Linux AXI Ethernet driver
Created by Confluence Wiki Admin
Last updated Nov 06, 2019 by Radhey Shyam Pandey
Axi Ethernet Linux driver for Microblaze and Zynq and Zynq Ultrascale+ MPSoC
Introduction
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- HW IP features
- AXI 1G/2.5G Ethernet Subsystem (PG138)
- 10 Gigabit Ethernet subsystem (PG157)
- 10G/25G Ethernet Subsystem (PG210)
- USXGMII Ethernet Subsystem (PG251)
- Features supported in the driver
- Missing Features and Known Issues/Limitations in Driver
- Kernel Configuration
- Device-tree
- Soft Ethernet MAC(1G, legacy 10G or 10G/25G MAC) Configured with MCDMA
- Related device tree information
- IEEE 1588 Support
- Performance
- 1G Ethernet with AXIDMA
- 10G Ethernet with AXIMCDMA
- Diagnostic and Protocol Tests
- Stress Test
- Performance Test
- 1588 Testing
- Mainline status
- Change Log
- Related Links
This page gives an overview of Axi Ethernet Linux driver which is available as part of the Linux distribution.Paths, files, links and documentation on this page are given relative to the Linux kernel source tree.
HW IP features
AXI 1G/2.5G Ethernet Subsystem (PG138)
- Support for MII, GMII, RGMII, SGMII, and 1000BASE-X PHY interfaces
- Support for 1000BASE-X and SGMII over select Input/Output (I/O) low voltage differential signaling (LVDS)
- Support for pause frames for flow control
- Media Independent Interface Management
- Ethernet Audio Video Bridging (AVB) support
- AXI4-Stream transmit/receive interface
- Support for 2.5G Ethernet
- IEEE Standard 1588 Support
- AXI4-Lite register interface
10 Gigabit Ethernet subsystem (PG157)
- Designed to 10 Gigabit Ethernet specification IEEE Standard 802.3-2012
- AXI4-Stream protocol support on client TX and RX interfaces
- Configured and monitored through an optional AXI4-Lite Management Data interface or using status and configuration vectors
- Supports 10GBASE-SR, -LR and -ER optical links in Zynq-7000, UltraScale™, Virtex-7, and Kintex-7 devices (LAN mode only)
- Supports 10GBASE-KR backplane links including Auto-Negotiation (AN), Training and Forward Error Correction (FEC)
- Supports Deficit Idle Count
- Comprehensive statistics gathering
- Supports 802.3 and 802.1Qbb flow control
- Supports VLAN and jumbo frames
- Custom Preamble mode
- Independent TX and RX Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) frame length
- Supports high accuracy IEEE Standard 1588-2008 1-step and 2-step timestamping on a 10GBASE-R network interface
10G/25G Ethernet Subsystem (PG210)
- Designed to the Ethernet requirements for 10/25 Gb/s operation specified by IEEE 802.3 Clause 49, IEEE 802.3by, and the 25G Ethernet Consortium
- Includes complete Ethernet MAC and PCS/PMA functions or standalone PCS/PMA for 25Gb/s operation
- Includes complete Ethernet MAC and PCS/PMA functions, standalone MAC or standalone PCS/PMA for 10 Gb/s operation
- Simple packet-oriented user interface
- Comprehensive statistics gathering
- Status signals for all major functional indicators
- BASE-R PCS sublayer operating at 10.3125Gb/s or 25.78125Gb/s
- Optional clause 74 BASE-KR FEC sublayer
- Optional Auto-Negotiation
- Optional clause 108 25G Reed-Solomon Forward Error Correction (RS-FEC) sublayer
- Custom Preamble mode
- Optional IEEE 1588 1-step and 2-step timestamping
- Runtime switchable between 10G and 25G
USXGMII Ethernet Subsystem (PG251)
- Designed to meet the USXGMII specification EDCS-1467841 revision 1.4
- Supports 10M, 100M, 1G, 2.5G, 5G, or 10GE data rates over a 10.3125 Gb/s link
- Both media access control (MAC) and PCS/PMA functions are included
- Code replication/removal of lower rates onto the 10GE link
- Rate adaption onto user clock domain
- Low data path latency
- 32-bit AXI4-Stream interface for datapath
- Optional AXI4-Lite register interface
- Support for 802.3x and priority-based pause operation
- Detailed statistics gathering
- Support for custom preambles
- Supports deficit idle count (DIC)
Features supported in the driver
- Support ethernet IPs- AXI 1G/2.5G Ethernet subsystem (PG138), 10G Ethernet subsystem(PG157), 10G/25G Ethernet Subsystem(PG210) and USXGMII(PG251).
