Servlet JSP Tutorial -- 1.15 50 Servlet Interview Questions and Answers
Servlet是Java EE非常重要的主题,所有的 Web 应用程序框架(如Spring和Struts)都建立在它之上。这使得 servlet 面试在面试中成为一个热门话题。
在这里,我提供了一个包含 50 个 servlet 面试问题的列表,其中包括解答大部分与 java 中的 servlet 和 web 应用程序有关的面试问题。
Servlet Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is different between web server and application server?
A web server responsibility is to handler HTTP requests from client browsers and respond with HTML response. A web server understands HTTP language and runs on HTTP protocol.
Apache Web Server is kind of a web server and then we have specific containers that can execute servlets and JSPs known as servlet container, for example Tomcat.
Application Servers provide additional features such as Enterprise JavaBeans support, JMS Messaging support, Transaction Management etc. So we can say that Application server is a web server with additional functionalities to help developers with enterprise applications.
1. Web 服务器和应用服务器的差别是什么?
Web 服务器的职责是处理来自客户端浏览器的 HTTP request,并用 HTML response 进行响应。Web 服务器了解 HTTP 语言并运行在 HTTP 协议之上。
Apache Web Server 是一种 Web 服务器,我们有特定的可以执行 servlet 和 JSP 的容器,就是 servlet 容器,栗如 Tomcat
应用程序服务器提供了额外的功能,栗如 Enterprise JavaBeans 支持, JMS 消息传递支持,事务管理等。所以我们可以说 Application Server 是一个具有附加功能的 Web 服务器,可以帮助开发人员使用企业应用程序。
2. Which HTTP method is non-idempotent?
A HTTP method is said to be idempotent if it returns the same result every time. HTTP methods GET, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, and OPTIONS are idempotent method and we should implement our application to make sure these methods always return same result. HTTP method POST is non-idempotent method and we should use post method when implementing something that changes with every request.
2. 哪个 HTTP 方法是非幂等的?
如果 HTTP 方法每次返回相同的结果,就说它是幂等的。HTTP 方法 GET、PUT、DELETE、HEAD 和 OPTIONS 是幂等方法,我们应该实现我们的应用程序来确保这些方法始终返回相同的结果。HTTP 方法 POST 是非幂等方法,我们应该使用 POST 方法来实现随每个请求而改变的东西。
3. What is the difference between GET and POST method?
- GET is a safe method (idempotent) where POST is non-idempotent method.
- We can send limited data with GET method and it’s sent in the header request URL whereas we can send large amount of data with POST because it’s part of the body.
- GET method is not secure because data is exposed in the URL and we can easily bookmark it and send similar request again, POST is secure because data is sent in request body and we can’t bookmark it.
- GET is the default HTTP method whereas we need to specify method as POST to send request with POST method.
- Hyperlinks in a page uses GET method.
3. GET 和 POST 方法有什么区别
- GET 是一个安全的方法(幂等),POST 是非幂等方法。
- 我们可以使用 GET 方法发送有限的数据,并将其发送到 header request URL 中,而我们可以使用 POST 发送大量数据,因为它是 body 的一部分。
- GET 方法是不安全的,因为数据暴露在 URL 中,我们可以很容易地将它加入书签帮再次发送类似的请求。POST 是安全的,因为数据是在 request body 发送的,我们不能将它加入书签。
- GET 是默认的 HTTP 方法,而我们需要使用 POST 方法指定方法作为 POST 发送请求
- 页面中的超链接使用 GET 方法
4. What is MIME Type?
The “Content-Type” response header is known as MIME Type. Server sends MIME type to client to let them know the kind of data it’s sending. It helps client in rendering the data for user. Some of the mostly used mime types are text/html, text/xml, application/xml etc.
We can use ServletContext getMimeType() method to get the correct MIME type of the file and use it to set the response content type. It’s very useful in downloading file through servlet from server.
4. 什么是 MIME 类型?
“Content-Type”response header 被称为MIME类型。服务器发送MIME类型给客户端,让他们知道它发送的数据的种类。 它帮助客户为用户呈现数据。一些最常用的MIME类型有text/html、text/xml和application/xml等。
我们可以使用ServletContext的getMimeType()方法获取文件的正确的MIME类型,并使用它来 response content 类型。从服务器通过 servlet 下载文件时非常有用。
5. What is a web application and what is it’s directory structure?
Web Applications are modules that run on server to provide both static and dynamic content to the client browser. Apache web server supports PHP and we can create web application using PHP. Java provides web application support through Servlets and JSPs that can run in a servlet container and provide dynamic content to client browser.
Java Web Applications are packaged as Web Archive (WAR) and it has a defined structure like below image.
