Java8的Stream流的使用
参考自 原作者
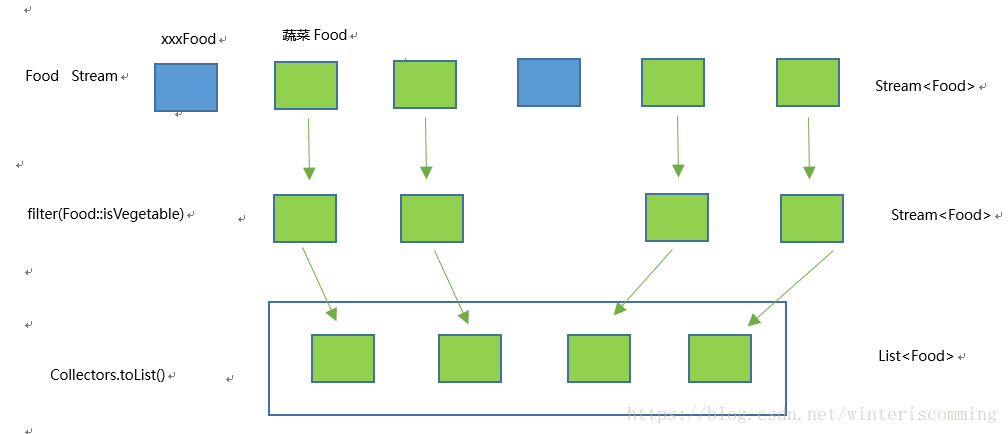
//过滤出蔬菜食物
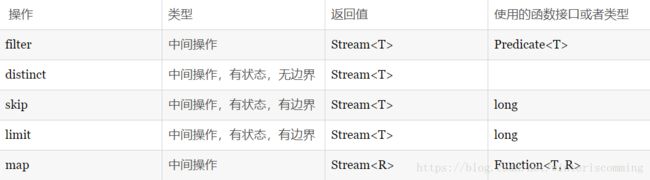
List vegetablesFood= menu.stream().filter(Food::isVegetable).collect(Collectors.toList()); //过滤出偶数,并且不重复的元素。
List numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 1, 3, 3, 2, 4);
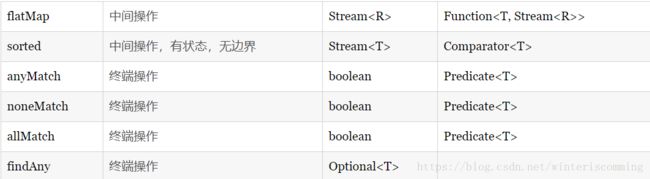
numbers.stream().filter(i->i%2==0).distinct().forEach(System.out::println); //截断流 热量大于300卡路里的食物 解析?
List foodList = allFoodList.stream().filter(f->f.getCalories()>300).limit(3).collect(toList()); //跳过元素 热量大于300卡路里的食物 解析?
ListfoodList = allFoodList.stream().filter(f->f.getCalories()>300).skip(2).collect(toList()); //映射 为啥不是f.getName()呢?
