回顾
剧本中可以使用判断的方式,减少hosts(play)的个数
template jinjia2
剧本中不能使用if判断,使用when判断,模糊匹配不能和and or一起使用
shutdown -a 取消关机
shutdown -s 关机
shutdown -f 强行关闭应用程序
shutdown -m \\计算机名 控制远程计算机
shutdown -i 显示“远程关机”图形用户界面,但必须是Shutdown的第一个参数
shutdown -l 注销当前用户
shutdown -r 关机并重启
shutdown -s -t 时间 设置关机倒计时
shutdown -h 休眠
centos6启动httpd /etc/init.d/httpd start
变量的使用并不能减少代码量,使用循环就可以减少代码量了
还原快照要重新推送m01上的公钥,才能使用ansible
bool值纯数字要加引号,字符串不用加
yum localinstall 在剧本中不会报错
文件类型:str 纯数字类型
int 字符串类型(整数),flouge(小数,浮点型)
bool true/false
path 路径类型(/root/1)
python中文件类型的区分是很严格的,有时候需要转化文件类型
剧本中变量加双引号,在路径中调用不同加引号(变量不能使用特殊符号.)
循环一般在启动服务或者copy的时候使用(同一主机,同一模块,同一动作)
yum支持列表,最好循环
命令行不支持字典的形式调用变量,playbook支持
ansible中的python-paramiko模块是ansible专门用来做ssh连接的
facts收集的信息是json格式的,其内任一项都可以当作变量被直接引用(如在playbook、jinja2模板中)引用
ls -1 结果以一列显示
with_items(循环),适合不支持列表的模块,也适合把重复调用的模块一体化
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
deprecation_warnings = False #关闭warnings警告
systemctl reload php-fpm.service #PHP支持reload
yml中上一个模块是否成功执行,直接影响下面的模块是否执行(有时候需要ignore_errors)
gather_facts: no #关闭信息采集
default :默认值
数据库中,用户名@主机域,这样才是一个完整的用户
root@'%'
root@'localhost'
root@'127.0.0.1'
roles是专门用来解耦的
可以自己去打包某一状态的WordPress,这样再次部署将还是这个状态
handlers不用加when判断,tags标签
根据不同的操作系统安装apache
官方示例:
官方
facts详解
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: "shut down Debian flavored systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -t now
when: ansible_facts['os_family'] == "Debian" #不等于表示:!= 0
# 注意,'所有变量'都可以直接在条件语句中使用,而无需使用双大括号
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Install CentOS Httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
#官方
when: ansible_['os_family'] == "CentOS" #判断系统
when: ansible.os_family == "CentOS"
#非官方()
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- name: Install Ubuntu Httpd
yum:
name: apache2
state: present
when: ansible_facts['os_family'] == "Ubuntu"
when后面既可以是变量,又可以是指定值,一般后面跟变量
[root@www ~]# ansible web01 -m setup |grep os_family
"ansible_os_family": "RedHat",
when的缩进和name注释一样
#facts 指的是 ansible_facts 变量,ansible 中使用 setup 模块来获取,包含系统的大部分基础硬件信息
#命令行中的setup只能过滤出中括号{}外的内容,里面的内容不能调用,但是在playbook中,可以进行更精确的调用
还可以使用括号,and , or对条件进行分组
tasks:
- name: "shut down CentOS 6 and Debian 7 systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -t now
when: (ansible_facts['distribution'] == "CentOS" and ansible_facts['distribution_major_version'] == "6") or
(ansible_facts['distribution'] == "Debian" and ansible_facts['distribution_major_version'] == "7")
#使用ansible_facts['distribution'] 判断系统 注意大小写
也可以指定多条件为列表(and 并且)
tasks:
- name: "shut down CentOS 6 systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -t now
when:
- ansible_facts['distribution'] == "CentOS"
- ansible_facts['distribution_major_version'] == "6"
#列表形式等效于and
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: dc
file:
path: /abc
state: touch
when: ansible_fqdn is match 'web*' or ansible_fqdn is match 'db*'
#错,系统只会web*创建
条件运算
tasks:
- shell: echo "only on Red Hat 6, derivatives, and later"
when: ansible_facts['os_family'] == "RedHat" and ansible_facts['lsb']['major_release']|int >= 6 #文件类型的转化(str转int)
rsync服务端推送配置文件
[root@m01 ~]# cat rsyncd/rsyncd.yml
- hosts: all ######
tasks:
- name: check rsync
shell: "ls /etc/rsyncd.conf"
register: check_rsync
- name: Install Rsyncd Server
yum:
name: rsync
state: present #可在这里使用ls -l 判断rsync是否安装
when: check_rsync.rc != 0
- name: Create www Group
group:
name: www
gid: 666
- name: Create www User
user:
name: www
group: www
uid: 666
create_home: false
shell: /sbin/nologin
- name: Scp Rsync Config
copy:
src: ./rsyncd.j2
dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