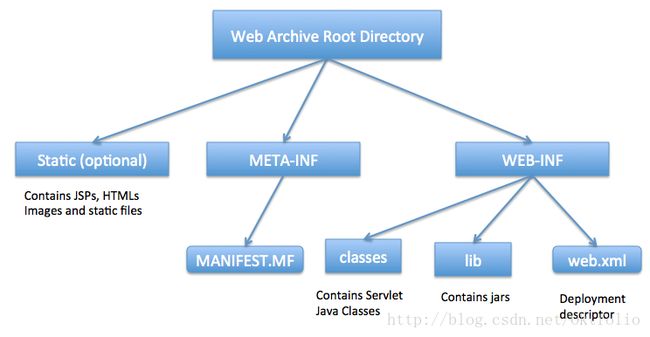
Read more about web applications at Java Web Application.
5. 什么是 Web 应用程序,它的目录结构是什么
Web 应用程序是服务器上用于向客户端提供静态和动态内容的模块。Apache Web 服务器支持 PHP,我们可以使用 PHP 创建 Web 应用程序。Java 通过在 servlet 容器中运行 Servlet 和 JSP 提供 Web 应用程序支持,并向客户端浏览器提供动态内容。
Java Web 应用程序打包为 Web Archive(WAR),并具有如下图所示的定义的结构

在Java Web Application 上阅读更多关于 Web 应用程序的信息。
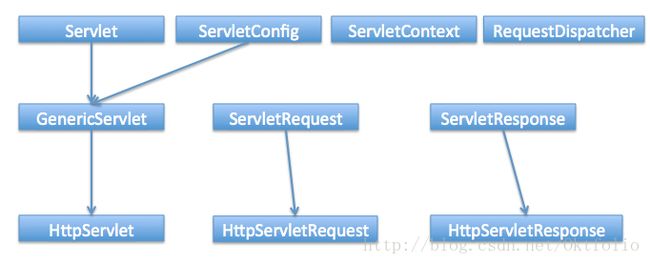
6. What is a servlet?
Java Servlet is server side technologies to extend the capability of web servers by providing support for dynamic response and data persistence.
The javax.servlet and javax.servlet.http packages provide interfaces and classes for writing our own servlets.
All servlets must implement the javax.servlet.Servlet interface, which defines servlet lifecycle methods. When implementing a generic service, we can extend the GenericServlet class provided with the Java Servlet API. The HttpServlet class provides methods, such as doGet() and doPost(), for handling HTTP-specific services.
Most of the times, web applications are accessed using HTTP protocol and thats why we mostly extend HttpServlet class. Servlet API hierarchy is shown in below image.
Read more at Servlet Tutorial.
6. 什么是 Servlet?
Java Servlet 是服务器端技术,通过提供动态响应和护具持久的支持来扩展 Web 服务器的功能。
java.servlet 和 javax.servlet.http 包提供了编写我们自己的 servlet 的接口和类。
所有的 servlet 必须实现 java.servlet.Servlet接口,该接口定义了 servlet 的生命周期方法。在实现通用服务时,我们可以扩展 Java Servlet API 提供的 GenericServlet 类。HttpServlet类提供了用于处理特定 HTTP 服务的方法,如doGet()和doPost()。
大多数情况下,Web 应用程序是使用 HTTP 协议访问的,这就是为什么我们能主要扩展 HttpServlet 类的原因。Servlet API层次结构如下图所示。
阅读更多:Servlet Tutorial.
7. What are the advantages of Servlet over CGI?
Servlet technology was introduced to overcome the shortcomings of CGI technology.
- Servlets provide better performance that CGI in terms of processing time, memory utilization because servlets uses benefits of multithreading and for each request a new thread is created, that is faster than loading creating new Object for each request with CGI.
- Servlets and platform and system independent, the web application developed with Servlet can be run on any standard web container such as Tomcat, JBoss, Glassfish servers and on operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Unix, Solaris, Mac etc.
- Servlets are robust because container takes care of life cycle of servlet and we don’t need to worry about memory leaks, security, garbage collection etc.
- Servlets are maintainable and learning curve is small because all we need to take care is business logic for our application.
