谷粒商城微服务分布式高级篇六——商城首页
文章目录
- 商城首页
- 效果
- Themeleaf
- 项目使用
- 引入依赖
- 关闭缓存
- 导入资源
- 一级分类
- 二级分类
- Nginx
- 搭建域名访问环境
商城首页
效果
Themeleaf
Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。相较与其他的模板引擎,它有如下三个极吸引人的特点:
1.Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 Thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
2.Thymeleaf 开箱即用的特性。它提供标准和 Spring 标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现 JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、改 Jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
3.Thymeleaf 提供 Spring 标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
常用:
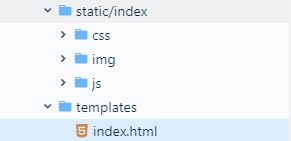
1、 使用SpingBoot Thymeleaf j静态文件默认放在templates下,静态资源默认放在static下
2、导入thymeleaf的名称空间
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
3、 ${}:取上下文环境中的message变量
<p th:text="${message}">被替换了!p>
<P>[[${message}]]P>
<div th:utext="${message}">被替换了!div>
<p data-th-text="${message}">被替换了!p>
4、{}:也是取上下文变量,但{}的上下文是父标签(th:object)所选择的对象
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p th:text="*{id}">p>
<p th:text="*{username}">p>
<p th:text="*{password}">p>
div>
<div>
<p th:text="${session.user.id}">p>
<p th:text="${session.user.username}">p>
<p th:text="${session.user.password}">p>
div>
<p th:text="*{session.user.username}">p>
<p th:text="${session.user.username}">p>
5、 @{}:用来处理URL链接地址的 实现跳转
<a th:href="@{https://fanlychie.github.io}">...a>
6、~{}:用来引用一段公共的HTML代码片段
~{templatename}:引用整个模板文件的代码片段
~{templatename :: selector}:selector 可以是 th:fragment 指定的名称或其他选择器。如类选择器、ID选择器等
~{::selector}:相当于 ~{this :: selector},表示引用当前模板定义的代码片段
前面是包名,后面是属性或选择器
<div th:insert="~{commons/common :: css }">div>
<div th:include="~{commons/common :: #footer}">div>
<div th:include="~{commons/common :: js }">div>
7、引用公共页
<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css}">
8、th:fragment:定义一段公共的代码片段,然后可以通过th:insert、th:replace、th:include将这些公共的代码引入到模板文件中
<div th:fragment="css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css}">
div>
通过th:insert属性引用一段公共的代码片段:
<div th:insert="~{base ::css}">div>
其中,~{}是可选的,我们可以去掉这层的包裹:
<div th:insert="base ::css">div>
若 index.html 与 base.html 不在同级目录,如 templates/commons/base.html:
<div th:insert="~{commons/base ::css}">div>
使用th:fragment属性定义代码片段时,你还可以声明一组参数:
<div th:fragment="crumbs(parent, child)">
<i th:text="${parent}">i> <i th:text="${child}">i>
div>
<div th:insert="::crumbs('用户中心', '我的订单')">div>
此外,我们还可以通过类选择器、ID选择器等来引用公共的代码片段:
<div th:insert="~{base :: #footer}">div>
th:replace也可以用来引用公共的代码片段。不同的是,th:insert是直接将代码片段插入到标签体内,而th:replace则是用代码片段直接替换标签体内容。
<div th:insert="~{base :: footerFragment}">div>
<div th:replace="~{base :: footerFragment}">div>
9、遍历(迭代)的语法th:each=“自定义的元素变量名称 : ${集合变量名称}”
<a href="login.html" th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user.username}">登录a>
结果:<a href="login.html">admin1a> <a href="login.html">admin2a> <a href="login.html">admin3a>
10、th:if 当表达式的评估结果为真时则显示内容,否则不显示
项目使用
引入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
开启代码热部署,ctrl+shift+F9 即可以修改html后不用重启服务器即可查看。
关闭缓存
application.properties新增thymeleaf配置
#这个开发配置为false,避免改了模板还要重启服务器
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
导入资源
