webrtc 点对点会话建立过程分析
关于 webrtc 建立点对点连接的文章很多,其中都提到了如何利用 stun 服务器获取本机的公网地址,本文侧重局域网(两台设备之间可以直接 ping 通)下webrtc 点对点连接建立问题分析。
1.局域网内连接建立过程
了解过 webrtc 的都知道,要在公网上使用 webrtc 建立 p2p 连接,必须要有 stun 服务器的支持才行,但在局域网内使用 webrtc 建立 p2p 连接,可以不需要 stun 服务器,但是信令服务器还是必须的。在局域网内,要获取 IceCandidate,只需要获取本机的地址和端口即可。除此之外,与在公网上建立 p2p 连接没有什么区别。
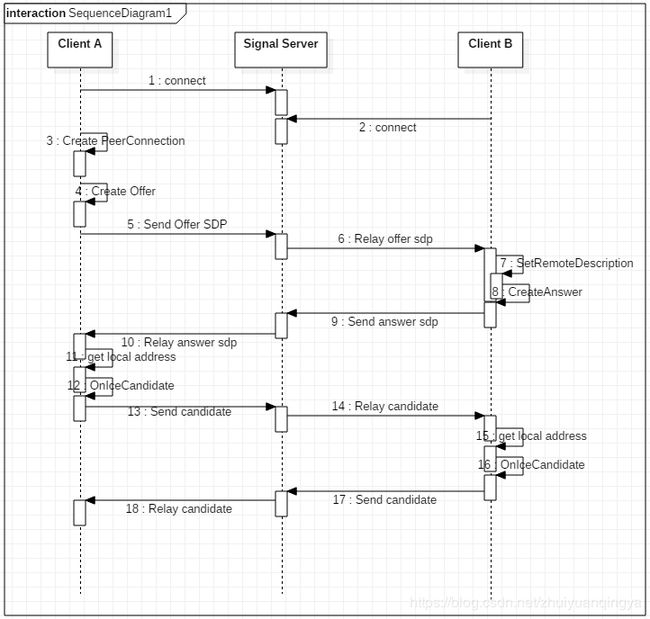
本文是通过 chromium 浏览器中的前端应用,来调起浏览器中内嵌的 webrtc,所以在分析过程中,会有涉及 chromium 和 webrtc 两部分的代码。接下来会对 CreateAnswer 和 OnIceCandidate 的流程进行分析。
2. webrtc 信号机制
webrtc 中大量采用了信号机制,类似 QT 的信号槽。后面的代码分析中不会显示指出调用是否由信号串起流程,所以这里会先介绍信号机制,后面很多地方都有用到。信号机制举例如下:
(1)定义信号
D:\chromium\code\src\third_party\webrtc\p2p\base\portallocator.h
sigslot::signal2&> SignalCandidatesReady;
(2)绑定信号
执行 SignalCandidatesReady.connect() 会将信号和指定的处理函数进行绑定,当接收到信号时,就会调用对应的处理函数。
D:\chromium\code\src\third_party\webrtc\p2p\base\p2ptransportchannel.cc
void P2PTransportChannel::AddAllocatorSession(
std::unique_ptr session) {
...
session->SignalCandidatesReady.connect(
this, &P2PTransportChannel::OnCandidatesReady);
...
}
allocator_sessions_.push_back(std::move(session));
// We now only want to apply new candidates that we receive to the ports
// created by this new session because these are replacing those of the
// previous sessions.
PruneAllPorts();
}
在这个函数中声明了 SignalCandidatesReady 的处理函数为 P2PTransportChannel::OnCandidatesReady()。当然,一个信号可以有多个处理函数,也就是可以在多处进行绑定,一旦发送信号,多处的处理函数都会被调起。
(3)发送信号
在需要发送信号时,调用 SignalCandidatesReady(this, candidates);即可,需要传入信号处理函数需要的参数。
D:\chromium\code\src\third_party\webrtc\p2p\client\basicportallocator.cc
void BasicPortAllocatorSession::OnCandidateReady(
Port* port, const Candidate& c) {
...
if (data->ready() && CheckCandidateFilter(c)) {
std::vector candidates;
candidates.push_back(SanitizeRelatedAddress(c));
SignalCandidatesReady(this, candidates);
} else {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Discarding candidate because it doesn't match filter.";
}
...