7. Servlet 对比 CGI 有什么优势?
引入了 Servlet 技术来克服 CGI 技术的缺点。
- Servlet 在处理时间、内存利用率方面提供了更好的性能,这就是 servlet 使用多线程并为每个请求创建一个新线程的好处,这比使用 CGI 为每个请求创建新对象要快。
- Servlet 于平台和系统无关,使用 Servlet 开发的 Web 应用程序可以运行在任何标准 Web 容器上,如Tomcat、JBoss、Glassfish 服务器以及 Windows、Linux、Unix、Solaris、Mac 等操作系统。
- Servlet 是健壮的,因为容器负责 servlet 的生命周期,沃恩不需要担心内存泄漏、安全性、垃圾回收等。
- Servlet 是可维护的,学习曲线很小,因为我们只需要注意的是我们的应用程序的业务逻辑。
8. What are common tasks performed by Servlet Container?
Servlet containers are also known as web container, for example Tomcat. Some of the important tasks of servlet container are:
Communication Support: Servlet Container provides easy way of communication between web client (Browsers) and the servlets and JSPs. Because of container, we don’t need to build a server socket to listen for any request from web client, parse the request and generate response. All these important and complex tasks are done by container and all we need to focus is on business logic for the applications.Lifecycle and Resource Management: Servlet Container takes care of managing the life cycle of servlet. From the loading of servlets into memory, initializing servlets, invoking servlet methods and to destroy them. Container also provides utility like JNDI for resource pooling and management.Multithreading Support: Container creates new thread for every request to the servlet and provide them request and response objects to process. So servlets are not initialized for each request and saves time and memory.JSP Support: JSPs doesn’t look like normal java classes but every JSP in the application is compiled by container and converted to Servlet and then container manages them like other servlets.Miscellaneous Task: Servlet container manages the resource pool, perform memory optimizations, execute garbage collector, provides security configurations, support for multiple applications, hot deployment and several other tasks behind the scene that makes a developer life easier.
8. Servlet 容器执行的常见任务有那些?
Servlet 容器也被称为 Web 容器,例如Tomcat。一些 servlet 容器的重要任务有:
Communication Support(通信支持):Servlet 容器提供了简单的 Web 客户端(浏览器)与 servlet 和 JSP 之间的通信方式。由于容器的原因,我们不需要构建 server socket(服务器套接字)来监听来自 Web 客户端的请求,解析请求并生成响应。所有这些重要而复杂的任务都是通过容器完成的,我们需要关注的只是应用程序的业务逻辑。Lifecycle and Resource Management(生命周期和资源管理):Servlet Container 负责管理 servlet 的生命周期。从将servlet 加载到内存中,初始化 servlet,调用 servlet 方法并销毁它们。容器也提供像 JNDI 这样的工具来进行资源池和管理。Multithreading Support(多线程支持):Container 为 servlet 的每个请求创建一个新线程,并为它们提供 request 和response 对象进行处理。所以 servlet 不会为每个请求初始化,并节省时间和内存。JSP Support(JSP支持):JSP 看起来不像普通的 Java 类,但应用程序中的每个 JSP 都是由容器编译并转换为 Servlet,然后容器像其他 servlet 一样管理它们。Miscellaneous Task(杂项任务):Servlet 容器管理资源池,执行内存优化,执行垃圾回收器,提供安全配置,支持多个应用程序,热部署和场景后面的几个其他任务,使开发人员生活变得更容易。
9. What is ServletConfig object?
javax.servlet.ServletConfig is used to pass configuration information to Servlet. Every servlet has it’s own ServletConfig object and servlet container is responsible for instantiating this object. We can provide servlet init parameters in web.xml file or through use of WebInitParam annotation. We can use getServletConfig() method to get the ServletConfig object of the servlet.
9. 什么是 ServletConfig 对象?
javax.servlet.ServletConfig被用于将配置信息传递给 Servle。每个 servlet 都有自己的 ServletConfig 对象,servlet 容器负责实例化这个对象。我们可以在web.xml文件中提供 Servlet 初始化参数,也可以使用 WebInitParam 注解。我们可以使用getServletConfig()方法类获取 Servlet 的ServletConfig对象。
10. What is ServletContext object?
javax.servlet.ServletContext interface provides access to web application parameters to the servlet. The ServletContext is unique object and available to all the servlets in the web application. When we want some init parameters to be available to multiple or all of the servlets in the web application, we can use ServletContext object and define parameters in web.xml using ServletContext object via the getServletContext() method of ServletConfig. Servlet containers may also provide context objects that are unique to a group of servlets and which is tied to a specific portion of the URL path namespace of the host.
ServletContext is enhanced in Servlet Specs 3 to introduce methods through which we can programmatically add Listeners and Filters and Servlet to the application. It also provides some utility methods such as getMimeType(), getResourceAsStream() etc.
