动手入门深度学习笔记-机器翻译(注意力机制与Seq2seq模型,Transformer)
机器翻译
1.定义
将一段文本从一种语言自动翻译为另一种语言,
用神经网络解决这个问题通常称为神经机器翻译(NMT)。
主要特征:输出是单词序列而不是单个单词。
输出序列的长度可能与源序列的长度不同。
2.code 实现
## 机器翻译定义
"""
主要是将一段文本从一种语言自动翻译成另外一种语言
输出是单词序列而不是单个单词。 输出序列的长度可能与源序列的长度不同
"""
import os
os.listdir('/home/kesci/input/')
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2l9528/')
import collections
import d2l
import zipfile
from d2l.data.base import Vocab
import time
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils import data
from torch import optim
## 数据预处理
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
print(raw_text[0:1000])
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and i > 0 and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
print(text[0:1000])
## 分词
## 字符串 -- 单词组成的列表
num_examples = 50000
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):
if i > num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
source[0:3], target[0:3]
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.hist([[len(l) for l in source], [len(l) for l in target]],label=['source', 'target'])
d2l.plt.legend(loc='upper right');
## 构建词典
## 单词组成的列表 -- 单词id 组成的列表
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return d2l.data.base.Vocab(tokens,min_freq =3,use_special_tokens =True)
src_vocab = build_vocab(source)
## 载入数据集
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):
if len(line) > max_len:
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
pad(src_vocab[source[0]], 10, src_vocab.pad)
def build_array(lines,vocab,max_len,is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab_eos] for line in lines]
array = torch.tensor([pad(line,max_len,vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1) ## 第一维度
return array,valid_len
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len): # This function is saved in d2l.
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = load_data_nmt(batch_size=2, max_len=8)
for X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len, in train_iter:
print('X =', X.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for X =', X_valid_len,
'\nY =', Y.type(torch.int32), '\nValid lengths for Y =', Y_valid_len)
break
## Encoder-Decoder
"""
encoder:输入到隐藏状态
decoder:隐藏状态到输出
"""
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Encoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def forward(self, X, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Decoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
raise NotImplementedError
def forward(self, X, state):
raise NotImplementedError
class EncoderDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, **kwargs):
super(EncoderDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, enc_X, dec_X, *args):
enc_outputs = self.encoder(enc_X, *args)
dec_state = self.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, *args)
return self.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)
## encoder
class Seq2SeqEncoder(d2l.Encoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,\
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqEncoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_hiddens=num_hiddens
self.num_layers=num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
def begin_state(self, batch_size, device):
return [torch.zeros(size=(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros(size=(self.num_layers, batch_size, self.num_hiddens), device=device)]
def forward(self, X, *args):
X = self.embedding(X) # X shape: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_size)
X = X.transpose(0, 1) # RNN needs first axes to be time
# state = self.begin_state(X.shape[1], device=X.device)
out, state = self.rnn(X)
# The shape of out is (seq_len, batch_size, num_hiddens).
# state contains the hidden state and the memory cell
# of the last time step, the shape is (num_layers, batch_size, num_hiddens)
return out, state
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
X = torch.zeros((4, 7),dtype=torch.long)
output, state = encoder(X)
output.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, state[1].shape
# decoder
class Seq2SeqDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens,vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, *args):
return enc_outputs[1]
def forward(self, X, state):
X = self.embedding(X).transpose(0, 1)
out, state = self.rnn(X, state)
# Make the batch to be the first dimension to simplify loss computation.
out = self.dense(out).transpose(0, 1)
return out, state
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
state = decoder.init_state(encoder(X))
out, state = decoder(X, state)
out.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, state[1].shape
## 损失函数
def SequenceMask(X, X_len,value=0):
maxlen = X.size(1)
mask = torch.arange(maxlen)[None, :].to(X_len.device) < X_len[:, None]
X[~mask]=value
return X
X = torch.tensor([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]])
SequenceMask(X,torch.tensor([1,2]))
X = torch.ones((2,3, 4))
SequenceMask(X, torch.tensor([1,2]),value=-1)
class MaskedSoftmaxCELoss(nn.CrossEntropyLoss):
# pred shape: (batch_size, seq_len, vocab_size)
# label shape: (batch_size, seq_len)
# valid_length shape: (batch_size, )
def forward(self, pred, label, valid_length):
# the sample weights shape should be (batch_size, seq_len)
weights = torch.ones_like(label)
weights = SequenceMask(weights, valid_length).float()
self.reduction='none'
output=super(MaskedSoftmaxCELoss, self).forward(pred.transpose(1,2), label)
return (output*weights).mean(dim=1)
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
loss(torch.ones((3, 4, 10)), torch.ones((3,4),dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor([4,3,0]))
def train_ch7(model, data_iter, lr, num_epochs, device): # Saved in d2l
model.to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
tic = time.time()
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs+1):
l_sum, num_tokens_sum = 0.0, 0.0
for batch in data_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, X_vlen, Y, Y_vlen = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
Y_input, Y_label, Y_vlen = Y[:,:-1], Y[:,1:], Y_vlen-1
Y_hat, _ = model(X, Y_input, X_vlen, Y_vlen)
l = loss(Y_hat, Y_label, Y_vlen).sum()
l.backward()
with torch.no_grad():
d2l.grad_clipping_nn(model, 5, device)
num_tokens = Y_vlen.sum().item()
optimizer.step()
l_sum += l.sum().item()
num_tokens_sum += num_tokens
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print("epoch {0:4d},loss {1:.3f}, time {2:.1f} sec".format(
epoch, (l_sum/num_tokens_sum), time.time()-tic))
tic = time.time()
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout = 32, 32, 2, 0.0
batch_size, num_examples, max_len = 64, 1e3, 10
lr, num_epochs, ctx = 0.005, 300, d2l.try_gpu()
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = d2l.load_data_nmt(
batch_size, max_len,num_examples)
encoder = Seq2SeqEncoder(
len(src_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
decoder = Seq2SeqDecoder(
len(tgt_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
model = d2l.EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder)
train_ch7(model, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, ctx)
def translate_ch7(model, src_sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, max_len, device):
src_tokens = src_vocab[src_sentence.lower().split(' ')]
src_len = len(src_tokens)
if src_len < max_len:
src_tokens += [src_vocab.pad] * (max_len - src_len)
enc_X = torch.tensor(src_tokens, device=device)
enc_valid_length = torch.tensor([src_len], device=device)
# use expand_dim to add the batch_size dimension.
enc_outputs = model.encoder(enc_X.unsqueeze(dim=0), enc_valid_length)
dec_state = model.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, enc_valid_length)
dec_X = torch.tensor([tgt_vocab.bos], device=device).unsqueeze(dim=0)
predict_tokens = []
for _ in range(max_len):
Y, dec_state = model.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)
# The token with highest score is used as the next time step input.
dec_X = Y.argmax(dim=2)
py = dec_X.squeeze(dim=0).int().item()
if py == tgt_vocab.eos:
break
predict_tokens.append(py)
return ' '.join(tgt_vocab.to_tokens(predict_tokens))
for sentence in ['Go .', 'Wow !', "I'm OK .", 'I won !']:
print(sentence + ' => ' + translate_ch7(
model, sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, max_len, ctx))
## 维特比算法
"""
选择整体分数最高的句子(搜索空间太大) 集束搜索
"""
注意力机制与Seq2Seq模型
注意力机制
1.提出背景
在“编码器—解码器(seq2seq)”⼀节⾥,解码器在各个时间步依赖相同的背景变量(context vector)来获取输⼊序列信息。当编码器为循环神经⽹络时,背景变量来⾃它最终时间步的隐藏状态。将源序列输入信息以循环单位状态编码,然后将其传递给解码器以生成目标序列。然而这种结构存在着问题,尤其是RNN机制实际中存在长程梯度消失的问题,对于较长的句子,我们很难寄希望于将输入的序列转化为定长的向量而保存所有的有效信息,所以随着所需翻译句子的长度的增加,这种结构的效果会显著下降。
与此同时,解码的目标词语可能只与原输入的部分词语有关,而并不是与所有的输入有关。例如,当把“Hello world”翻译成“Bonjour le monde”时,“Hello”映射成“Bonjour”,“world”映射成“monde”。在seq2seq模型中,解码器只能隐式地从编码器的最终状态中选择相应的信息。然而,注意力机制可以将这种选择过程显式地建模。
2. 原理
3.code 实现
## 注意力机制框架
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2len9900')
import d2l
import os
def file_name_walk(file_dir):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir):
# print("root", root) # 当前目录路径
print("dirs", dirs) # 当前路径下所有子目录
print("files", files) # 当前路径下所有非目录子文件
file_name_walk("/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506")
## 先介绍一个softmax 操作符的一个屏蔽操作
def SequenceMask(X, X_len,value=-1e6):
maxlen = X.size(1)
#print(X.size(),torch.arange((maxlen),dtype=torch.float)[None, :],'\n',X_len[:, None] )
mask = torch.arange((maxlen),dtype=torch.float)[None, :] >= X_len[:, None]
#print(mask)
X[mask]=value
return X
def masked_softmax(X,valid_length):
softmax = nn.Softmax()
if valid_length is None:
return softmax(x)
else:
shape = X.shaoe
if valid_length.dim() == 1:
try:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.numpy().repeat(shape[1],axis=0))
except:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.cpu().numpy().repeat(shape[1],axis=0))
else:
valid_length = valid_length.reshape((-1,))
## fill masked elements with a large negative,whose exp is 0
X = SequenceMask(X.reshape((-1,shape[-1])),valid_length)
return softmax(X).reshape(shape)
masked_softmax(torch.rand((2,2,4),dtype=torch.float), torch.FloatTensor([2,3]))
## 超过2维的矩阵的乘法
torch.bmm(torch.ones((2,1,3),dtype=torch.float),torch.ones((2,3,2),dtype=torch.float))
##点积注意力
class DotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dropout, **kwargs):
super(DotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# query: (batch_size, #queries, d)
# key: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, d)
# value: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, dim_v)
# valid_length: either (batch_size, ) or (batch_size, xx)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length=None):
d = query.shape[-1]
# set transpose_b=True to swap the last two dimensions of key
scores = torch.bmm(query, key.transpose(1,2)) / math.sqrt(d)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
print("attention_weight\n",attention_weights)
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
## 测试
atten = DotProductAttention(dropout=0)
keys = torch.ones((2,10,2),dtype=torch.float)
values = torch.arange((40), dtype=torch.float).view(1,10,4).repeat(2,1,1)
atten(torch.ones((2,1,2),dtype=torch.float), keys, values, torch.FloatTensor([2, 6]))
## 多层感知机注意力
class MLPAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, units,ipt_dim,dropout, **kwargs):
super(MLPAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# Use flatten=True to keep query's and key's 3-D shapes.
self.W_k = nn.Linear(ipt_dim, units, bias=False)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(ipt_dim, units, bias=False)
self.v = nn.Linear(units, 1, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length):
query, key = self.W_k(query), self.W_q(key)
#print("size",query.size(),key.size())
# expand query to (batch_size, #querys, 1, units), and key to
# (batch_size, 1, #kv_pairs, units). Then plus them with broadcast.
features = query.unsqueeze(2) + key.unsqueeze(1)
#print("features:",features.size()) #--------------开启
scores = self.v(features).squeeze(-1)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
atten = MLPAttention(ipt_dim=2,units = 8, dropout=0)
atten(torch.ones((2,1,2), dtype = torch.float), keys, values, torch.FloatTensor([2, 6]))
"""
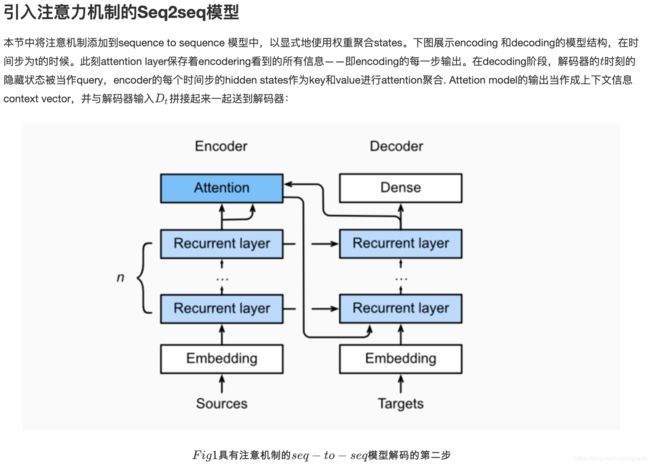
本节中将注意机制添加到sequence to sequence 模型中,
以显式地使用权重聚合states。
下图展示encoding 和decoding的模型结构,
在时间步为t的时候。此刻attention layer保存着encodering看到的所有信息——即encoding的每一步输出。
在decoding阶段,解码器的时刻的隐藏状态被当作query,encoder的每个时间步的hidden states
作为key和value进行attention聚合.
Attetion model的输出当作成上下文信息context vector,并与解码器输入拼接起来一起送到解码器:
"""
class Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers,
dropout=0, **kwargs):
super(Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.attention_cell = MLPAttention(num_hiddens,num_hiddens, dropout)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embed_size+ num_hiddens,num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout=dropout)
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens,vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, enc_valid_len, *args):
outputs, hidden_state = enc_outputs
# print("first:",outputs.size(),hidden_state[0].size(),hidden_state[1].size())
# Transpose outputs to (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)
return (outputs.permute(1,0,-1), hidden_state, enc_valid_len)
#outputs.swapaxes(0, 1)
def forward(self, X, state):
enc_outputs, hidden_state, enc_valid_len = state
#("X.size",X.size())
X = self.embedding(X).transpose(0,1)
# print("Xembeding.size2",X.size())
outputs = []
for l, x in enumerate(X):
# print(f"\n{l}-th token")
# print("x.first.size()",x.size())
# query shape: (batch_size, 1, hidden_size)
# select hidden state of the last rnn layer as query
query = hidden_state[0][-1].unsqueeze(1) # np.expand_dims(hidden_state[0][-1], axis=1)
# context has same shape as query
# print("query enc_outputs, enc_outputs:\n",query.size(), enc_outputs.size(), enc_outputs.size())
context = self.attention_cell(query, enc_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_valid_len)
# Concatenate on the feature dimension
# print("context.size:",context.size())
x = torch.cat((context, x.unsqueeze(1)), dim=-1)
# Reshape x to (1, batch_size, embed_size+hidden_size)
# print("rnn",x.size(), len(hidden_state))
out, hidden_state = self.rnn(x.transpose(0,1), hidden_state)
outputs.append(out)
outputs = self.dense(torch.cat(outputs, dim=0))
return outputs.transpose(0, 1), [enc_outputs, hidden_state,
enc_valid_len]
encoder = d2l.Seq2SeqEncoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,
num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
# encoder.initialize()
decoder = Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder(vocab_size=10, embed_size=8,
num_hiddens=16, num_layers=2)
X = torch.zeros((4, 7),dtype=torch.long)
print("batch size=4\nseq_length=7\nhidden dim=16\nnum_layers=2\n")
print('encoder output size:', encoder(X)[0].size())
print('encoder hidden size:', encoder(X)[1][0].size())
print('encoder memory size:', encoder(X)[1][1].size())
state = decoder.init_state(encoder(X), None)
out, state = decoder(X, state)
out.shape, len(state), state[0].shape, len(state[1]), state[1][0].shape
import zipfile
import torch
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from torch.utils import data
import sys
import collections
## 训练
class Vocab(object): # This class is saved in d2l.
def __init__(self, tokens, min_freq=0, use_special_tokens=False):
# sort by frequency and token
counter = collections.Counter(tokens)
token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])
token_freqs.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
if use_special_tokens:
# padding, begin of sentence, end of sentence, unknown
self.pad, self.bos, self.eos, self.unk = (0, 1, 2, 3)
tokens = ['', '', '', '']
else:
self.unk = 0
tokens = ['']
tokens += [token for token, freq in token_freqs if freq >= min_freq]
self.idx_to_token = []
self.token_to_idx = dict()
for token in tokens:
self.idx_to_token.append(token)
self.token_to_idx[token] = len(self.idx_to_token) - 1
def __len__(self):
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
else:
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
def to_tokens(self, indices):
if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):
return self.idx_to_token[indices]
else:
return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len, num_examples=1000):
"""Download an NMT dataset, return its vocabulary and data iterator."""
# Download and preprocess
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
# Tokenize
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):
if i >= num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
# Build vocab
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return Vocab(tokens, min_freq=3, use_special_tokens=True)
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
# Convert to index arrays
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):
if len(line) > max_len:
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
def build_array(lines, vocab, max_len, is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab.eos] for line in lines]
array = torch.tensor([pad(line, max_len, vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1)
return array, valid_len
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout = 32, 32, 2, 0.0
batch_size, num_steps = 64, 10
lr, num_epochs, ctx = 0.005, 500, d2l.try_gpu()
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = load_data_nmt(batch_size, num_steps)
encoder = d2l.Seq2SeqEncoder(
len(src_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
decoder = Seq2SeqAttentionDecoder(
len(tgt_vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout)
model = d2l.EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder)
d2l.train_s2s_ch9(model, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, ctx)
for sentence in ['Go .', 'Good Night !', "I'm OK .", 'I won !']:
print(sentence + ' => ' + d2l.predict_s2s_ch9(
model, sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps, ctx))