- IEEE 1588 Support for 1G and legacy 10G MAC (PG157) and 10G/25G MAC (PG210)
- Speed support for 10/100/1000 Mbps for 1G MAC
- 10G Base-R support for Legacy 10G MAC(PG157) and 10G/25G MAC (PG210)
- Support for GMII/RGMII/SGMII/1000Base-X Phy Configurations
- Supports Independent 4K, 8K, 16K, or 32KB TX and RX frame buffer memory
- Support for common ethtool queries.
- NAPI support.
- Full/Partial Checksum offload support
- Support for Jumbo Frames
- Supports AXI DMA and AXI MCDMA dma configuration.
- Multi-queue support
Missing Features and Known Issues/Limitations in Driver
- The driver assumes that Axi Ethernet IP is connected to the DMA at the hardware level.
- The driver doesn't use dma engine framework and contains DMA programming sequence i.e doesn't use separate DMA driver. Hence compatibility string of axidma node (DTS) is set to a dummy device-tree property compatible = "xlnx,eth-dma";
- The driver doesn't support software time-stamping. It supports only hardware time-stamping.
- No support for fixed-link.
- For 1588 testing the Current driver assumes that AXI Stream FIFO is connected to the MAC TX Time stamp Stream interface at the design level.
- 10G/25G and USXGMII configurations do not support dynamic link status/change in the background as there is no external PHY using PHY framework.
- Pause frame solution is not supported and hence there could be RX overruns errors in bidirectional throughput.
- The driver supports MCDMA using kernel config i.e CONFIG_AXIENET_HAS_MCDMA option. So in multi-instance scenario driver will only support a single DMA type i.e 1G + MCDMA and 10G + MCDMA.
Kernel Configuration
The following config options should be enabled in order to build the Axi Ethernet driver
CONFIG_ETHERNET
CONFIG_NET_VENDOR_XILINX
CONFIG_XILINX_AXI_EMAC
CONFIG_AXIENET_HAS_MCDMA (Select this option In the design if Axi Ethernet is configured with Axi MCDMA)
CONFIG_XILINX_PHY (For testing SGMII/1000Base-x Configuration with PCS/PMA Core)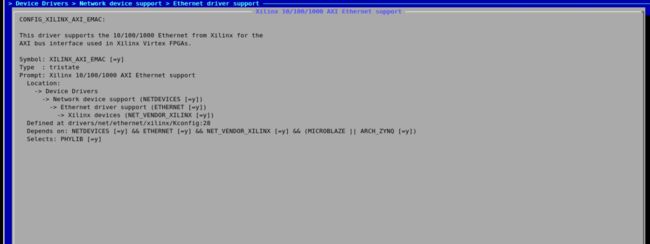
Device-tree
For more details on phy bindings please refer "Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/phy.txt"
|
|
Soft Ethernet MAC(1G, legacy 10G or 10G/25G MAC) Configured with MCDMA
When Axi Ethernet (10G/25G MAC) configured with MCDMA device-tree node will be like below
|
|
When Soft Ethernet MAC configured with MCDMA, The driver supports several features of the MCDMA-
- The driver supports random Queue/Channel selection.
Assume in vivado design MCDMA is configured for 16 channels and user don't want Linux driver to use all the 16 channels.
Below example, pl.dtsi ( AXI ethernet node) marks channel 2, 5 and 10 to be used by Linux driver.
xlnx,num-queues = <0x3>;
xlnx,channel-ids = "2","5","10";
- The driver supports channel observer feature through sysfs. This custom feature is useful in multi-core (Observer) system where MCDMA is a shared resource for all cores. MCDMA IP supports a maximum of six cores and 16 Channels can be distributed across each core as a static configuration. The Channel Observer is available for each group and provides the status about the channels in a group being serviced.
- The driver supports per channel weight configuration through sysfs. This custom feature specifies the channel weight i.e number of packets to be sent in one iteration.
-
The driver supports Linux multiqueue networking. It uses the alloc_etherdev_mq() function to allocate the subqueues for the device.
The userspace command 'tc,' part of the iproute2 package, is used to configure qdiscs. To add the MULTIQ qdisc assuming the device is called eth0, run the following command:
# tc qdisc add dev eth0 root handle 1: multiq
The qdisc will allocate the number of bands to equal the number of queues that the device reports, and bring the qdisc online.
