Spring之AOP基本概念及配置AOP
为什么使用AOP
传统方法
AOP前前奏
首先考虑一个问题,假设我们要设计一个计算器,有如下两个需求: - 在程序运行期间追踪正在放生的活动 - 希望计算器只能处理正数的运算 通常我们会用如下代码进行实现: 定义一个接口:public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("The method add begins with [" + i + "," + j + "]");
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("The method add ends with " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("The method sub begins with [" + i + "," + j + "]");
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("The method sub ends with " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("The method mul begins with [" + i + "," + j + "]");
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("The method mul ends with " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("The method div begins with [" + i + "," + j + "]");
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("The method div ends with " + result);
return result;
}
}传统方法存在的问题
- 代码混乱:越来越多的非业务需求(日志和验证等)加入后, 原有的业务方法急剧膨胀. 每个方法在处理核心逻辑的同时还必须兼顾其他多个关注点. - 代码分散: 以日志需求为例, 只是为了满足这个单一需求, 就不得不在多个模块(方法)里多次重复相同的日志代码. 如果日志需求发生变化, 必须修改所有模块.使用动态代理解决上述问题
- 代理设计模式的原理: 使用一个代理将对象包装起来, 然后用该代理对象取代原始对象. 任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理. 代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上.
/**
* 动态代理
* @author Megustas
*
*/
public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy {
//要代理的对象
private ArithmeticCalculator target;
public ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
//返回代理对象
public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy(){
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = null;
//代理对象由哪一个类加载器加载
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
//代理对象的类型,即其中有哪些方法
Class [] interfaces = new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculator.class};
//当调用代理对象其中的方法时,该执行的代码
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* proxy:正在返回的那个代理对象, 一般情况下,在invoke方法中不使用该对象
* method: 正在被调用的方法
* args: 调用方法传入的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
//打印日志,此种方式对日志进行维护和更改就十分简洁
System.out.println("[before] The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args));
//调用目标方法
Object result = null;
try {
//前置通知
//invoke:通过函数名反射相应的函数
result = method.invoke(target, args);
//返回通知, 可以访问到方法的返回值
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//异常通知, 可以访问到方法出现的异常
}
//后置通知. 因为方法可以能会出异常, 所以访问不到方法的返回值
//打印日志
System.out.println("[after] The method ends with " + result);
return result;
}
};
/**
* loader: 代理对象使用的类加载器。
* interfaces: 指定代理对象的类型. 即代理代理对象中可以有哪些方法.
* h: 当具体调用代理对象的方法时, 应该如何进行响应, 实际上就是调用 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 方法
* 以下是代理对象,不同于基本对象通过new生成
*/
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}但是写动态代理,难度却不小,不是很容易掌握。
AOP简介
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程): 是一种新的方法论, 是对传统 OOP(Object-Oriented Programming, 面向对象编程) 的补充.
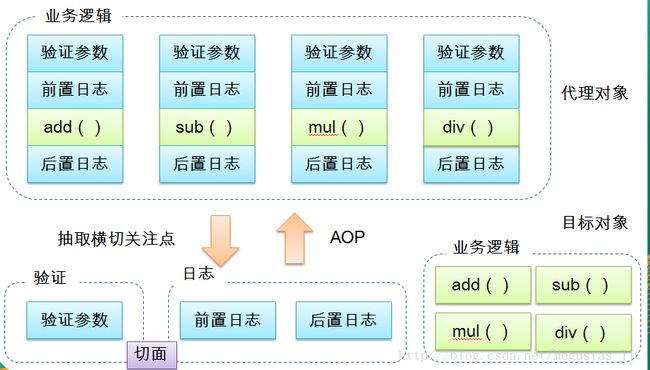
- AOP 的主要编程对象是切面(aspect), 而切面模块化横切关注点(即对象里放入的是一个个横切关注点的方法).
- 在应用 AOP 编程时, 仍然需要定义公共功能, 但可以明确的定义这个功能在哪里, 以什么方式应用, 并且不必修改受影响的类. 这样一来横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里.
AOP 的好处: 每个事物逻辑位于一个位置, 代码不分散, 便于维护和升级 业务模块更简洁, 只包含核心业务代码.
这里的一个个需求,例如验证参数、日志功能等都是横切关注点,我们将横切关注点抽取出来
- 通过切面和业务逻辑的结合实现目标功能,即为面向切片编程。
AOP术语
- 切面(Aspect): 横切关注点(一个个具体需求)(跨越应用程序多个模块的功能)被模块化的特殊对象
- 通知(Advice): 切面必须要完成的工作(比如说切面需要完成验证,即切面中的每一个方法)
- 目标(Target): 被通知的对象(即业务逻辑)
- 代理(Proxy): 向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象(将切面和目标混合)
- 连接点(Joinpoint):程序执行的某个特定位置:如类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法抛出异常后等。连接点由两个信息确定:方法表示的程序执行点;相对点表示的方位。例如 ArithmethicCalculator#add() 方法执行前的连接点,执行点为 ArithmethicCalculator#add(); 方位为该方法执行前的位置
- 切点(pointcut):每个类都拥有多个连接点:例如 ArithmethicCalculator 的所有方法实际上都是连接点,即连接点是程序类中客观存在的事务。AOP通过切点定位到特定的连接点。类比:连接点相当于数据库中的记录,切点相当于查询条件。切点和连接点不是一对一的关系,一个切点匹配多个连接点,切点通过 org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
AOP配置
用注解方式声明切面
首先介绍一个AOP框架,AspectJ,是Java社区里最完整最流行的AOP框架,在Spring2.0以上版本中,可以使用基于AspectJ注解来配置AOP。
要在 Spring 应用中使用 AspectJ 注解, 必须在 classpath 下包含 AspectJ 类库: aopalliance.jar、aspectj.weaver.jar 和 spring-aspects.jar,即导入包:
com.springsource.net.sf.cglib-2.2.0.jar
com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar
com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar将 aop Schema 添加到
- 要在 Spring IOC 容器中启用 AspectJ 注解支持, 只要在 Bean 配置文件中定义一个空的 XML 元素
- 当 Spring IOC 容器侦测到 Bean 配置文件中的
要在 Spring 中声明 AspectJ 切面, 只需要在 IOC 容器中将切面声明为 Bean 实例. 当在 Spring IOC 容器中初始化 AspectJ 切面之后, Spring IOC 容器就会为那些与 AspectJ 切面相匹配的 Bean 创建代理.在 AspectJ 注解中, 切面只是一个带有 @Aspect 注解的 Java 类. 通知是标注有某种注解的简单的 Java 方法.