when: ansible_hostname == "backup" #判断主机名
#when: ansible_hostname is match "backup*" #模糊匹配
- name: Create Passwd File
copy:
content: 'rsync_backup:123'
dest: /etc/rsync.passwd
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0600
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Create backup Directory
file:
path: /backup
state: directory
mode: 0755
owner: www
group: www
recurse: yes
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
- name: Start Rsyncd Server
systemd:
name: rsyncd
state: started
when: ansible_hostname == "backup"
rsync客户端推送脚本
[root@m01 ~]# vim rsync.yml
- hosts: rsync_server
tasks:
- name: SCP Backup Shell
copy:
src: ./backup.sh
dest: /root/backup.sh
when: ansible_hostname is match "web*" #when支持通配符(模糊匹配)
#when: ansible_hostname == "backup" or ansible_hostname == "nfs"
#这两种方式类似模糊匹配,都可以匹配多台服务器
#模糊匹配和and or不能一起使用?
when: (ansible_hostname is match "web*") or (ansible_hostname is match "nfs*")
通过register将命令执行结果保存至变量,然后通过when语句进行判断
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Check Httpd Server
command: "systemctl is-active httpd" #查看服务状态
ignore_errors: yes #忽略报错,继续执行
register: check_httpd #将命令的执行结果注册变量
- name: debug outprint
debug: var=check_httpd #偶尔调试
msg: "{{ check_httpd.rc }}"
- name: Httpd Restart
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
when: check_httpd.rc == 0
#通过变量注册的方式可以进行非系统变量的调用,注意变量名(不能使用特殊符号-.)
#htpd
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl is-active httpd
active
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl stop httpd
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl is-active httpd
unknown
#nginx
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl is-active nginx
active
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl is-active nginx
failed
Python中变量的定义,类型,打印,判断
[root@m01 ~]# python
>>> age='99' #定义变量
>>> print type(age) #查看变量类型
>>> print int(age) #转换变量类型同时打印变量
99
>>> syy_age=int(age) #转化变量类型,重新定义变量
>>> print type(syy_age) #查看变量类型
>>> if age == 99: #Python中判断的格式
... print '9'
... else:
... print '0'
...
0
>>> if age == '99': #判断无效
... print '9'
...
9
>>> print '9'
9
>>> quit()
[root@m01 ~]#
playbook循环语句
详解
启动多个服务
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: start service
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}" #直接调用加",在路径里面不加"
state: started
with_items:
- httpd #可以直接调用,也可以写成 { "" }
- php-fpm
- mariadb
定义变量循环
- name: ensure a list of packages installed
yum:
name: "{{ packages }}"
vars: #模块内定义变量
packages:
- httpd
- httpd-tools
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: ensure a list of packages installed
yum: name= "{{ item }}" state=present #可以使用多个'='
with_items:
- httpd
- httpd-tools
#with_items一般放到模块的末尾,与模块同一缩进级别
字典循环
1.创建用户
[root@m01 ~]# cat loop.yml
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Add Users
user:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
groups: "{{ item.groups }}"
state: present
with_items:
- { name: 'zls', groups: 'linux' }
- { name: 'egon', groups: 'python' }
2.拷贝文件
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: copy conf and code
copy:
src: "{{ item.src }}"
dest: "{{ item.dest }}"
mode: "{{ item.mode }}"
with_items:
- { src: "./httpd.conf", dest: "/etc/httpd/conf/", mode: "0644" }
- { src: "./upload_file.php", dest: "/var/www/html/", mode: "0600" }
#with_items: 中,可以再次使用变量
playbook handlers
handlers用来执行某些条件下的任务,比如当配置文件发生变化的时候,通过notify触发handler去重启服务。
功能:监控playbook中的某一个步骤,如果该步骤的状态为chage,那么该触发器将会启动,然后再执行指定的一个或多个模块
notify:监控,通过name触发指定的模块
headlers是否启动要看notify是否被触发(状态是否改变,有的模块的状态会一直改变,但是不会不影响handlers的作用)
notify不能和判断一起使用,不然要多次调用restart
