Spring框架笔记
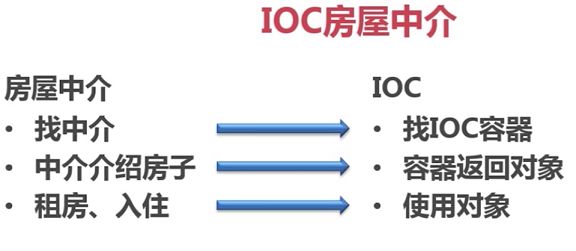
Spring介绍
Spring是一个开源框架,为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的,但现在已将不止应用于企业应用,是一个轻量级的控制反转(Ioc)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
相对于 java 官方重量级的框架 EJB 来说,Spring 是一个轻量级的框架,而且完成功能只需要简单的 java 类,并且 Spring 开源。
Spring 对主流 java 技术的支持,(持久层Hibernate、JDBC、mybatis)也可以把 Spring 看做 java 应用的综合体。
Spring 主要应用方案:
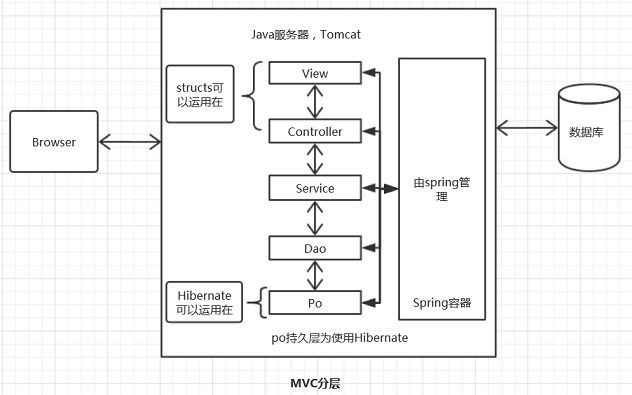
SSH: Structs(MVC经典) +Hibernate(持久层技术的代表)+Spring(管理整个工程)
Spring的优点:
1.解耦
以往,service层与dao层耦合,当dao层报错,service也报错,service层和dao层严重耦合
通过控制反转(IOC)的技术达到松耦合的目的。
2.AOP编程的支持
3.声明式的事务支持
4.方便程序的测试
5.方便继承各种优秀的框架
6.降低了 java EE 使用难度
7.Spring 的源码可以作为学习范例
Spring 4中文参考文档:https://github.com/b2gats/stone-docs/blob/master/spring-4-beans.md#beans-factory-properties-detailed
1 面向接口编程
- 结构设计中,分清层次及调用关系,每层只向外(上层)提供一组功能接口,各层间仅依赖接口而非实现类
- 接口实现的变动不影响各层间的调用,这点在公共服务中尤其重要
- “面向接口编程”中的“接口”是用于隐藏具体实现和实现多态性的组件
public interface Oninterface {
public String hello(String word);
}public class Oninterfaceiml implements Oninterface {
@Override
public String hello(String word) {
return "HEllo world"+word;
}
}public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Oninterface oif = new Oninterfaceiml();
//实现接口类的对象赋值给接口的引用
System.out.println(oif.hello("peng"));
}
}2 IOC
对象创建统一托管
规范的生命周期管理
灵活的依赖注入
一致的获取对象
所有类的创建和销毁,都由spring控制,也就是说,控制对象生存周期的,不再是引用它的对象,而是spring;对于某个具体的对象而言,以前是它控制其他对象,现在是所有的对象都被spring控制,所以这就是反转。
IOC本质就是要抛弃new的方法取得对象,通过配置来取得对象。
IOC的理论背景:

当对象A运行到需要对象B时,IOC容器主动创建对象B注入到对象A需要的地方。对象A获取对象B的行为从主动变为被动行为。
在 spring 的配置文件中,下面的配置
<bean id="date" class="java.util.Date">bean>相当于:
Date date = new Date(); 并且 date 是单例的IOC通俗例子理解
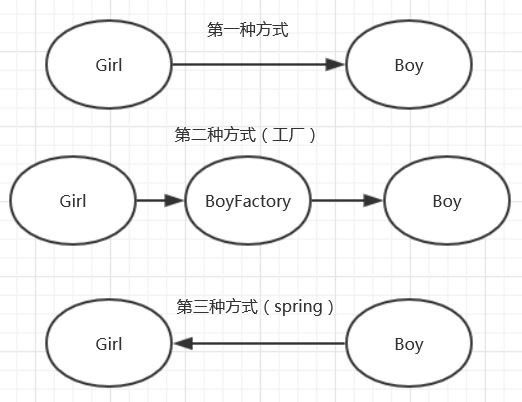
需求:现在一个女孩要找一个男朋友
女孩—>?—>男朋友
a.自己去找
public void getBoyFriend(){
boy = new Boy();//自己创建一个男朋友对象
}b.通过中介(中介是用来得到相关服务的)
BoyFactory 对应的方法:
public Boy getBoy(){
return new Boy();
}Girl 类对应的方法:
public void getBoyFriend(){
boy = BoyFactory.getBoy();
}c.父母包办
女孩达到年龄后,男朋友就自动出现在面前(spring抽象理解)
private Boy boy;//需要有注入代码实现
public void getBoyFriend(){
this.boy;//外界传入的一个对象
}IOC注入
3 Bean
在IOC中,所有的对象称作Bean
命名规则
id 的命名由数字、字母和$组成(首字母不能是数字)
java 的属性命名除了上面的命名规则,还要注意首字母小写,接下来单词的首字母大写
如果第一个单词只有一个字母,第二个单词的首字母也要小写
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" scope="session">bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" scope="prototype">bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" scope="singleton">bean>| 作用域 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| singleton(默认单例) | 在每个Spring IOC容器中一个bean定义对应一个对象实例。 |
| prototype(原型) | 一个bean定义对应多个对象实例。 |
| request | 在一次HTTP请求中,一个bean定义对应一个实例;即每次HTTP请求将会有各自的bean实例, 它们依据某个bean定义创建而成。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext 情形下有效。 |
| session | 在一个HTTP Session 中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。该作用域仅在基于web的SpringApplicationContext 情形下有效 |
| global session | 在一个全局的HTTP Session 中,一个bean定义对应一个实例。典型情况下,仅在使用portlet context的时候有效。该作用域仅在基于web的Spring ApplicationContext 情形下有效。 |
在单例中,每个Spring IoC容器只有一个实例,无论多少次调用 getBean()方法获取它,它总是返回同一个实例。
CustomerService custA = (CustomerService)context.getBean("customerService");
custA.setMessage("Message by custA");