10. 什么是 ServletContext 对象?
javax.servlet.ServletContext接口提供对 servlet 的 Web 应用程序参数的访问。ServletContext是可用于 Web 应用程序中所有的 servlet 的唯一的对象。当我们想要一些初始化参数可用于 Web 应用程序中的多个或所有 servlet 时,我们可以使用ServletContext对象并使用web.xml中定义参数。我们可以通过ServletConfig的getServletContext()方法获取ServletContext对象。Servlet 容器还提供 context 对象,这些 context 对象对于一组 servlet 时唯一的。并且绑定到主机的 URL 路径名称空间的特定部分。
Servlet Specs 3 中增强了ServletContext,以引入方法,同故宫这些方法我们可以以编程方式将Listener和Filters以及Servlet添加到应用程序中。它还提供了一些实用的方法,如getMimeType()、getResourceAsStream()等。
11. What is difference between ServletConfig and ServletContext?
Some of the differences between ServletConfig and ServletContext are:
ServletConfigis a unique object per servlet whereas ServletContext is a unique object for complete application.ServletConfigis used to provide init parameters to the servlet whereasServletContextis used to provide application level init parameters that all other servlets can use.- We can’t set attributes in
ServletConfigobject whereas we can set attributes inServletContextthat other servlets can use in their implementation.
11. ServletConfig 和 ServletContext 之间的区别是什么?
ServletConfig 和 ServletContext 之间的区别有:
ServletConfig是每个 servlet 的唯一对象。ServletContext是整个应用程序的唯一对象。ServletConfig用于给 servlet 提供 init parameters。ServletContext用于提供应用程序级别的可供所有其他 servlet使用的 init parameters。
12. What is Request Dispatcher?
RequestDispatcher interface is used to forward the request to another resource that can be HTML, JSP or another servlet in same application. We can also use this to include the content of another resource to the response. This interface is used for inter-servlet communication in the same context.
There are two methods defined in this interface:
1. void forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)– forwards the request from a servlet to another resource (servlet, JSP file, or HTML file) on the server.
2. void include(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) – includes the content of a resource (servlet, JSP page, HTML file) in the response.
3. We can get RequestDispatcher in a servlet using ServletContext getRequestDispatcher(String path) method. The path must begin with a / and is interpreted as relative to the current context root.
12. 什么是Request Dispatcher?
RequestDispatcher接口是用于将请求转发到另一个资源的,该资源可以是同一应用程序中的 HTML、JSP 或其他 servlet。我们也可以使用这个来将其他资源的内容包含到 response 中。该接口用于在相同上下文中进行 内部 servlet 通信。
这个接口定义了两个方法:
1. void forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)– 将请求从 servlet 转发到服务器上的另一个资源。
2. void include(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) – 在响应中包含资源(servlet、JSP 页面、HTML 文件)
3. 我们在 servlet 中可以使用ServletContext、getRequestDispatcher(String path)方法来获得RequestDispatcher。该路径必须以“/”开始,并解释为相对于当前上下文跟。
13. What is difference between PrintWriter and ServletOutputStream?
PrintWriter is a character-stream class whereas ServletOutputStream is a byte-stream class. We can use PrintWriter to write character based information such as character array and String to the response whereas we can use ServletOutputStream to write byte array data to the response.
We can use ServletResponse getWriter() to get the PrintWriter instance whereas we can use ServletResponse getOutputStream() method to get the ServletOutputStream object reference.
You can read more about IO in java at Java IO Tutorial.
13. PrintWriter 和 ServletOutputStream 之间的区别?
PrintWriter是字符流类,而ServletOutputStream是字节流类。我们可以使用PrintWriter将基于字符的信息(如字符数组和字符串)写入 response,而我们使用ServletOutputStream将字节数组数据写入 response。
可以使用ServletResponse的getWriter()获取PrintWriter实例。使用ServletResponse的getOutputStream()方法获取ServletOutputStream对象的引用。
你可以在Java IO Tutorial上阅读更多关于 IO 的信息。
14. Can we get PrintWriter and ServletOutputStream both in a servlet?
We can’t get instances of both PrintWriter and ServletOutputStream in a single servlet method, if we invoke both the methods; getWriter() and getOutputStream() on response; we will get java.lang.IllegalStateException at runtime with message as other method has already been called for this response.
14. 我们能在一个 servlet 中获取 PrintWriter 和 ServletOutputStream 吗?
如果我们调用两个方法,不能在一个 servlet 中同时获取PrintWriter和ServletOutputStream的实例;getWriter()和getOutputStream()作为响应;我们将在运行时得到java.lang.IllegalStateException消息,其他方法已经为响应被调用。
15. How can we create deadlock situation in servlet?
We can create deadlock in servlet by making a loop of method invocation, just call doPost() method from doGet() method and doGet() method to doPost() method to create deadlock situation in servlet.
Read more about deadlock in multithreading at Java Deadlock Example.
15. 在 servlet 中我们如何去创建一个死锁状态?
我们可以通过创建一个方法调用的循环来创建 servlet 死锁,只要从doGet()方法调用doPost()方法,doPost()方法调用doGet()方法在 servlet 中创建死锁情况。
在 Java Deadlock Example 中阅读更多有关多线程死锁的信息。
16. What is the use of servlet wrapper classes?
Servlet HTTP API provides two wrapper classes – HttpServletRequestWrapper and HttpServletResponseWrapper. These wrapper classes are provided to help developers with custom implementation of servlet request and response types. We can extend these classes and override only specific methods we need to implement for custom request and response objects. These classes are not used in normal servlet programming.