导入首页html和静态资源,静态资源可直接访问,发现静态资源无法获取到,增加配置
#我们应该以什么样的路径来访问静态资源
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
#告诉Spring Boot应该在何处查找静态资源文件
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/static/
一级分类
@GetMapping({"/", "index.html" })
public String indexPage(Model model) {
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = categoryservice.getLevel1Categorys();
model.addAttribute("categorys", categoryEntities);
return "index";
}
/**
* 查询所有一级分类
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Categorys() {
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));
return categoryEntities;
}
html
<ul>
<li th:each="category:${categorys}">
<a href="#" class="header_main_left_a" th:attr="ctg-data=${category.catId}"><b
th:text="${category.name}"></b></a>
</li>
</ul>
二级分类
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/index/json/catalog.json")
public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJson() {
Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> map = categoryservice.getCatalogJson();
return map;
}
/**
* 查出所有分类 返回首页json
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJson() {
//所有一级分类
List<CategoryEntity> level1Categorys = getLevel1Categorys();
//封装数据 map k,v 结构
Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> map = level1Categorys.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(k -> k.getCatId().toString(), v -> {
//每一个的一级分类,查到这个一级分类的二级分类
List<CategoryEntity> category2Entities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", v.getCatId()));
List<Catalog2Vo> catelog2Vos = null;
if (category2Entities != null) {
catelog2Vos = category2Entities.stream().map(level2 -> {
//封装catalog2Vo
Catalog2Vo catalog2Vo = new Catalog2Vo(v.getCatId().toString(), null, level2.getCatId().toString(), level2.getName());
//每一个二级分类,查到三级分类
List<CategoryEntity> category3Entities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", level2.getCatId()));
if (category3Entities != null) {
List<Object> catalog3List = category3Entities.stream().map(level3 -> {
//封装catalog3Vo
Catalog2Vo.Catalog3Vo catalog3Vo = new Catalog2Vo.Catalog3Vo(level2.getCatId().toString(), level3.getCatId().toString(), level3.getName());
return catalog3Vo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//封装catalog3Vo到catalog2Vo
catalog2Vo.setCatalog3List(catalog3List);
}
return catalog2Vo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
//返回v=catalog2Vo
return catelog2Vos;
}));
return map;
}
Nginx
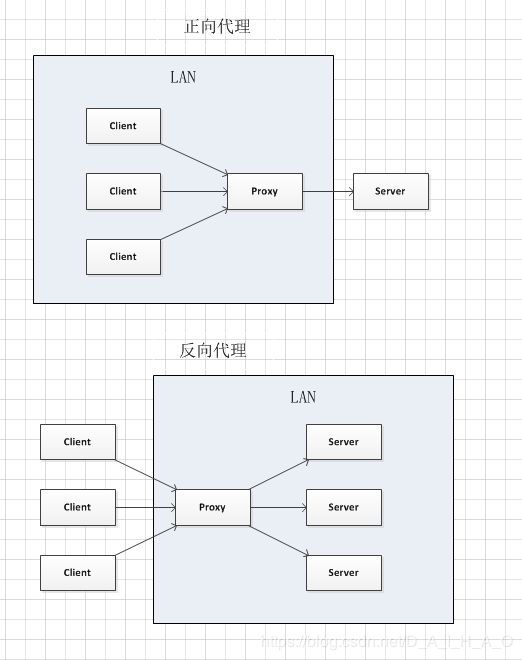
Nginx与Tomact,Apache:nginx和apache是静态的web服务器,tomcat是动态的web服务器。
Nginx除了具有web服务器的属性外,还有反向代理的功能,还有负载均衡功能。
Nginx所以叫Web服务器,反向代理服务器,负载均衡服务器.
正向代理 隐藏客户端
反向代理 隐藏服务端
搭建域名访问环境
虚拟机ip 域名
这样当请求域名时则转发到虚拟机
2、在nginx挂载目录下有一个conf.d文件,nginx会读取这下面所有的配置文件,创建一个mall.conf为商城服务做配置,这里转发请求到网关

server {
listen 80;
server_name 域名;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/log/host.access.log main;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_pass http://网关中配置的名字;
}
}
3、修改Nginx的nginx.conf,代理到windos下88端口(网关服务)
upstream mall{
server 192.168.175.1:88;
}
4、网关配置
#nginx 要放最后
- id: mall_host_route
uri: lb://produc服务名
predicates:
- Host=**.网关中配置的名字
监听nginx转发来的请求 再转发到商城服务