基于SVM的图像二分类算法
本实验是用的python代码实现图像的二分类问题,我是在eclipse中搭建python环境。首先需要读入训练数据,代码如下:
X = []
Y = []
for i in range(0, 2):
#遍历文件夹,读取图片
for f in os.listdir("G:/Download_Data_bishe/leaf_data/pepper_bellSmall/%s" % i):
#打开一张图片并灰度化
Images = cv2.imread("G:/Download_Data_bishe/leaf_data/pepper_bellSmall/%s/%s" % (i, f))
image=cv2.resize(Images,(256,256),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
hist = cv2.calcHist([image], [0,1], None, [256,256], [0.0,255.0,0.0,255.0])
X.append(((hist/255).flatten()))
Y.append(i)
X = np.array(X)
Y = np.array(Y)然后调用自动调参函数GridSearchCV(网格搜索)对SVC()中的几个重要参数进行调参,注意,GridSearchCV函数要求的数据集很小,否则调参时间会很长,甚至调不出来,具体代码如下:
#自动调参函数
tuned_parameters = [{'kernel': ['rbf'], 'gamma': [1e-3, 1e-4],
'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]},
{'kernel': ['linear'], 'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]}]
scores = ['precision', 'recall']
for score in scores:
print("# Tuning hyper-parameters for %s" % score)
print()
# 调用 GridSearchCV,将 SVC(), tuned_parameters, cv=5, 还有 scoring 传递进去,
clf = ms.GridSearchCV(svm.SVC(), tuned_parameters, cv=10,
scoring='%s_macro' % score) #cv为迭代次数。#基于交叉验证的网格搜索,cv:确定交叉验证拆分策略。
# 用训练集训练这个学习器 clf
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Best parameters set found on development set:")
print()
# 再调用 clf.best_params_ 就能直接得到最好的参数搭配结果
print(clf.best_params_)
print()
print("Grid scores on development set:")
print()
means = clf.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
stds = clf.cv_results_['std_test_score']
# 看一下具体的参数间不同数值的组合后得到的分数是多少
for mean, std, params in zip(means, stds, clf.cv_results_['params']):
print("%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r"
% (mean, std * 2, params))
print()
print("Detailed classification report:")
print()
print("The model is trained on the full development set.")
print("The scores are computed on the full evaluation set.")
print()
y_true, y_pred = y_test, clf.predict(X_test)
# 打印在测试集上的预测结果与真实值的分数
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))
print()以上代码可以得出最优的参数组合,然后就是训练模型了,我用的是sklearn包中封装好的SVC()算法,利用了10折交叉检验和ROC曲线来评价模型,代码如下:
#交叉验证+roc曲线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
#交叉验证
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10) #导入该模型,后面将数据划分6份
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=0.0001,C=1000, probability=True,random_state=0) # SVC模型 可以换作AdaBoost模型试试
# 画平均ROC曲线的两个参数
mean_tpr = 0.0 # 用来记录画平均ROC曲线的信息
mean_fpr = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
cnt = 0
for i, (train, test) in enumerate(cv.split(X,Y)): #利用模型划分数据集和目标变量 为一一对应的下标
cnt +=1
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[train], Y[train]).predict_proba(X[test]) # 训练模型后预测每条样本得到两种结果的概率
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(Y[test], probas_[:, 1]) # 该函数得到伪正例、真正例、阈值,这里只使用前两个
mean_tpr += np.interp(mean_fpr, fpr, tpr) # 插值函数 interp(x坐标,每次x增加距离,y坐标) 累计每次循环的总值后面求平均值
mean_tpr[0] = 0.0 # 将第一个真正例=0 以0为起点
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr) # 求auc面积
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lw=1, label='ROC fold {0:.2f} (area = {1:.2f})'.format(i, roc_auc)) # 画出当前分割数据的ROC曲线
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], '--', color=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), label='Luck') # 画对角线
mean_tpr /= cnt # 求数组的平均值
mean_tpr[-1] = 1.0 # 坐标最后一个点为(1,1) 以1为终点
mean_auc = auc(mean_fpr, mean_tpr)
plt.plot(mean_fpr, mean_tpr, 'k--',label='Mean ROC (area = {0:.2f})'.format(mean_auc), lw=2)
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05]) # 设置x、y轴的上下限,设置宽一点,以免和边缘重合,可以更好的观察图像的整体
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') # 可以使用中文,但需要导入一些库即字体
plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic example')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()最后,如果想要将训练好的模型保存下来,可以用以下代码:
#保存模型
from sklearn.externals import joblib
os.chdir("G:/Download_Data_bishe/save_model")
joblib.dump(classifier,"train_model.m")
其实我还是很疑惑10折交叉检验到底是用来评价模型的还是用来选择最优模型的???