System.out.println("Message : " + custA.getMessage());
//retrieve it again
CustomerService custB = (CustomerService)context.getBean("customerService");
System.out.println("Message : " + custB.getMessage());两次结果都是第一次第一次设置的结果。
Message : Message by custA
Message : Message by custA 在原型模式中,则是下面的结果
Message : Message by custA
Message : nullSpring自动装载bean
所谓自动装配,就是将一个Bean注入到其他Bean的Property中,类似于以下:
id="customer" class="com.lei.common.Customer" autowire="byName" /> Spring支持5种自动装配模式,如下:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| no | 默认情况下,不自动装配,通过“ref”attribute手动设定。 |
| buName | 根据Property的Name自动装配,如果一个bean的name,和另一个bean中的Property的name相同,则自动装配这个bean到Property中。 |
| byType | 根据Property的数据类型(Type)自动装配,如果一个bean的数据类型,兼容另一个bean中Property的数据类型,则自动装配。 |
| constructor | 根据构造函数参数的数据类型,进行byType模式的自动装配。 |
| autodetect | 如果发现默认的构造函数,用constructor模式,否则,用byType模式。 |
实例http://www.yiibai.com/spring/spring-auto-wiring-beans-in-xml.html
测试
Customer.java
//package com.peng.dao.impl;
public class Customer {
private Person person = null;
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public void First(){
System.out.println("我是Customer,获取到的Person方法的内容"+person.getMsg());
}
}Person.java
//package com.peng.dao.impl;
public class Person {
public String getMsg(){
return "我是person里的消息";
}
}applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
<bean id="customer" class="com.peng.dao.impl.Customer" autowire="byName">
bean>
<bean id="person" class="com.peng.dao.impl.Person">bean>
beans>Test.java
//package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.peng.dao.UserDAO;
import com.peng.dao.impl.Customer;
public class Test {
public void testAutoWrie(){
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
Customer c = context.getBean("customer",Customer.class);
c.First();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
test.testAutoWrie();
}
}
我是Customer,获取到的Person方法的内容我是person里的消息4 Junit测试
6 AOP面向切面
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
配置Spring环境
Spring jar包下载地址
http://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/
Spring Tool Suite
Spring Tool Suite下载地址:
http://spring.io/tools/sts/all
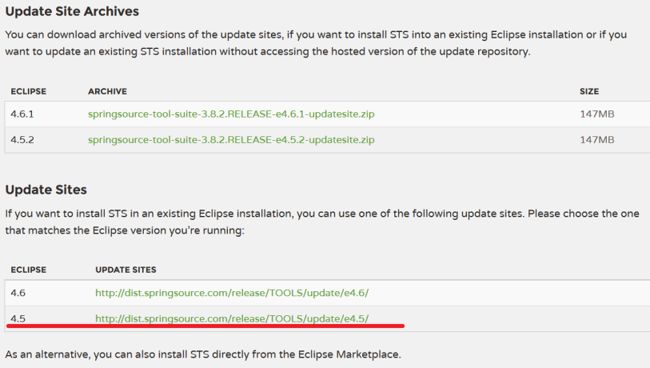
Eclipse 版本是 4.6.0,通过Eclipse Marketplace 不能下载sts,安装会出错,通过install new software 安装4.5的update sites 可以成功,但是,new spring project 时,没有spring project,有spring starter project 等等。
下载的最新版本的4.6.1版本的 Eclipse 可以用4.61版本的

上面的zip包,有的是sts的离线包和Update Site Archives,也只有springsource…才能在install new software时安装,就是下载的Update Site Archives下的包
建立Java project测试spring
课程学习地址:http://www.chuanke.com/v7232853-198066-1144815.html
这里Junit 包还用不上,commons -logging的包可以在structs包中找到,没有这个包会报错。
UserDAO.java
//package com.peng.dao;
public interface UserDAO {
public void sayHello();
}UserDAOImpl.java
//package com.peng.dao.impl;
import com.peng.dao.UserDAO;
public class UserDAOImpl implements UserDAO {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}applicationContext.xml
xml文件名可以随意
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
beans>
Test.java
//package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.peng.dao.UserDAO;
public class Test {
/**
* 1.读取spring的容器