16. servlet 包装类?
Servlet HTTP API 提供两个包装类 - HttpServletRequestWrapper和HttpServletResponseWrapper。提供这些包装类是为了帮助开发人员定制实现 servlet 请求和响应类型。我们可以扩展这些类并重写我们需要为自定义请求和响应对象实现的特定方法。这些类不用于通常的 servlet 编程。
17.What is SingleThreadModel interface?
SingleThreadModel interface was provided for thread safety and it guarantees that no two threads will execute concurrently in the servlet’s service method. However SingleThreadModel does not solve all thread safety issues. For example, session attributes and static variables can still be accessed by multiple requests on multiple threads at the same time, even when SingleThreadModel servlets are used. Also it takes out all the benefits of multithreading support of servlets, thats why this interface is Deprecated in Servlet 2.4.
17. 什么是 SingleThreadModel 接口?
SingleThreadModel接口是为了线程安全而提供的,它保证 servlet 的服务方法中不会同时执行两个线程。但是SingleThreadModel并不能解决所有的线程安全问题。栗如,即使在使用SingleThreadModelservlet 的时候,会话属性和静态变量依旧可以被多个线程上的多个请求访问。同时它抵消了 servlet 的多线程支持的所有好处,这就是这个接口在 Servlet 2.4 被弃用的原因。
18. Do we need to override service() method?
When servlet container receives client request, it invokes the service() method which in turn invokes the doGet(), doPost() methods based on the HTTP method of request. I don’t see any use case where we would like to override service() method. The whole purpose of service() method is to forward to request to corresponding HTTP method implementations. If we have to do some pre-processing of request, we can always use servlet filters and listeners.
18, 我们需要去重写 service() 方法吗?
当 servlet 容器收到客户端请求时,它会调用service()方法,然后调用基于请求的 HTTP 方法的doGet()、doPost()方法。我没有看到任何我们想要重写service()方法的用例。service()方法的全部用途是转发请求到相应的 HTTP 方法实现。如果我们需要做一些预处理请求,我们可以使用 servlet 过滤器和监听器。
19. Is it good idea to create servlet constructor?
We can define a constructor for servlet but I don’t think its of any use because we won’t be having access to the ServletConfig object until unless servlet is initialized by container. Ideally if we have to initialize any resource for servlet, we should override init() method where we can access servlet init parameters using ServletConfig object.
19. 创建 servlet 构造器是个好主意吗?
我们为 servlet 可以定义一个构造器,但是我不认为它有任何用处,除非 servlet 被容器初始化,否则不能将不能访问ServletConfig对象。理想情况下,如果我们必须初始化 servlet 的任何资源,我们应该重写init()方法,在那里我们可以使用ServletConfig对象来访问 Servlet 初始化参数。
20. What is difference between GenericServlet and HttpServlet?
GenericServlet is protocol independent implementation of Servlet interface whereas HttpServlet is HTTP protocol specific implementation. Most of the times we use servlet for creating web application and that’s why we extend HttpServlet class. HttpServlet class extends GenericServlet and also provide some other methods specific to HTTP protocol.
20. GenericServlet 和 HttpServlet 之间的区别是什么?
GenericServlet是 Servlet 接口的独立协议实现,而HttpServlet是 HTTP 协议特定的实现。大多数情况下,我们使用 servlet 里创建 Web 应用程序,这就是我们扩展HttpServlet类的原因。HttpServlet类扩展了GenericServlet,还提供了一些特定于 HTTP 协议的其他方法。
21. What is the inter-servlet communication?
When we want to invoke another servlet from a servlet service methods, we use inter-servlet communication mechanisms. We can invoke another servlet using RequestDispatcher forward() and include() methods and provide additional attributes in request for other servlet use.
21. 什么是 servlet 间的通信?
当我们想要从一个 servlet 服务方法中调用另一个 servlet 时,我们使用了 servlet 间通信机制。我们可以使用RequestDispatcher forward()和include()方法调用另一个 servlet,并在请求其他 servlet 时提供其他属性。
22. Are Servlets Thread Safe? How to achieve thread safety in servlets?
HttpServlet init() method and destroy() method are called only once in servlet life cycle, so we don’t need to worry about their synchronization. But service methods such as doGet() or doPost() are getting called in every client request and since servlet uses multithreading, we should provide thread safety in these methods.
If there are any local variables in service methods, we don’t need to worry about their thread safety because they are specific to each thread but if we have a shared resource then we can use synchronization to achieve thread safety in servlets when working with shared resources.