实践案例
[root@m01 ~]# cat handler.yml
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- http_port: 8080
tasks:
- name: Install Http Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: config httpd server
template:
src: ./httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/conf
notify: #notify一般跟在配置文件的拷贝后面
- Restart Httpd Server #通过name注释触发
- Restart PHP Server
- name: start httpd server
service:
name:httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers: #一般指定重启服务(前面两个空格)
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- name: Restart PHP Server #同一主机,同一模块,同一的动作
systemd:
name: php-fpm
state: restarted
练习:多个nginx配置文件的推送及触发器
注意:
1.无论多少个task通知了相同的handlers,handlers仅会在所有tasks结束后运行一次。(一次)
2.Handlers只有在其所在的任务被执行时,才会被运行;如果一个任务中定义了notify调用Handlers,但是由于条件判断等原因,该任务未被执行,那么Handlers同样不会被执行。(绑定)
3.Handlers只会在每一个play的末尾运行一次(单独一个handlers的位置不固定);如果想在一个playbook中间运行Handlers,则需要使用meta模块来实现。例如: - meta: flush_handlers。(加在哪,就在哪执行一次)(notify和handlers之间不能出现报错)
4.如果一个play在运行到调用Handlers的语句之前失败了,那么这个Handlers将不会被执行。我们可以使用meta模块的 --force-handlers选项来强制执行Handlers,即使Handlers所在的play中途运行失败也能执行。(强制执行,触发器将毫无意义)
5.不能使用handlers替代tasks(否则就是循环了)
playbook任务标签(tag标签)
默认情况下,Ansible在执行一个playbook时,会执行playbook中定义的所有任务,
Ansible的标签(tag)功能可以给单独任务甚至整个playbook打上标签,然后利用这些标签来指定要运行playbook中的个别任务,或不执行指定的任务。
打标签的方式
1.对一个task(任务)打一个标签(tags)
2.对一个task打多个标签
3.对多个task打一个标签
打完标签如何使用
-t:执行指定的tag标签任务
--skip-tags:执行--skip-tags之外的标签任务(不执行此标签)
tag标签的作用就是,只执行一个yml中的有指定tag的模块(可以触发handlers),一般作用于多个模块的yml文件,来达到单一的目的
tags不用加handlers,加在notify就好,
[root@m01 m01]# cat tag.yml
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- http_port: 8080
tasks:
- name: if httpd install
shell: "rpm -q httpd" #判断
ignore_errors: yes #忽略错误
register: check_httpd #变量注册
- name: Install Http Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
tags: #同一个task打上多个标签
- install_httpd
- httpd_server
when: check_httpd.rc !=0 #非系统变量的调用
- name: configure httpd server
template:
src: ./httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
tags:
- config_httpd
- httpd_server
- name: start httpd server
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
tags: service_httpd
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted
#查看标签项
[root@m01 m01]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --list-tags
#执行指定的tag标签任务
[root@m01 m01]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t httpd_server
#执行多个标签任务
[root@m01 m01]# ansible-playbook tag.yml -t install_httpd,confiure_httpd
#不执行该标签,只要有某一tag的都不执行该模块
[root@m01 m01]# ansible-playbook tag.yml --skip-tags httpd_server
- http_port: 8080
tasks:
- name: if httpd install
shell: "rpm -q httpd"
ignore_errors: yes
register: check_httpd
- name: Install Http Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
tags:
- install_httpd
- httpd_server
when: check_httpd.rc !=0
#tags的执行会受到when的影响,所以执行以下命令将报错
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-playbook tags.yml -t httpd_server
playbook文件复用
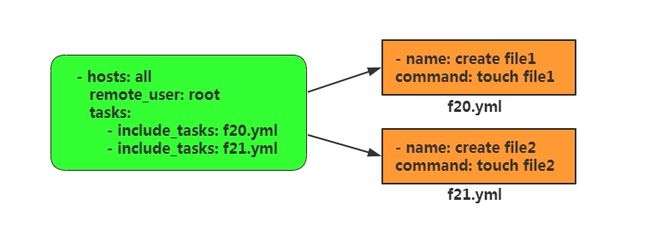
在之前写playbook的过程中,我们发现,写多个playbook没有办法,一键执行,这样我们还要单个playbook挨个去执行,很鸡肋。所以在playbook中有一个功能,叫做include用来动态调用task任务列表。
只调用task:include_tasks
调用整个task 文件:include (新版本ab:import_playbook)
在saltstack中,叫做top file入口文件。
示例一:
[root@m01 m01]# cat task.yml
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- http_port: 8080
tasks: #调用指定yml文件的 tasks
- include_tasks: task_install.yml
- include_tasks: task_configure.yml
- include_tasks: task_start.yml
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted
[root@m01 m01]# cat task_install.yml
- name: Install Http Server
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