}
3. CreateAnswer 流程
CreateAnswer 这个动作是应答端执行,用于生成该端的会话描述信息,会话描述信息主要包括:媒体类型、编解码器、带宽等元数据,下面给出一个 SDP 的示例:
v=0
o=- 6220557467521116672 2 IN IP4 127.0.0.1
s=-
t=0 0
a=group:BUNDLE audio video
a=msid-semantic: WMS
m=audio 9 UDP/TLS/RTP/SAVPF 111 103 104 9 0 8 106 105 13 110 112 113 126
c=IN IP4 0.0.0.0
a=rtcp:9 IN IP4 0.0.0.0
a=ice-ufrag:LjWt
a=ice-pwd:1/eNkEa0sLVOz0wm0krK7sot
a=ice-options:trickle
a=fingerprint:sha-256 85:2D:B2:69:9C:85:26:82:96:D5:87:C6:40:4B:DE:C5:CB:47:4E:06:57:20:88:1F:11:C4:B9:5A:7B:EB:D3:9A
a=setup:active
a=mid:audio
a=extmap:1 urn:ietf:params:rtp-hdrext:ssrc-audio-level
a=recvonly
a=rtcp-mux
a=rtpmap:111 opus/48000/2
a=rtcp-fb:111 transport-cc
a=fmtp:111 minptime=10;useinbandfec=1
a=rtpmap:103 ISAC/16000
a=rtpmap:104 ISAC/32000
a=rtpmap:9 G722/8000
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
a=rtpmap:8 PCMA/8000
a=rtpmap:106 CN/32000
a=rtpmap:105 CN/16000
a=rtpmap:13 CN/8000
a=rtpmap:110 telephone-event/48000
a=rtpmap:112 telephone-event/32000
a=rtpmap:113 telephone-event/16000
a=rtpmap:126 telephone-event/8000
m=video 9 UDP/TLS/RTP/SAVPF 96 97 98 99 100 101 127 123 125
c=IN IP4 0.0.0.0
a=rtcp:9 IN IP4 0.0.0.0
a=ice-ufrag:LjWt
a=ice-pwd:1/eNkEa0sLVOz0wm0krK7sot
a=ice-options:trickle
a=fingerprint:sha-256 85:2D:B2:69:9C:85:26:82:96:D5:87:C6:40:4B:DE:C5:CB:47:4E:06:57:20:88:1F:11:C4:B9:5A:7B:EB:D3:9A
a=setup:active
a=mid:video
a=extmap:2 urn:ietf:params:rtp-hdrext:toffset
a=extmap:3 http://www.webrtc.org/experiments/rtp-hdrext/abs-send-time
a=extmap:4 urn:3gpp:video-orientation
a=extmap:5 http://www.ietf.org/id/draft-holmer-rmcat-transport-wide-cc-extensions-01
a=extmap:6 http://www.webrtc.org/experiments/rtp-hdrext/playout-delay
a=extmap:7 http://www.webrtc.org/experiments/rtp-hdrext/video-content-type
a=extmap:8 http://www.webrtc.org/experiments/rtp-hdrext/video-timing
a=recvonly