The thread safety mechanisms are similar to thread safety in standalone java application, read more about them at Thread Safety in Java.
22. Servlet 是线程安全的吗?如何在 servlet 中实现线程安全
HttpServlet的init()方法和destroy()方法在 servlet 声明周期中只会被调用一次。所以我们不要去担心它们的同步。但是诸如doGet()或doPost()等服务方法在每个客户端请求中都会被调用,并且由于 servlet 使用多线程,所以我们应该在这些方法中提供线程安全性。
如果服务方法中有任何局部变量,我们不必担心它们的线程安全性,因为它们是针对每个线程的,但是如果我们有一个共享的资源,那么在使用共享时,我们可以使用同步来实现 servlet 中的线程安全资源。
线程安全机制类似于独立 Java 应用程序中的线程安全性,在 Thread Safety in Java 中阅读更多内容。
23. What is servlet attributes and their scope?
Servlet attributes are used for inter-servlet communication, we can set, get and remove attributes in web application. There are three scopes for servlet attributes – request scope, session scope and application scope.
ServletRequest, HttpSession and ServletContext interfaces provide methods to get/set/remove attributes from request, session and application scope respectively.
Servlet attributes are different from init parameters defined in web.xml for ServletConfig or ServletContext.
23. 什么是 servlet 属性和它们的范围?
Servlet 属性用于 servlet 间的通信,我们可以在 Web 应用程序中set、get 和 remove 属性。servlet 属性有三个范围 - request scope、session scope 和 application scope。
24. How do we call one servlet from another servlet?
We can use RequestDispatcher forward() method to forward the processing of a request to another servlet. If we want to include the another servlet output to the response, we can use RequestDispatcher include() method.
24. 我们如何在一个 servlet 中调用另一个 servlet?
我们可以使用RequestDispatcher的forward()方法来将请求处理转发给另一个 servlet。如果我们想要将另一个 servlet 输出包含到 response 中,我们可以使用RequestDispatcher的include()方法。
25. How can we invoke another servlet in a different application?
We can’t use RequestDispatcher to invoke servlet from another application because it’s specific for the application. If we have to forward the request to a resource in another application, we can use ServletResponse sendRedirect() method and provide complete URL of another servlet. This sends the response to client with response code as 302 to forward the request to another URL. If we have to send some data also, we can use cookies that will be part of the servlet response and sent in the request to another servlet.
25. 我们如何在一个应用程序中调用另一个应用程序中的 servlet
我们不能使用RequestDispatcher从另一个程序中调用 servlet,因为它是特定于应用程序的。如果我们必须将请求转发到另一个应用程序中的资源,我们可以使用ServletResponse 的sendRedirect()方法,并提供另一个 servlet 的完整 URL。这将 响应代码为 302 的 response 发送给客户端,将请求转发到另一个 URL。如果我们还要发送一些数据,我们可以使用 cookie 作为 servlet response 的一部分,并将请求发送到另一个 servlet。
26. What is difference between ServletResponse sendRedirect() and RequestDispatcher forward() method?
RequestDispatcherforward()is used to forward the same request to another resource whereasServletResponsesendRedirect()is a two step process. InsendRedirect(), web application returns the response to client with status code 302 (redirect) with URL to send the request. The request sent is a completely new request.forward()is handled internally by the container whereassendRedirect()is handled by browser.- We should use
forward()when accessing resources in the same application because it’s faster thansendRedirect()method that required an extra network call. - In
forward()browser is unaware of the actual processing resource and the URL in address bar remains same whereas insendRedirect()URL in address bar change to the forwarded resource. forward()can’t be used to invoke a servlet in another context, we can only usesendRedirect()in this case.
26. ServletResponse 的 sendRedirect() 方法和RequestDispatcher 的 forward() 方法有什么区别?
RequestDispatcher的forward()方法用来转发相同的请求到另一个资源,而ServletResponse的sendRedirect()方法则是一个两步的过程。在sendRedirect()中,Web 应用程序使用 URL 向客户端返回具有 302 状态码的发送请求。这个请求将发送一个全新的请求。forward()由容器内部处理,而sendRedirect()由浏览器处理。- 当访问统一应用程序中的资源时,我们应该使用
forward(),因为它比需要额外网络调用的sendRedirect()方法要快。 - 在
forward()中,浏览器并不知道实际处理资源,地址栏的 URL 保持不变,而在sendRedirect()中,URL 转换为转发的资源。 forward()不能用于在一个上下文中调用一个 servlet,这种情况下我梦只能使用sendRedirect()。
27.Why HttpServlet class is declared abstract?