[root@m01 m01]# cat task_configure.yml
- name: configure httpd server
template:
src: ./httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server #notify触发器
[root@m01 m01]# cat task_start.yml
- name: start httpd server
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
示例二
- include: httpd.yml
- include: nfs.yml
- include: rsync.yml
示例三 (ansible向下兼容,小心向上不兼容的情况),导入的是完整的playbook
- import_playbook: httpd.yml
- import_playbook: nfs.yml
- import_playbook: rsync.yml
#查看安装ansible的时候,安装的命令
[root@m01 ansible]# rpm -ql ansible |grep bin
/usr/bin/ansible #
/usr/bin/ansible-2
/usr/bin/ansible-2.7
/usr/bin/ansible-config
/usr/bin/ansible-connection
/usr/bin/ansible-console
/usr/bin/ansible-console-2
/usr/bin/ansible-console-2.7
/usr/bin/ansible-doc #
/usr/bin/ansible-doc-2
/usr/bin/ansible-doc-2.7
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy #
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy-2
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy-2.7
/usr/bin/ansible-inventory
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook #
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook-2
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook-2.7
#创建roles目录
[root@m01 ansible]# ansible-galaxy init rsync
- Role rsync was created successfully
[root@m01 ansible]# ll
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 154 Jun 17 05:39 rsync
[root@m01 ansible]# tree rsync/
rsync/
├── defaults
│ └── main.yml
├── files
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── meta
│ └── main.yml
├── README.md
├── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── templates
├── tests
│ ├── inventory
│ └── test.yml
└── vars
└── main.yml
#创建主目录(控制所有的yml文件)
vim /rsync/site.yml
playbook忽略错误(继续执行)
默认playbook会检测task执行的返回状态,如果遇到错误则会立即终止playbook的后续task执行,然鹅有些时候playbook即使执行错误了也要让其继续执行。
加入参数:ignore_errors:yes 忽略错误
[root@m01 ~]# cat ignore.yml
---
- hosts: web_group
tasks:
- name: Ignore False
command: /bin/false #错误的命令,用于执行错误
ignore_errors: yes #一般与变量注册 command或shell模块一起使用
- name: touch new file
file:
path: /tmp/zls.txt
state: touch
playbook错误处理(强制执行)
如上所述,当task执行失败时,playbook将不再继续执行,包括如果在task中设置了handler也不会被执行。(一般用于notify没有执行 导致handler无法执行的情况)
但是我们可以采取强制措施...
强制调用handler(触发器将毫无意义)
[root@m01 ~]# cat handler.yml
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- http_port: 8080
force_handlers: yes #强制执行handlers
tasks:
- name: config httpd server
template:
src: ./httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/conf
notify:
- Restart Httpd Server
- Restart PHP Server
- name: Install Http Server
yum:
name: htttpd
state: present
- name: start httpd server
service:
name:httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted
- name: Restart PHP Server
systemd:
name: php-fpm
state: restarted
抑制changed
问题:有些模块的执行反馈的状态永远都是change,但是明明没有什么改变
被管理主机没有发生变化,可以使用参数将change状态改为ok
[root@m01 ~]# cat handler.yml
- hosts: web_group
vars:
- http_port: 8080
force_handlers: yes
tasks:
- name: shell
shell: netstat -lntup|grep httpd
register: check_httpd
changed_when: false
#抑制该模块状态的改变(抑制绿),不会影响模块的执行
- name: debug
debug: msg={{ check_httpd.stdout.lines }}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@m01 project2]# cat changed_when.yml
- hosts: webservers
vars:
- http_port: 8080
tasks:
- name: configure httpd server
template:
src: ./httpd.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
- name: Check HTTPD
shell: /usr/sbin/httpd -t
register: httpd_check
changed_when: #改变运行结果的显示
- httpd_check.stdout.find('OK')
- false
- name: start httpd server
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted