如何在阿里云上搭建Redis高可用集群
如何在阿里云上搭建Redis高可用集群。
搭建Redis-Cluster
需知
需要搭建 6 台 redis 服务器。搭建伪集群。
需要 搭建6 个 redis 实例。
需要运行在不同的端口 7001-7006
准备工作
1.安装gcc,Redis 是 c 语言开发的。安装 redis 需要 c 语言的编译环境。如果安装 了gcc,那么此步就省略。
yum install gcc-c++
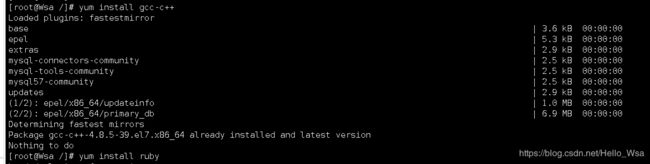
如果出现Nothing to do,说明您已经安装过了,就不需在安装了
2.使用yum命令安装 ruby (我们需要使用ruby脚本来实现集群搭建)
// 安装ruby
yum install ruby
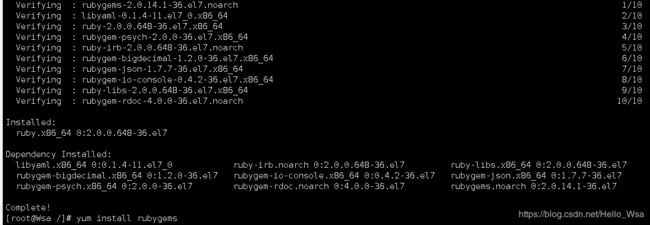
yum install rubygems
// 下载redis
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-5.0.6.tar.gz
//解压redis
tar -zxvf redis-5.0.6.tar.gz
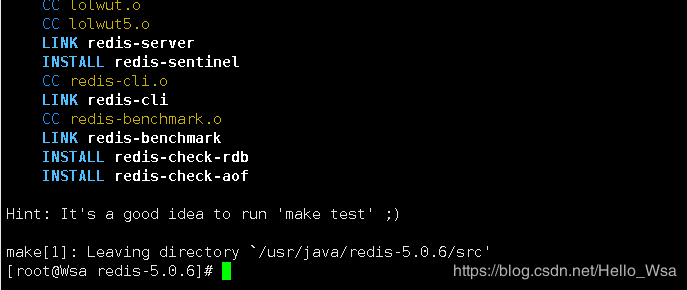
4.进入redis源码文件夹进行编译
// 编译redis源码
make
![]()
看到以下输出结果,表示编译成功
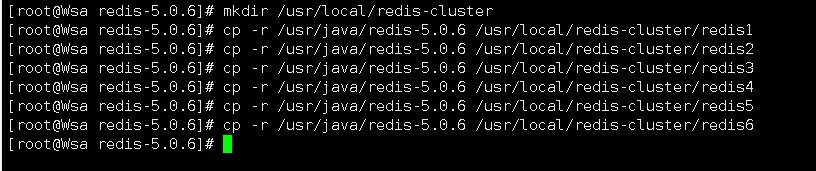
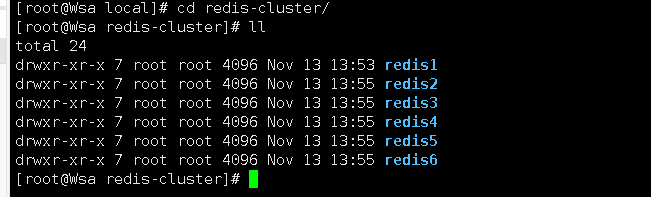
5.创建目录/usr/local/redis-cluster目录, 安装6个redis实例,分别安装在以下目录
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis1
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis2
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis3
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis4
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis5
/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis6
编译redis源码
make install PREFIX=/usr/local/redis-cluster/redis1
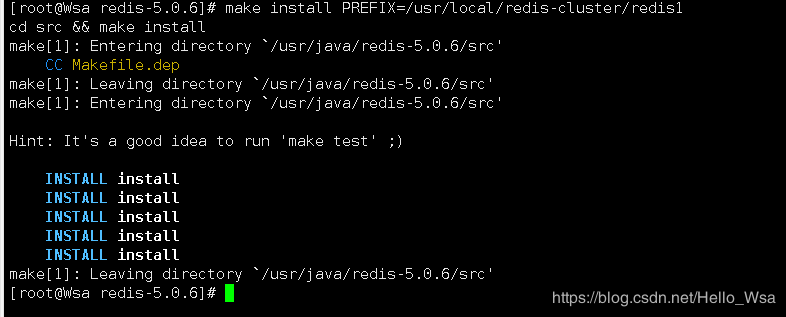
分别再执行一遍
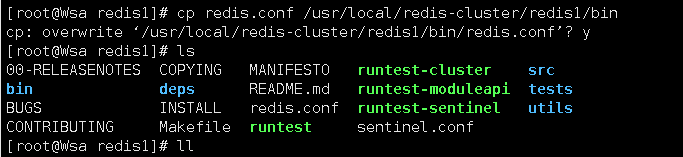
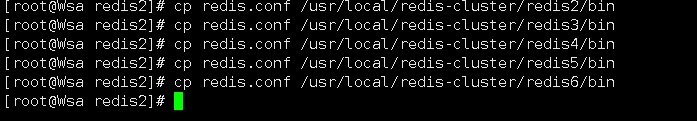
6.复制配置文件 将 /redis-5.0.6/redis.conf 复制到redis下的bin目录下
cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis-cluster/redis1/bin
配置集群
1.用编辑修改每个redis节点的配置文件redis.conf(推荐使用EditPlus3编辑器,方便修改)
把bind注释