Assuming eth0 has 4 Tx queues, the band mapping would look like:
band 0 => queue 0
band 1 => queue 1
band 2 => queue 2
band 3 => queue 3
The behavior of tc filters remains the same. However, a new tc action, skbedit, has been added.
Assuming we want to route all traffic to a specific host, for example 192.168.0.3, through a specific queue we could use this action and establish a filter such as:
# tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1: protocol ip prio 1 u32 match ip dst 192.168.0.3 action skbedit queue_mapping 3
For details refer Linux kernel Documentation/networking/multiqueue.txt
To support USXGMII + MCDMA, use above devicetree as reference and select:
xlnx,phy-type = <0x7>;
Related device tree information
For PHY related DT information, refer to
https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/phy.txt
When selecting phy specific settings, make sure to mention interface type, speed (if limited/fixed) and phy address properties.
PHY/Converter devices that may be used with this MAC:
-> Xilinx GMII2RGMII converter (https://github.com/Xilinx/linux-xlnx/blob/master/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/xilinx_gmii2rgmii.txt)
-> Xilinx PCS PMA PHY
IEEE 1588 Support
The Existing Axi Ethernet driver in the Xilinx git hub supports 1588 for 1G MAC and legacy 10G MAC and 10G/25G MAC
It does timestamp at the MAC level. 1588 is supported in 7-series and Zynq.
The Current driver assumes that AXI Stream FIFO is connected to the MAC TX Time stamp Stream interface at the design level.
Note:
In order to test the hardware platform, a 1588 timestamp capable timer is required at the h/w level.
Prerequisite for 1588 testing:
Need to enable XILINX_AXI_EMAC_HWTSTAMP in the kernel config which does the timestamping at the MAC level (Tx/Rx)
Users should write their own timer driver for time stamping which does time adjustment/ freq adjustment.
For testing 1588 please refer to Testing tools section below.
1588 Device-tree Example Node
|
|
Performance
These benchmark performance numbers were obtained by connecting Xilinx boards to Linux PCs/server machines (Ubuntu/Red Hat Enterprise).
The tools used are netperf or iperf (Refer to tool information below).
Performance benchmark numbers mentioned in below tables are for reference and dependent on multiple factors i.e setup , vivado design configuration etc.
NOTE: CPU utilization reported in below performance tables is an aggregate of all CPU's. i.e on ZynqMP platform, it reports combined utilization of all four A53 cores.
1G Ethernet with AXIDMA
Kernel version: 4.19AXI 1G/2.5G Ethernet Subsystem : TX and RX full checksum offload enabled.
ZynqMP
Board: ZCU102 board (production silicon) + SFP Module
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP (Mbps) | |||||||
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 940 |
19.2 |
940 |
58.4 |
961 |
15.7 |
961 |
31.8 |
| 8192 | 988 |
9.0 |
988 |
17.4 |
754 |
3.3 |
980 |
15.5 |
Zynq
Board: ZC706 board + SFP Module
| TCP (Mbps) | UDP (Mbps) | |||||||
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 824 |
70.7 |
651 |
89.5 |
583 |
54.4 |
565 |
66.2 |
| 8192 | 988 |
45.8 |
818 |
55.3 |
737 |
33.6 |
876 |
85.8 |
10G Ethernet with AXIMCDMA
Kernel version: 4.19
ZynqMP
Board: ZCU102 board (production silicon) + SFP Module
| TCP (Gbps) | UDP (Gbps) | |||||||
| MTU | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) | TX | CPU(%) | RX | CPU(%) |
| 1500 | 2.9 | 70.48 | 1.7 | 37.54 | 2.9 | 99.9 | 2.05 | 70.04 |
| 9000 | 5.0 | 66.2 | 4.07 | 53.9 | 7.53 | 87.5 | 5.33 | 64.7 |
NOTE: In this design 1588 is not enabled.