a=rtcp-mux
a=rtcp-rsize
a=rtpmap:96 VP8/90000
a=rtcp-fb:96 goog-remb
a=rtcp-fb:96 transport-cc
a=rtcp-fb:96 ccm fir
a=rtcp-fb:96 nack
a=rtcp-fb:96 nack pli
a=rtpmap:97 rtx/90000
a=fmtp:97 apt=96
a=rtpmap:98 VP9/90000
a=rtcp-fb:98 goog-remb
a=rtcp-fb:98 transport-cc
a=rtcp-fb:98 ccm fir
a=rtcp-fb:98 nack
a=rtcp-fb:98 nack pli
a=rtpmap:99 rtx/90000
a=fmtp:99 apt=98
a=rtpmap:100 H264/90000
a=rtcp-fb:100 goog-remb
a=rtcp-fb:100 transport-cc
a=rtcp-fb:100 ccm fir
a=rtcp-fb:100 nack
a=rtcp-fb:100 nack pli
a=fmtp:100 level-asymmetry-allowed=1;packetization-mode=1;profile-level-id=420032
a=rtpmap:101 rtx/90000
a=fmtp:101 apt=100
a=rtpmap:127 red/90000
a=rtpmap:123 rtx/90000
a=fmtp:123 apt=127
a=rtpmap:125 ulpfec/90000
CreateAnswer 生成会话描述信息的流程如下图所示:
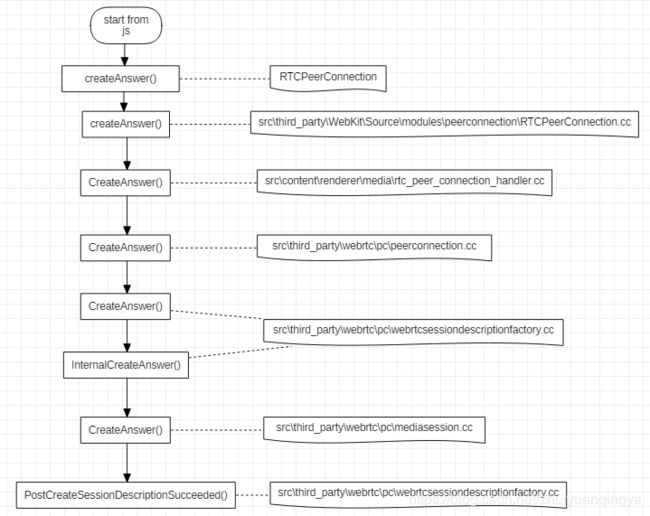
从流程可以看出, CreateAnswer 是由 js 代码发起的,其中 RTCPeerConnection 是浏览器提供的前端 api,之后传入 webkit 处理,再进入浏览器的 renderer 进程处理,最后还是到了 webrtc 代码中执行真正的生成 SDP 的动作。在 src\third_party\webrtc\pc\mediasession.cc 这个文件的 CreateAnswer 函数中,会确定本地支持的音视频编解码等具体信息。
CreateOffer 执行的流程与上图类似。
关于 SDP 可以参考: WebRTC SDP协议
4. AddIceCandidate 流程
AddIceCandidate 是在对端发来了 Candidate 后,本地来添加保存这些 candidate,candidate 信息主要包括 IP 和端口号,以及所采用的协议类型等。Candidate 从前端发起添加流程到真正被保存,这个过程的流程图如下:

整个流程很长,最终远端传来的 Candidate 被保存 P2PTransportChannel 中。
5. OnIceCandidate 流程
OnIceCandidate 代表收集本地 Candidate 的过程,起始于 PeerConnection::SetLocalDescription() 函数,具体启动代码如下:
transport_controller_->MaybeStartGathering();
收集本地 Candidate 的执行流程如下,过程比较长,其中有些环节比较难以连贯起来,对这些环节后面会做简单介绍。
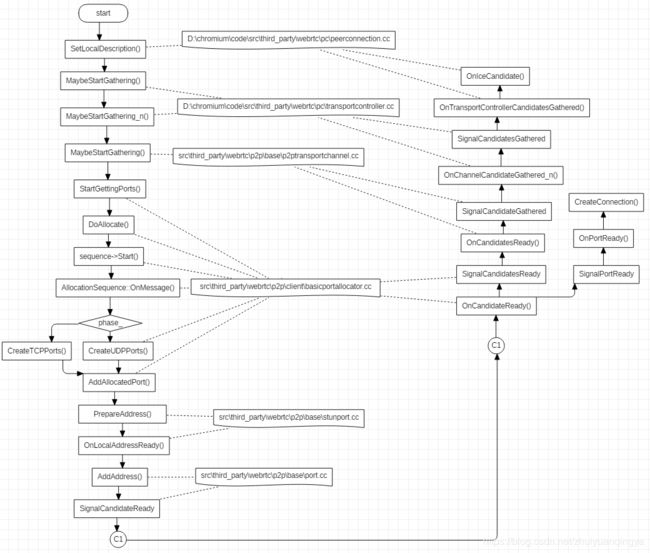
在函数 UDPPort::OnLocalAddressReady() 中,会执行函数 UDPPort::MaybePrepareStunCandidate(),这个函数会尝试获取 STUN 类型的 candidates,具体代码如下:
void UDPPort::MaybePrepareStunCandidate() {
// Sending binding request to the STUN server if address is available to
// prepare STUN candidate.
if (!server_addresses_.empty()) {