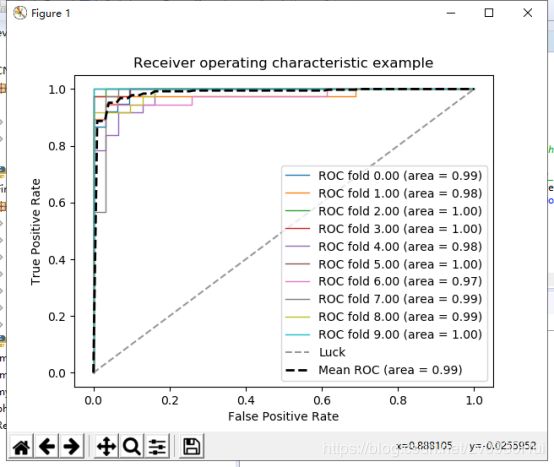
最后,放一张结果图
SVM的识别效果还是可以的,不过也可能我的数据集不大的原因。
完整代码如下:
#SVM算法
import datetime
starttime = datetime.datetime.now()
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
X = []
Y = []
for i in range(0, 2):
#遍历文件夹,读取图片
for f in os.listdir("G:/Download_Data_bishe/leaf_data/pepper_bellSmall/%s" % i):
#打开一张图片并灰度化
Images = cv2.imread("G:/Download_Data_bishe/leaf_data/pepper_bellSmall/%s/%s" % (i, f))
image=cv2.resize(Images,(256,256),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
hist = cv2.calcHist([image], [0,1], None, [256,256], [0.0,255.0,0.0,255.0])
X.append(((hist/255).flatten()))
Y.append(i)
X = np.array(X)
Y = np.array(Y)
#切分训练集和测试集
#X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
#随机率为100%选取其中的30%作为测试集
#交叉验证+roc曲线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
#交叉验证
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10) #导入该模型,后面将数据划分6份
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=0.0001,C=1000, probability=True,random_state=0) # SVC模型 可以换作AdaBoost模型试试
# 画平均ROC曲线的两个参数
mean_tpr = 0.0 # 用来记录画平均ROC曲线的信息
mean_fpr = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
cnt = 0
for i, (train, test) in enumerate(cv.split(X,Y)): #利用模型划分数据集和目标变量 为一一对应的下标
cnt +=1
probas_ = classifier.fit(X[train], Y[train]).predict_proba(X[test]) # 训练模型后预测每条样本得到两种结果的概率
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(Y[test], probas_[:, 1]) # 该函数得到伪正例、真正例、阈值,这里只使用前两个
mean_tpr += np.interp(mean_fpr, fpr, tpr) # 插值函数 interp(x坐标,每次x增加距离,y坐标) 累计每次循环的总值后面求平均值
mean_tpr[0] = 0.0 # 将第一个真正例=0 以0为起点
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr) # 求auc面积
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, lw=1, label='ROC fold {0:.2f} (area = {1:.2f})'.format(i, roc_auc)) # 画出当前分割数据的ROC曲线
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], '--', color=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), label='Luck') # 画对角线
mean_tpr /= cnt # 求数组的平均值
mean_tpr[-1] = 1.0 # 坐标最后一个点为(1,1) 以1为终点
mean_auc = auc(mean_fpr, mean_tpr)
plt.plot(mean_fpr, mean_tpr, 'k--',label='Mean ROC (area = {0:.2f})'.format(mean_auc), lw=2)
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05]) # 设置x、y轴的上下限,设置宽一点,以免和边缘重合,可以更好的观察图像的整体
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') # 可以使用中文,但需要导入一些库即字体
plt.title('Receiver operating characteristic example')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
#保存模型
from sklearn.externals import joblib
os.chdir("G:/Download_Data_bishe/save_model")
joblib.dump(classifier,"train_model.m")
# #只有交叉验证
# clf = SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=0.001,C=100)
# scores = cross_val_score(clf, X , Y , cv=5) #cv为迭代次数。
# print(scores) # 打印输出每次迭代的度量值(准确度)
# print(scores.mean())
# print()
#普通的一次性模型训练预测
#clf = SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=0.001,C=100)
# clf.fit(X_train, y_train)#训练
# predictions0 = clf.predict(X_test)
# #predictions0=pred_test_y
# print(confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions0))
# print (classification_report(y_test, predictions0))
# endtime = datetime.datetime.now()
# print (endtime - starttime)
# #自动调参函数
# tuned_parameters = [{'kernel': ['rbf'], 'gamma': [1e-3, 1e-4],
# 'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]},
# {'kernel': ['linear'], 'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]}]
# scores = ['precision', 'recall']
# for score in scores:
# print("# Tuning hyper-parameters for %s" % score)
# print()
#
# # 调用 GridSearchCV,将 SVC(), tuned_parameters, cv=5, 还有 scoring 传递进去,
# clf = ms.GridSearchCV(svm.SVC(), tuned_parameters, cv=10,
# scoring='%s_macro' % score) #cv为迭代次数。#基于交叉验证的网格搜索,cv:确定交叉验证拆分策略。
# # 用训练集训练这个学习器 clf
# clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
#
# print("Best parameters set found on development set:")
# print()
#
# # 再调用 clf.best_params_ 就能直接得到最好的参数搭配结果
# print(clf.best_params_)
#
# print()
# print("Grid scores on development set:")
# print()
# means = clf.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
# stds = clf.cv_results_['std_test_score']
#
# # 看一下具体的参数间不同数值的组合后得到的分数是多少
# for mean, std, params in zip(means, stds, clf.cv_results_['params']):
# print("%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r"
# % (mean, std * 2, params))
#
# print()
#
# print("Detailed classification report:")
# print()
# print("The model is trained on the full development set.")
# print("The scores are computed on the full evaluation set.")
# print()
# y_true, y_pred = y_test, clf.predict(X_test)
#
# # 打印在测试集上的预测结果与真实值的分数
# print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))
#
# print()