AspectJ支持的5种类型的通知注解
@Before: 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
@After: 后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行
@AfterRunning: 返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
@AfterThrowing: 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后
@Around: 环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
/**
* 日志切面
* @author Megustas
*
*/
//把这个类声明为一个切面:首先需要把该类放入到IOC容器中,通过注解@Component、再声明为一个切面,通过注解@Aspect,并且在配置文件中加入配置
//通过Order注解来指定切面的优先级,优先级数字越小代表优先级越高,越先执行
@Order(2)
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
//这个方法在哪些类的哪些方法前执行,通过注解来规定
//声明该方法是一个前置通知,在目标方法开始之前执行,".add"方法说明在add方法之前执行,".*"则表示在包下所有方法之前执行
@Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl.add(int, int))")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
ListBean的配置:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.aop">context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
验证方法:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建 IOC 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2. 从 IOC 容器中获取 bean 实例
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = (ArithmeticCalculator)ctx.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
//3. 调用 bean 的方法
int result1 = arithmeticCalculator.add(3, 6);
System.out.println("result1:" + result1);
//int result2 = arithmeticCalculator.div(1000, 0);//通过异常通知显示
//System.out.println("result2:" + result2);
//4. 关闭容器
ctx.close();
}
}指定切面的优先级及重用切入点
指定切面的优先级
实例可以参照上诉代码的@Order
- 在同一个连接点上应用不止一个切面时, 除非明确指定, 否则它们的优先级是不确定的.
- 切面的优先级可以通过实现 Ordered 接口或利用 @Order 注解指定.
- 实现 Ordered 接口, getOrder() 方法的返回值越小, 优先级越高.
- 若使用 @Order 注解, 序号出现在注解中
@Aspect
@Order(0)
public class CalculaotorValidationAspect{}@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class CalculaotorLoggingAspect{}重用切入点
- 在编写 AspectJ 切面时, 可以直接在通知注解中书写切入点表达式. 但同一个切点表达式可能会在多个通知中重复出现.
- 在 AspectJ 切面中, 可以通过 @Pointcut 注解将一个切入点声明成简单的方法. 切入点的方法体通常是空的, 因为将切入点定义与应用程序逻辑混在一起是不合理的.
- 切入点方法的访问控制符同时也控制着这个切入点的可见性. 如果切入点要在多个切面中共用, 最好将它们集中在一个公共的类中. 在这种情况下, 它们必须被声明为 public. 在引入这个切入点时, 必须将类名也包括在内. 如果类没有与这个切面放在同一个包中, 还必须包含包名.
- 其他通知可以通过方法名称引入该切入点.
(总结就是一句话:将切入点的表达式“封装”为一个方法,通过方法调用来实现)
同类中使用:
/**
* 实现重用切面表达式
* 定义一个方法,用于声明切入点表达式。一般该方法中不需要再填入其他的代码
* 使用@Pointcut来声明切入点表达式
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl.add(int, int))")
public void declareJointPointExpression(){
}
@Before("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void beforeMethod1(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
List在外部类中使用:
//在类的外部使用重用切面表达式,再指定其所在类即可,若不同包下,则再引入包名
@Before("LoggingAspect.declareJointPointExpression()")
public void validateArgs1(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("-->validate: " + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}在外部包使用同理。
用基于XML的配置声明切面
- 除了使用 AspectJ 注解声明切面, Spring 也支持在 Bean 配置文件中声明切面. 这种声明是通过 aop schema 中的 XML 元素完成的.
- 正常情况下, 基于注解的声明要优先于基于 XML 的声明. 通过 AspectJ 注解, 切面可以与 AspectJ 兼容, 而基于 XML 的配置则是 Spring 专有的. 由于 AspectJ 得到越来越多的 AOP 框架支持, 所以以注解风格编写的切面将会有更多重用的机会.
- 在 Bean 配置文件中, 所有的 Spring AOP 配置都必须定义在
- 切面 Bean 必须有一个标示符, 供
- 切入点使用
- 切入点必须定义在 元素下, 或者直接定义在 元素下.
定义在
定义在 - 基于 XML 的 AOP 配置不允许在切入点表达式中用名称引用其他切入点.
- 通知元素需要使用
具体的一个实例如下(注:此处bean代码的实现不再具体列举):
<bean id="arithmeticCalculator" class="com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl">bean>
<bean id="LoggingAspect" class="com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.LoggingAspect">bean>
<bean id="vlidationAspect" class="com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.VlidationAspect">bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="* com.atguigu.spring.aop.impl.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int)" id="pointcut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="LoggingAspect" order="2">
<aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="vlidationAspect" order="1">
<aop:before method="validateArgs" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>