Setup Details
Host setup: Dell System Precision Tower 7910 (0619)
Iperf: iperf 3-CURRENT (cJSON 1.5.2)
OS : Linux xhdpunnaia40 3.13.0-147-generic #196-Ubuntu SMP Wed May 2 15:51:34 UTC 2018 x86_64
NIC (10G Solarflare's SFN6322F Dual-Port 10GbE SFP+ Adapter) : Default
Performance benchmarking
Pre-requisites:
- Set Ethernet MCDMA TX interrupt affinity to core-1
root@10g-mcdma-no1588-build:~# echo 2 > /proc/irq/xx/smp_affinity
- Run iperf servers on ZynqMP (core2 and core3)
root@10g-mcdma-no1588-build:~# taskset -c 2 iperf3 -s -p 5101 &
root@10g-mcdma-no1588-build:~# taskset -c 3 iperf3 -s -p 5102 &
- CPU Utilization reporting
root@10g-mcdma-no1588-build:~# ./mpstat -P ALL 1 50
- Run iperf servers on the remote host
server:~# iperf3 -s -p 5101 & ; iperf3 -s -p 5102 & ; iperf3 -s -p 5103 & ; iperf3 -s -p 5104 &
Test Procedure
Diagnostic and Protocol Tests
PING
This utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol(IP) network and to measure the round trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer
How to Run
ping
Telnet
telnet
Pkt Generator
Please refer the below link for how to run and various options
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/pktgen.txt
Stress Test
Iperf with option -d
Run iperf in dual testing mode. This will cause the server to connect back to the client on the port specified in the -L option (or defaults to the port the client connected to the server on). This is done immediately therefore running the tests simultaneously.
./iperf -c
Ping flood test
Users can send hundred or more packets per second using -f option. It prints a ‘.’ when a packet is sent, and a backspace is printed when a packet is received
|
|
Performance Test
Netperf
More information please refer to the below link
http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
How to Run
Server:
netserver
Client:
taskset 2 ./netperf -H
taskset 2 ./netperf -H
Iperf
More information please refer to the below link
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iperf
How to Run
Server:
./iperf -s -u
./iperf -s
Client:
./iperf -c
./iperf -c
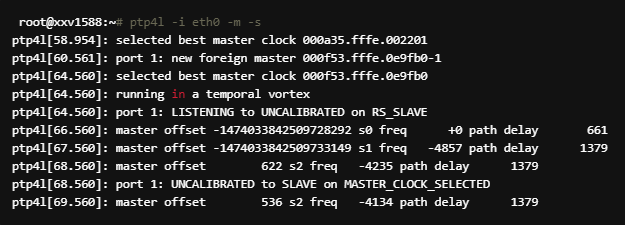
1588 Testing
ptp4l implements the PTP boundary clock and ordinary clock. When hardware time stamping is enabled, ptp4l synchronizes the PTP hardware clock to the master clock. With software time stamping, it synchronizes the system clock to the master clock. phc2sys is needed only with hardware time stamping to synchronize the system clock to the PTP hardware clock on the network interface card (NIC).
Build Instructions for ptp4l application
- Get the source
git clone http://git.code.sf.net/p/linuxptp/code linuxptp
- Set the CROSS_COMPILE environment variable arm toolchain
- Install the kernel headers
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/kbuild/headers_install.txt
- Include the headers path in makefile
INC = -I/proj/epdsw/punnaiah/git/test/ethernet/1588/header/include
CFLAGS = -Wall $(VER) $(incdefs) $(DEBUG) $(INC) $(EXTRA_CFLAGS)
- run make
Execution steps
In order to perform master-slave sync, run the following:
Master (linux server) : ptp4l -i < interface name> -m
Slave (xilinx board) : ptp4l -i
NOTE: If intended before synchronization phc2sys -s
Synchronization is stabilized in a few secs.
Mainline status
The current Axi Ethernet driver is currently in sync with mainline except for the following
- SGMII/1000Base-x support
- NAPI Support
- Support for 1588
- Support for legacy 10G MAC
- Support for 1G MAC Non-processor Mode
- Support for 10G/25G MAC with 1588
- Support for 2.5G MAC with 1588
- Support for Axi Ethernet with AXI MCDMA Configuration
- Support for USXGMII IP.
Change Log
2019.2
- Regression fixes i.e crash in axienet_recv , kernel bug in ndo_open and 1588.
- Enhance error and debug reporting.
Commit IDs:
be66caf net: xilinx: axiethernet: Add error reporting for DMA probe
5917934 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Remove clk_init error message for probe defer
1076feb net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix kernel bug in ndo_open
fb9853e net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix crash in axienet_recv
3aecd4f net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix xxv mac short frame handling
7069a2f net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fixed dev_info message
725b6e3 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Add debug messages for TX timestamp
8f09da4 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix xxv mac tx timestamp
9c0e07f net: xilinx: axiethernet: In axienet_device_reset add missing txts fifo reset
2019.1
- Fix crash in ifconfig down
- Fix axiethernet register description
- Check for queue full in transmit path
- Add 64-bit support
- Extend clocking support
- Fix kernel crash on MII ioctl
- use channel-id for mcdma interrupt names
- Fix netconsole implementation
- Trivial code cleanup
Commit IDs:
33ebfdb net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix crash in ifconfig down
f5b9e58 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix axiethernet register description
e491e78 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Check for queue full in transmit path
0ba2b93 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix code checker warnings
d4c6c09 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Use %pa format specifier for phys_addr_t type
270968c net: xilinx: axiethernet: Add 64-bit support
d139077 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Extend clocking support
fdce589 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix kernel crash on MII ioctl
3f2d6cd net: xilinx: axiethernet: use channel-id for mcdma interrupt names
aaad9c0 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix netconsole implementation
2018.3
- Sync kconfig description.