HttpServlet class provide HTTP protocol implementation of servlet but it’s left abstract because there is no implementation logic in service methods such as doGet() and doPost() and we should override at least one of the service methods. That’s why there is no point in having an instance of HttpServlet and is declared abstract class.
Read more about abstract class.
27. 为什么 HttpServlet 类被声明为 abstract?
HttpServlet类提供 servlet 的 HTTP 协议实现,但是由于在doGet()和doPost()这样的服务方法中没有实现逻辑,并且我们应该重写至少一个服务方法,所以它是抽象的。这就是为什么有一个HttpServlet实例没有意义,被声明为抽象类的原因。
阅读更多关于 abstract class。
28. What are the phases of servlet life cycle?
We know that Servlet Container manages the life cycle of Servlet, there are four phases of servlet life cycle.
- Servlet Class Loading – When container receives request for a servlet, it first loads the class into memory and calls it’s default no-args constructor.
- Servlet Class Initialization – Once the servlet class is loaded, container initializes the
ServletContextobject for the servlet and then invoke it’s init method by passing servlet config object. This is the place where a servlet class transforms from normal class to servlet. - Request Handling – Once servlet is initialized, its ready to handle the client requests. For every client request, servlet container spawns a new thread and invokes the
service()method by passing the request and response object reference. - Removal from Service – When container stops or we stop the application, servlet container destroys the servlet class by invoking it’s
destroy()method.
28. 什么是 servlet 声明周期的阶段?
我们知道 Servlet 容器管理 Servlet 的生命周期,Servlet 生命周期有四个阶段。
- Servlet 类加载 - 当容器接收到对 servlet 的请求时,它首先将类加载到内存中,并调用它的默认无参构造方法。
- Servlet类的初始化 - 一旦 servlet 类被加载,容器就初始化 servlet 的
ServletContext对象,然后通过传递 servlet config 对象来调用它的 init 犯法。这是 servlet 类从普通类转换为 servlet 的地方。 - 请求处理 - 一旦 servlet 被初始化,它就准备好处理客户端请求。对于米格客户端请求,servlet 容器都派生一个新线程,并通过传递 request 和 response 对象来调用
service()方法。 - 从服务中删除 - 当容器停止或者我们停止应用程序时,servlet 容器通过它的
destroy()方法来销毁 servlet 类。
29. What are life cycle methods of a servlet?
Servlet Life Cycle consists of three methods:
public void init(ServletConfig config)– This method is used by container to initialize the servlet, this method is invoked only once in the lifecycle of servlet.public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)– This method is called once for every request, container can’t invoke service() method until unless init() method is executed.public void destroy()– This method is invoked once when servlet is unloaded from memory.
29. servlet 的声明周期方法有哪些?
Servlet 生命周期包含三种方法:
public void init(ServletConfig config)– 这个方法被容器调用来初始化 servlet,在 servlet 生命周期中只被调用一次。public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)– 对于每个请求,这个方法都将会被调用一次,除非init()方法被执行,否则容器不能调用service()方法。public void destroy()– 当 servlet 从内存中卸载时,调用此方法一次。
30. why we should override only no-agrs init() method.
If we have to initialize some resource before we want our servlet to process client requests, we should override init() method. If we override init(ServletConfig config) method, then the first statement should be super(config) to make sure superclass init(ServletConfig config) method is invoked first. That’s why GenericServlet provides another helper init() method without argument that get’s called at the end of init(ServletConfig config) method. We should always utilize this method for overriding init() method to avoid any issues as we may forget to add super() call in overriding init method with ServletConfig argument.
30. 我们为什么需要重写无参的 init() 方法?
如果我们想要我们的 servlet 在处理客户端请求之前必须初始化一些资源,我们应该重写init()方法。如果我们重写init(ServletConfig config)方法,那么第一个语句应该是super(config)以确保首先调用超类的init()方法。这就是为什么GenericServlet提供了另一个助手 - 在init(ServletConfig config)结束的时候调用的无参的init() 方法。我们应该总是使用这个方法来重写init()方法来避免任何因为我们能在重写没有ServletConfig参数的 init 方法时忘记添加super()调用而产生的问题。
31. What is URL Encoding?
URL Encoding is the process of converting data into CGI form so that it can travel across the network without any issues. URL Encoding strip the white spaces and replace special characters with escape characters. We can use java.net.URLEncoder.encode(String str, String unicode) to encode a String. URL Decoding is the reverse process of encoding and we can use java.net.URLDecoder.decode(String str, String unicode) to decode the encoded string. For example “Pankaj’s Data” is encoded to “Pankaj%27s+Data”.
31. 什么是 URL Encoding?