* 2.从spring的容器中查找我们需要的对象
* 3.从得到的对象中调用需要的方法
* @param args
*/
public void doFirst(){
//1.读取Spring的容器
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.从spring容器中查找我们需要的对象
UserDAO dao = context.getBean("userDao",UserDAO.class);
//只需要调用接口,不管它的实现
dao.sayHello();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
test.doFirst();
}
} 运行结果:
十一月 09, 2016 8:56:20 下午 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7eda2dbb: startup date [Wed Nov 09 20:56:20 CST 2016]; root of context hierarchy
十一月 09, 2016 8:56:20 下午 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions
信息: Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [applicationContext.xml]
hello world!1 利用JUnit测试spring
UserDAO.java
//package com.peng.dao;
public interface UserDAO {
public void sayHello();
}UserDAOImpl.java
//package com.peng.dao.impl;
import com.peng.dao.UserDAO;
public class UserDAOImpl implements UserDAO {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
beans>TestUserDAO.java
//package junit.com.peng.dao;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.peng.dao.UserDAO;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//spring对junit的支持
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
//读取spring的配置文件
public class TestUserDAO {
@Autowired//自动加载
private UserDAO dao = null;
//Spring的junit测试代码
@Test
public void testSayHello(){
dao.sayHello();
}
/*简单copy代码测试
* @Test
public void testSayHello(){
//1.读取Spring的容器
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.从spring容器中查找我们需要的对象
UserDAO dao = context.getBean("userDao",UserDAO.class);
//只需要调用接口,不管它的实现
dao.sayHello();
}*/
}测试结果:
.....
十一月 10, 2016 9:54:57 上午 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext@380fb434: startup date [Thu Nov 10 09:54:57 CST 2016]; root of context hierarchy
hello world!2 Spring注入测试
推荐使用set注入
set注入,可以一个一个的注入进去,需要给哪一个注入值,就写一个对应的property注入就可以了
构造方法注入,非要一次性给所有的参数注入值,才可以正确的创建对象
设值注入测试
MyTime .java 为设值注入的类
MyTime2.java 为构造注入的类
TestMyTime 为 JUnit 测试类
MyTime.java
//package com.peng.spring.ioc;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Title: MyTime
* Description: 设值注入
* @author Peng
* @date 上午10:50:36
*/
public class MyTime {
private Date date;
private String username;
public String getNowTime(){
return this.username+"说:现在的时间是:"+this.date.toLocaleString();
//return "现在的时间是:"+new Date();
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}
TestMyTime.java
//package junit.com.peng.dao;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime;
import com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime2;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//spring对junit的支持
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
//读取spring的配置文件
public class TestMyTime {
@Autowired
private MyTime myTime = null;
@Test
public void testGetNowTImeBySet(){
System.out.println(myTime.getNowTime());
}
}applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
<bean id="mytime" class="com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime">
<property name="date" ref="mydate">property>
<property name="username" value="王尼美">property>
bean>
<bean id="mydate" class="java.util.Date">bean>
beans>测试结果:
..