- In axienet_skb_tstsmp() failure return TX_BUSY.
- Add error output on DMA allocation failed.
- Fix memory leak in axienet bd_free().
- Refactor and split axidma and mcdma programming in separate sources.
- Fix dma name buffer size and skb_free in xmit.
- Format XXV error output.
- Fix compiler warnings.
Commit IDs:
462eb9d net: xilinx: Sync kconfig description
fbb56dc net: xilinx: axiethernet: Move axienet_bd_free() to xilinx_axienet_dma.c
6d3669b net: xilinx: axiethernet: Refactor mcdma_tx/rx_probes
83241b6 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Reordered ethtool status to print all Tx & Rx stats
1fd503a net: xilinx: axiethernet: Have separate num_queues for tx and rx queues
7758b67net: xilinx: axiethernet: In axienet_skb_tstsmp() correct return NETDEV_TX_BUSY on failure
7107ea5 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Add error output on DMA allocation failed
f16fc2d net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix memory leak in axienet bd_free()
528a9db net: xilinx: axiethernet: Split AXIMCDMA implementation in separate file
7169681 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Split AXIDMA implementation in separate file
8e2082e net: xilinx: axiethernet: Correct skb free function
3e1c99a net: xilinx: axiethernet: Correct dma name buffer size
aa644d2 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Format XXV MAC error output
dc81819 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix compiler warnings
127d458 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Fix compiler warnings
2018.2
- None
2018.1
- Fix xxv mac padding issue.
- Add support for USXGMII IP.
- Update interrupt-names property.
- Code cleanup of tx with no DRE.
- Fix remove() bug for XXV no MDIO.
Commit IDs:
10681b8 net: ethernet: xilinx: update interrupt-names property with ip interupt naming convention
fe44c16 net: ethernet: xilinx: Fix xxv mac padding issue - only pad last element.
cea5c97 net: ethernet: xilinx: axienet cleanup of tx with no dre
f5de0cd net: ethernet: xilinx: only teardown mdio when available
9733c76 net: xilinx: axiethernet: Add USXGMII support
2017.4
- None
2017.3
- Added Support for Ethernet MCDMA Configuration
- Added Support for 1588 in buffered mode configuration.
- Fixed race condition in the transmit path
- Fixed race condition in the random queue selection for Ethernet MCDMA configuration
Commit Id's:
2108c9fnet: ethernet: xilinx: Add support for mcdma
2108c9fnet: ethernet: xilinx: Add support for 1588 in buffered mode
2108c9fnet: ethernet: xilinx: Fix race condition in the tx path
2108c9fnet: ethernet: xilinx: Fix race in the random queue selection
2017.2
- None
2017.1
- Added Support for 10G/25G MAC (PG210)
- Added Support for 2.5G MAC
- Fixed issues with the without DRE DMA based design on zynqMP SOC
- Added Clock Support
- Fixed bug in the rx reject interrupt handling.
Commit Id's:
22fa015 net: ethernet : xilinx Add config structure to different axienet macs
e3c3b23 net: ethernet: Add quirk checks in the driver
453042c net: ethernet: Add Support for 10G/25G MAC
4027f19 net: ethernet: Add 1588 support for 10G/25G MAC
f475798 net: ethernet: Fix race condition in the driver for 10G/25G MAC
486d636 net: ethernet: Add support for 2.5G MAC
2857aee net: ethernet: Fix issues in the driver when DRE is not enabled in the h/w
a15cd73 net: ethernet: Add Clock support
9b904af net: ethernet: Fix Bug in rx reject interrupt handling.
2016.4
- None
2016.3
- Fix kernel crash on the 64-bit platform reported while testing 1588 on Zynq UltraScale+ MPSOC.
Commit Id's:
ea9f81c net: ethernet: xilinx: Fix kernel crash on 64-bit platform
Related Links
---> http://www.wiki.xilinx.com/Linux+Drivers
No labels