URL Encoding 是将数据转换为 CGI 格式的过程,以便它可以在网络上传输,而不会出现任何问题。URL 编码去掉空格并用转义字符替换特殊字符。我们可以使用java.net.URLEncoder.encode(String str, String unicode)来编码一个 String。URL 解码时编码的逆向过程,我们可以使用java.net.URLDecoder.decode(String str, String unicode)来解码编码的字符串。栗如例如“Pankaj’s Data”被编码为“Pankaj%27s + Data”。
32. What are different methods of session management in servlets?
Session is a conversional state between client and server and it can consists of multiple request and response between client and server. Since HTTP and Web Server both are stateless, the only way to maintain a session is when some unique information about the session (session id) is passed between server and client in every request and response.
Some of the common ways of session management in servlets are:
- User Authentication
- HTML Hidden Field
- Cookies
- URL Rewriting
- Session Management API
Read more about these session management approaches in detail at Servlet Session Management Tutorial.
32. servlet 中会话管理的不同方法有哪些?
会话是客户端和服务器之间的转换状态,它可以由客户端和服务器之间的多个 request 和 response 组成。由于 HTTP 和 Web 服务器都是无状态的,因此维护会话的唯一方法是在每个 request 和 response 中,在服务器和客户端支架传递有关会话(会话ID)的一些唯一信息。
servlet 中会话管理的一些常见方式是:
- 用户认证
- HTML 隐藏字段
- Cookies
- URL 重写
- 会话管理 API
在 Servlet Session Management Tutorial 中了解这些会话管理方法。
33. What is URL Rewriting?
We can use HttpSession for session management in servlets but it works with Cookies and we can disable the cookie in client browser. Servlet API provides support for URL rewriting that we can use to manage session in this case.
The best part is that from coding point of view, it’s very easy to use and involves one step – encoding the URL. Another good thing with Servlet URL Encoding is that it’s a fallback approach and it kicks in only if browser cookies are disabled.
We can encode URL with HttpServletResponse encodeURL()method and if we have to redirect the request to another resource and we want to provide session information, we can use encodeRedirectURL() method.
Read More at Servlet URL Rewriting.
33. 什么是 URL Rewriting?
我们可以在 Servlet 中使用HttpSession进行会话管理,但是它需要与 Cookies 协同工作,我们可以在客户端浏览器中禁用 Cookie。这种情况下 Servlet API 提供了对 URL 重写的支持,我们可以使用它来管理会话。
最棒的是从编码的角度来看,只需要一个步骤 - 对 URL 进行编码。Servlet URL Encoding 的另一个好处是它是一个备用方法,只有在历览器 cookies 被禁用的情况下才会启动。
我们可以使用HttpServletResponse的encodeURL()方法编码 URL,如果我们必须将请求重定向到另一个资源,并且我们想提供会话信息,我们可以使用encodeRedirectURL()方法。
阅读更多:Servlet URL Rewriting
34. How does Cookies work in Servlets?
Cookies are used a lot in web client-server communication, it’s not something specific to java. Cookies are text data sent by server to the client and it gets saved at the client local machine.
Servlet API provides cookies support through javax.servlet.http.Cookie class that implements Serializable and Cloneable interfaces.
HttpServletRequest getCookies() method is provided to get the array of Cookies from request, since there is no point of adding Cookie to request, there are no methods to set or add cookie to request.
Similarly HttpServletResponse addCookie(Cookie c) method is provided to attach cookie in response header, there are no getter methods for cookie.
Read more at Cookies in Servlets.
34. Cookies 在 Servlet 中是怎么工作的?
Cookies 在 web 客户端-服务器 通信中使用很多,这不是 Java 特有的。Cooikie 是由服务器发送给客户端并保存客户端本地机器上的文本数据。
Servlet API 通过实现Serializable和Cloneable接口的javax.servlet.http.Cookie类提供了 cookies 的支持。
HttpServletRequest的getCookies()方法来用于从请求中获取 Cookies 数组,因为添加 Cookie 到 request 没有任何意义,所以没有方法来 set 或者 add cookie 到 request。
同样提供了HttpServletResponse的addCookie(Cookie c)方法来在响应头中附加 cookie,没有针对 cookie 的 getter 方法。
阅读更多: Cookies in Servlets.
35. How to notify an object in session when session is invalidated or timed-out?
If we have to make sure an object gets notified when session is destroyed, the object should implement javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener interface. This interface defines two callback methods – valueBound() and valueUnbound() that we can define to implement processing logic when the object is added as attribute to the session and when session is destroyed.
Recommended reading Servlet Listener.
35. 当会话失效或超时时如何通知绘画中的对象?
如果我们必须却奥一个对象在会话销毁时得到通过,那么该对象应该实现javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener接口。这个接口定义了两个回调方法 - valueBound()和valueUnbound()我们可以定义它们来实处理逻辑,当对象作为属性添加到会话中并且会话被销毁时。
未完待续