。 |
| T:<接口名称> | 类型参数必须是指定的接口或实现指定的接口。 可以指定多个接口约束。 约束接口也可以是泛型的。 |
1、基类约束
上面打印的方法约束T类型必须是People类型。
///
/// 基类约束:约束T必须是People类型或者是People的子类
/// 1 可以使用基类的一切属性方法---权利
/// 2 强制保证T一定是People或者People的子类---义务
///
///
///
/// (T tParameter) where T : People
{
Console.WriteLine($"{tParameter.Id}_{tParameter.Name}");
tParameter.Hi();
}
注意:
基类约束时,基类不能是密封类,即不能是sealed类。sealed类表示该类不能被继承,在这里用作约束就无任何意义,因为sealed类没有子类。
2、接口约束
///
/// 接口约束
///
/// (T t) where T : ISports
{
t.Pingpang();
return t;
}
3、引用类型约束 class
引用类型约束保证T一定是引用类型的。
/// 引用类型约束
///
/// (T t) where T : class
{
return t;
}
4、值类型约束 struct
值类型约束保证T一定是值类型的。
/// 值类型类型约束
///
/// (T t) where T : struct
{
return t;
}
5、无参数构造函数约束 new()
/// new()约束
///
/// (T t) where T : new()
{
return t;
}
泛型约束也可以同时约束多个,例如:
///
/// 泛型:不同的参数类型都能进来;任何类型都能过来,你知道我是谁?
/// 没有约束,也就没有自由
/// 泛型约束--基类约束(不能是sealed):
/// 1 可以使用基类的一切属性方法---权利
/// 2 强制保证T一定是People或者People的子类---义务
///
/// (T tParameter)
where T : People, ISports, IWork, new()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{tParameter.Id}_{tParameter.Name}");
tParameter.Hi();
tParameter.Pingpang();
tParameter.Work();
}
注意:有多个泛型约束时,new()约束一定是在最后。
泛型的协变和逆变
public class Animal
{
public int Id { get; set; }
}
public class Cat : Animal
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 协变和逆变
// 直接声明Animal类
Animal animal = new Animal();
// 直接声明Cat类
Cat cat = new Cat();
// 声明子类对象指向父类
Animal animal2 = new Cat();
// 声明Animal类的集合
List listAnimal = new List();
// 声明Cat类的集合
List listCat = new List();
#endregion
}
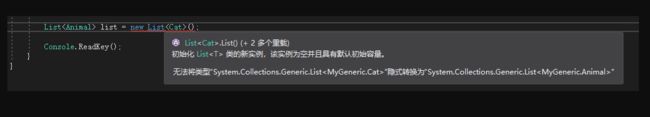
那么问题来了:下面的一句代码是不是正确的呢?
1 List list = new List();
可能有人会认为是正确的:因为一只Cat属于Animal,那么一群Cat也应该属于Animal啊。但是实际上这样声明是错误的:因为List 和List 之间没有父子关系。
这时就可以用到协变和逆变了。
1 // 协变
2 IEnumerable List1 = new List();
3 IEnumerable List2 = new List();
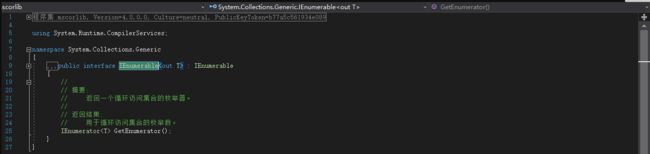
F12查看定义:
可以看到,在泛型接口的T前面有一个out关键字修饰,而且T只能是返回值类型,不能作为参数类型,这就是协变。使用了协变以后,左边声明的是基类,右边可以声明基类或者基类的子类。
协变除了可以用在接口上面,也可以用在委托上面:
Func func = new Func(() => null);
除了使用.NET框架定义好的以为,我们还可以自定义协变,例如:
///
/// out 协变 只能是返回结果
///
///
{
T Get();
}
public class CustomerListOut : ICustomerListOut
{
public T Get()
{
return default(T);
}
}
使用自定义的协变:
// 使用自定义协变
ICustomerListOut customerList1 = new CustomerListOut();
ICustomerListOut customerList2 = new CustomerListOut();
在来看看逆变。
在泛型接口的T前面有一个In关键字修饰,而且T只能方法参数,不能作为返回值类型,这就是逆变。请看下面的自定义逆变:
///
/// 逆变 只能是方法参数
///
///
{
void Show(T t);
}
public class CustomerListIn : ICustomerListIn
{
public void Show(T t)
{
}
}
使用自定义逆变:
// 使用自定义逆变
ICustomerListIn customerListCat1 = new CustomerListIn();
ICustomerListIn customerListCat2 = new CustomerListIn();
协变和逆变也可以同时使用,看看下面的例子:
///
/// inT 逆变
/// outT 协变
///
///
{
void Show(inT t);
outT Get();
outT Do(inT t);
}
public class MyList : IMyList
{
public void Show(T1 t)
{
Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
}
public T2 Get()
{
Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
return default(T2);
}
public T2 Do(T1 t)
{
Console.WriteLine(t.GetType().Name);
Console.WriteLine(typeof(T2).Name);
return default(T2);
}
}
使用:
IMyList myList1 = new MyList();
IMyList myList2 = new MyList();//协变
IMyList myList3 = new MyList();//逆变
IMyList myList4 = new MyList();//逆变+协变
有关可变性的注意事项
- 变化只适用于引用类型,因为不能直接从值类型派生其他类型
- 显示变化使用in和out关键字只适用于委托和接口,不适用于类、结构和方法
- 不包括in和out关键字的委托和接口类型参数叫做不变
泛型缓存
在前面我们学习过,类中的静态类型无论实例化多少次,在内存中只会有一个。静态构造函数只会执行一次。在泛型类中,T类型不同,每个不同的T类型,都会产生一个不同的副本,所以会产生不同的静态属性、不同的静态构造函数,请看下面的例子:
public class GenericCache
{
static GenericCache()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is GenericCache 静态构造函数");
_TypeTime = string.Format("{0}_{1}", typeof(T).FullName, DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyyMMddHHmmss.fff"));
}
private static string _TypeTime = "";
public static string GetCache()
{
return _TypeTime;
}
}
public class GenericCacheTest
{
public static void Show()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
Console.WriteLine(GenericCache.GetCache());
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
}
Main()方法里面调用:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 泛型缓存
GenericCacheTest.Show();
#endregion
}
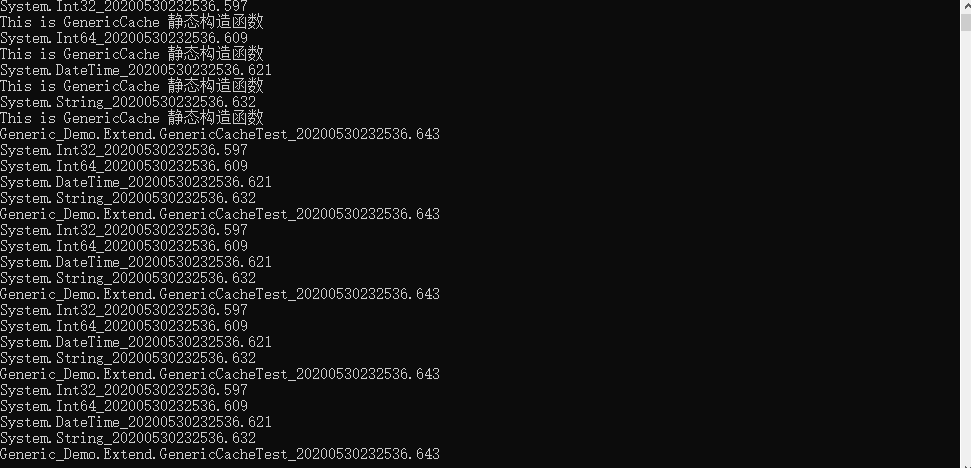
结果:
从上面的截图中可以看出,泛型会为不同的类型都创建一个副本,所以静态构造函数会执行5次。 而且每次静态属性的值都是一样的。利用泛型的这一特性,可以实现缓存。
注意:只能为不同的类型缓存一次。泛型缓存比字典缓存效率高。泛型缓存不能主动释放。
注意
1.泛型代码中的 default 关键字
在泛型类和泛型方法中会出现的一个问题是,如何把缺省值赋给参数化类型,此时无法预先知道以下两点:
-
T将是值类型还是引用类型
-
如果T是值类型,那么T将是数值还是结构
对于一个参数化类型T的变量t,仅当T是引用类型时,t = null语句才是合法的; t = 0只对数值的有效,而对结构则不行。这个问题的解决办法是用default关键字,它对引用类型返回空,对值类型的数值型返回零。而对于结构,它将返回结构每个成员,并根据成员是值类型还是引用类型,返回零或空。下面GenericList 类的例子显示了如何使用default关键字。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 泛型代码默认关键字default
// 使用非空的整数列表进行测试.