List foodNameList = allFoodList.stream().map(Food::getName).collet(toList());
List foodNameList = Arrays.asList("apple","pear","balana","tomato","onion");
ListwordLengthList = foodNameList.stream().map(String::length).collect(toList);
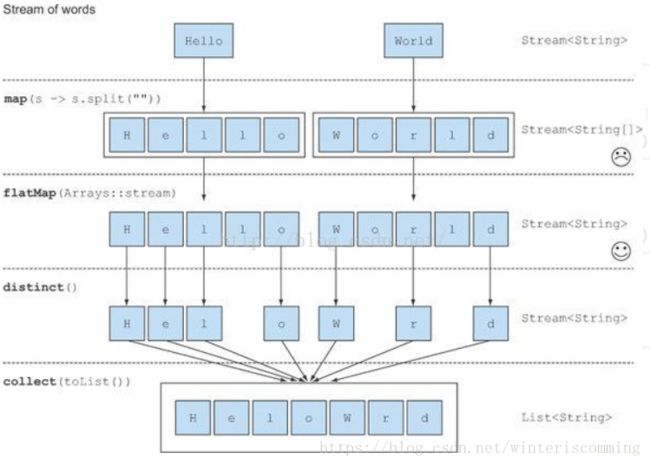
//展开流
String words = "Hello world"
List uniqueCharacters = words.stream().map(w->w.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream).distinct().collet(Collectors.toList());
/*
*查找和匹配
*
*/
//任意匹配 判断的条件里,任意一个元素匹配成功,返回true
if(allFoodList.stream().anyMatch(Food::isVegetable)){
System.out.println("The food is so good!");
}
//全部匹配 判断条件里的元素,所有的都是XXX时候,返回true
Boolean isHealthy = allFoodList.stream().allMatch(f->f.getCalories<1000);
//全部不匹配 判断条件里的元素,所有的都不是XXX时候,返回true
Boolean isHealthy = allFoodList.stream().noneMatch(f->f.getCalories<1000);
//获取任意一个元素
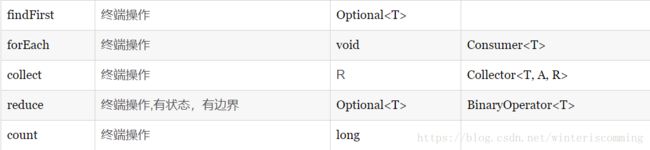
Optional food = allFoodList.stream().filter(Food::isVegetable).findAny();
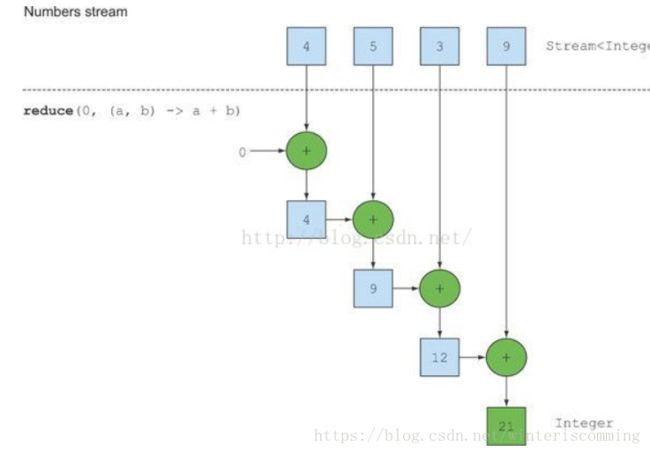
/*
*归约 将一个流中的元素,反复结合运算得到一个值
*/
//使用循环求和
List numbers = new ArrayList();
int sum = 0;
for(int x:numbers){
sum+=x;
}
//使用流的API求和
int sum2 = numbers.stream().reduce(0,(a,b)->a+b);
//求最大值
Optional max = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::max);
//求最小值
Optional min = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::min);
//使用reduce相对于使用逐步迭代的好处在于,外部迭代改成了内部迭代,在需要实现并行执行的操时作变得简单。
JAVA8的排序实现:
receivedProducts.sort(Comparator.comparing(rp->rp.getPlant().getOrgName()));persions.sort(Comparator.comparing(Persion::getAge).reversed());persions.sort((t1,t2)->{
if(t1.getAge() > t2.getAge()){
return -1;
}
return 1;
});
注:使用toMap()函数之后,返回的就是一个Map了,自然会需要key和value。
toMap()的第一个参数就是用来生成key值的,第二个参数就是用来生成value值的。
第三个参数用在key值冲突的情况下:如果新元素产生的key在Map中已经出现过了,第三个参数就会定义解决的办法。
假如: .collect(Collectors.toMap(UserBo::getUserId, v -> v, (v1, v2) -> v1));
第一个参数UserBo::getUserId 表示选择UserBo的getUserId作为map的key值;
第二个参数v -> v表示选择将原来的对象作为map的value值;
第三个参数(v1, v2) -> v1中,如果v1与v2的key值相同,选择v1作为那个key所对应的value值