SendStunBindingRequests();
} else {
// Port is done allocating candidates.
MaybeSetPortCompleteOrError();
}
}
函数 UDPPort::SendStunBindingRequests() 执行具体的发送 stun 请求的过程,如果设置了 stun server 地址,那么就会发送请求,否则就会跳过请求 stun 地址的步骤:
void UDPPort::SendStunBindingRequests() {
// We will keep pinging the stun server to make sure our NAT pin-hole stays
// open until the deadline (specified in SendStunBindingRequest).
RTC_DCHECK(requests_.empty());
for (ServerAddresses::const_iterator it = server_addresses_.begin();
it != server_addresses_.end(); ++it) {
SendStunBindingRequest(*it);
}
}
分配端口
src\third_party\webrtc\p2p\client\basicportallocator.cc
在 void BasicPortAllocatorSession::DoAllocate() 中的 sequence->Start() 这句代码启动针对某个网卡的 Candidate 进行收集,Start() 函数如下:
void AllocationSequence::Start() {
state_ = kRunning;
session_->network_thread()->Post(RTC_FROM_HERE, this, MSG_ALLOCATION_PHASE);
// Take a snapshot of the best IP, so that when DisableEquivalentPhases is
// called next time, we enable all phases if the best IP has since changed.
previous_best_ip_ = network_->GetBestIP();
}
其中post 的原型位于文件 src\jingle\glue\thread_wrapper.cc :
void JingleThreadWrapper::Post(const rtc::Location& posted_from,
rtc::MessageHandler* handler,
uint32_t message_id,
rtc::MessageData* data,
bool time_sensitive)
在 AllocationSequence::Start() 中调用 Post 设置的 MessageHandler 为 this 指针,也就是 AllocationSequence 对象本身,因此调用会进入到 AllocationSequence::OnMessage() 函数中,AllocationSequence 的 phase_ 成员在对象创建时初始化为 0, 等于 PHASE_UDP ,所以首先会进入 PHASE_UDP 的处理过程,在处理完毕后,会调用:
if (state() == kRunning) {
++phase_;
session_->network_thread()->PostDelayed(RTC_FROM_HERE,
session_->allocator()->step_delay(),
this, MSG_ALLOCATION_PHASE);
}
之后,会进入下一个 phase,也就是 PHASE_RELAY 。
上面的流程执行到最后,会一路回调 OnIceCandidate() ,最终通过 webkit 传递到前端代码中。
6.小结
本文对 webrtc 建立连接过程中的一些步骤进行了具体分析,但还有较多的东西没有弄清楚,例如,两端协商 sdp 的过程等,后续再补充吧。