修改protected-mode yes 改为protected-mode no

将cluster-enabled yes 前的注释去掉

修改运行端口为7001 (7002 7003 …)(在第92行)
注意:不注释的顶头,注释的后面加空格
3.启动每个redis实例,以第一个实例为例,命令如下
cd /usr/local/redis-cluster/redis1/bin/
./redis-server redis.conf
查看是否全部运行
ps -ef | grep redis

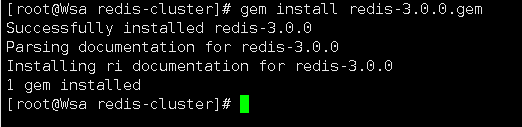
4.上传redis-3.0.0.gem ,安装 ruby用于搭建redis集群的脚本,然后执行下面代码
gem install redis-3.0.0.gem
5.使用 ruby 脚本搭建集群,进入redis源码目录中的src目录 执行下面的命令,然后打yes命令完成
// 进入redis源码目录中的src目录
cd /usr/java/redis-5.0.6/src
//5.0.0以上的版本使用一下命令(C语言)
./redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 公网ip:7001 公网ip:7002 公网ip:7003 公网ip:7004 公网ip:7005 公网ip:7006
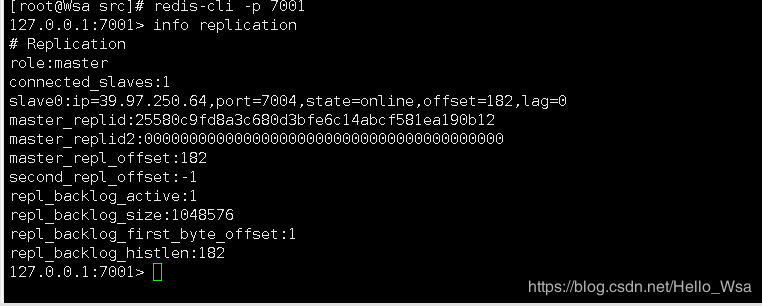
6.最后一步测试 :
例:
//例如进入 端口为7001的redis
redis-cli -p 7001
//查看redis 信息 :
info replication
建立小Demo,连接测试Redis-Cluster
1.在pom.xml配置redis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
2.application.yml中配置
spring:
redis:
cluster:
nodes: 公网ip:7001,公网ip:7002,公网ip:7003,公网ip:7004,公网ip:7005,公网ip:7006
max-redirects: 6
3.测试类中配置
package com.wsa;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@SpringBootTest
class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
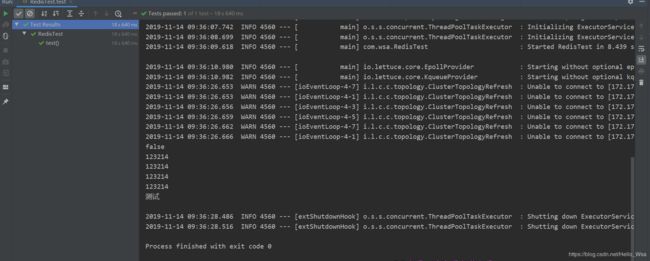
public void test(){
System.out.println(redisTemplate.hasKey("name"));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "123214");
String name = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name2", "123214");
String name2 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name2);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name3", "123214");
String name3 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name3);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name4", "123214");
String name4 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name4);
HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hashOperations.put("user", "test", "测试");
System.out.println(hashOperations.get("user", "test"));
ArrayList