GenericList gll = new GenericList();
gll.AddNode(5);
gll.AddNode(4);
gll.AddNode(3);
int intVal = gll.GetLast();
// 下面一行显示5.
Console.WriteLine(intVal);
// 用一个空的整数列表进行测试.
GenericList gll2 = new GenericList();
intVal = gll2.GetLast();
// 下面一行显示0.
Console.WriteLine(intVal);
// 使用非空字符串列表进行测试.
GenericList gll3 = new GenericList();
gll3.AddNode("five");
gll3.AddNode("four");
string sVal = gll3.GetLast();
// 下面一行显示five.
Console.WriteLine(sVal);
// 使用一个空字符串列表进行测试.
GenericList gll4 = new GenericList();
sVal = gll4.GetLast();
// 下面一行显示一条空白行.
Console.WriteLine(sVal);
#endregion
Console.ReadKey();
}
public class GenericList
{
private class Node
{
// 每个节点都有一个指向列表中的下一个节点的引用.
public Node Next;
// 每个节点都有一个T类型的值.
public T Data;
}
// 这个列表最初是空的.
private Node head = null;
// 在列表开始的时候添加一个节点,用t作为它的数据值.
public void AddNode(T t)
{
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.Next = head;
newNode.Data = t;
head = newNode;
}
// 下面的方法返回存储在最后一个节点中的数据值列表. 如果列表是空的, 返回类型T的默认值.
public T GetLast()
{
// 临时变量的值作为方法的值返回.
// 下面的声明初始化了临时的温度
// 类型T的默认值. 如果该列表为空返回默认值.
T temp = default(T);
Node current = head;
while (current != null)
{
temp = current.Data;
current = current.Next;
}
return temp;
}
}
2.泛型集合
通常情况下,建议您使用泛型集合,因为这样可以获得类型安全的直接优点而不需要从基集合类型派生并实现类型特定的成员。下面的泛型类型对应于现有的集合类型:
1、List 是对应于 ArrayList 的泛型类。
2、Dictionary 是对应于 Hashtable 的泛型类。
3、Collection 是对应于 CollectionBase 的泛型类。
4、ReadOnlyCollection 是对应于 ReadOnlyCollectionBase 的泛型类。
5、Queue、Stack 和 SortedList 泛型类分别对应于与其同名的非泛型类。
6、LinkedList 是一个通用链接列表,它提供运算复杂度为 O(1) 的插入和移除操作。
7、SortedDictionary 是一个排序的字典,其插入和检索操作的运算复杂度为 O(log n),这使得它成为 SortedList 的十分有用的替代类型。
8、KeyedCollection 是介于列表和字典之间的混合类型,它提供了一种存储包含自己键的对象的方法。
总结
- 作为一个开发人员,当我们程序代码有相同的逻辑,有可能是方法、接口、类或者委托,只是某些参数类型不同,我们希望代码可以通用、复用,甚至是说为了偷懒,也可以说是在不确定类型的情况下,就应该考虑用泛型的思维去实现。
- 在非泛型编程中,虽然所有的东西都可以作为Object传递,但是在传递的过程中免不了要进行类型转换。而类型转换在运行时是不安全的。使用泛型编程将可以减少不必要的类型转换,从而提高安全性。不仅是值类型,引用类型也存在这样的问题,因此有必要的尽量的去使用泛型集合。
- 在非泛型编程中,将简单类型作为Object传递时会引起装箱和拆箱的操作,这两个过程都是具有很大开销的。使用泛型编程就不必进行装箱和拆箱操作了。
参考 文档 《C#图解教程》
注:搜索关注公众号【DotNet技术谷】--回复【C#图解】,可获取 C#图解教程文件