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext@668bc3d5: startup date [Thu Nov 10 11:28:01 CST 2016]; root of context hierarchy
王尼美说:现在的时间是:2016-11-10 11:28:01如果把
null说:现在的时间是:2016-11-10 11:17:15引入P标签
xml头部加入
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"上面的设置可以简写为
id="mytime" class="com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime"
p:date-ref="mydate" p:username="王尼美">
构造注入
MyTime2.java
//package com.peng.spring.ioc;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyTime2 {
private Date date;
private String username;
private MyTime2(){
}
private MyTime2(Date date,String username){
this.date = date;
this.username = username;
}
public String getNowTime(){
return this.username+"说:现在的时间是:"+this.date.toLocaleString();
//return "现在的时间是:"+new Date();
}
}
TestMyTime.java
//package junit.com.peng.dao;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime;
import com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime2;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//spring对junit的支持
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
//读取spring的配置文件
public class TestMyTime {
@Autowired
private MyTime myTime = null;
@Autowired
private MyTime2 myTime2 = null;
@Test
public void testGetNowTImeBySet(){
System.out.println(myTime.getNowTime());
}
@Test
public void testGetNowTImeByConstructor(){
System.out.println(myTime2.getNowTime());
}
}applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
<bean id="mytime" class="com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime">
<property name="date" ref="mydate">property>
<property name="username" value="王尼美">property>
bean>
<bean id="mydate" class="java.util.Date">bean>
<bean id="mytime2" class="com.peng.spring.ioc.MyTime2">
<constructor-arg name="date" ref="mydate">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="username" value="王尼玛">constructor-arg>
bean>
beans>
测试结果:
王尼玛说:现在的时间是:2016-11-10 11:33:11如果
Ambiguous argument values for parameter of type [java.lang.String] - did you specify the correct bean references as arguments?spring支持的资源类型的地址前缀
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
//读取spring的配置文件//1.读取Spring的容器
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");| 地址前缀 | 示 例 | 对应资源类型 |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/coder/beanfactory/beans.xml |
从类路径中加载资源,classpath:和classpath:/是等价的,都是相对于类的根路径。资源文件可以在标准的文件系统中,也可以在jar或zip的类包中 |
| file: | file:/conf/com/coder/beanfactory/beans.xml |
使用UrlResource从文件系统目录中装载资源,可采用绝对或相对路径 |
| http:// | http://www.coder.xxx/resource/beans.xml |
使用UrlResource从Web服务器中装载资源 |
| ftp:// | ftp://www.coder.xxx/resource/beans.xml |
使用UrlResource从FTP服务器中装载资源 |
| 没有前缀 | com/coder/beanfactory/beans.xml |
根据ApplicationContext具体实现类采用对应的类型的Resource |
Ant 风格资源匹配地址支持的3种匹配符
?:匹配文件名中的一个字符;
*:匹配文件名中任意个字符;
**:匹配多层路径
BeanFactory 、ApplicationContext和WebApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 继承于 BeanFactory BeanFactory
BeanFactory是一个容器
Spring 的 IOC 容器能够帮我们自动 new 对象,对象交给 spring 管理之后不用自己手动 new 对象了。
Spring 使用 BeanFactory 来实例化、配置和管理对象,但是它只是一个接口,里面有一个 getBean() 方法。我们一般都不直接用 BeanFactory ,而是用它的实现类 ApplicationContext,这个类会自动解析我们配置的 applicationContext.xml 文件,然后根据我们配置的 bean 来 new 对象,将 new 号的对象放进一个 Map 中,键就是我们 bean 的 id,值就是 new 出来的对象。
public void testBeanFactory(){
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Resource resource = resolver.getResource("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
UserDAO userDao = factory.getBean("userDao",UserDAO.class);
userDao.sayHello();
}ApplicationContext
从类路径下查找资源文件,即src目录
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");从工程的资源文件开始查找文件,即WebContent目录 下
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("bin/applicationContext.xml");上面两种方式对应着
classpath:applicationContext.xml
file:applicationContext.xmlWebApplicationContext
用到了structs 时,会用到
web.xml读取spring 文件的配置
让 web 容器,知道一个地址参数,改地址参数就是 spring 容器的地址。
spring 的监听器:在容器启动的时候,就读取 spring 的bean对象进入内存。
spring 的多个配置文件
1.第一个可以在总配置文件中,采用 import 标签导入进来
<import resource="spring.xml"/>applicationContext.xml 导入 spring.xml
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" >
<import resource="spring.xml"/>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.peng.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl">bean>
beans>2.直接在 ApplicationContext 读取多个配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml","spring.xml","....");3.在 web.xml 文件中,直接配置多个 spring 的资源,如
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/applicationContext.xml,
/WEB-INF/classes/spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>Spring xml头信息
aop标签
1.
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"2.
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsdtx标签
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd 异常信息
配置内部Bean的时候出错
id="CustomerBean" class="com.peng.pc.Customer">
<property name="person" ref="PersonBean" />
The fully qualified name of the bean's class, except if it serves only as a parent definition for child bean definitions.Customer
package com.peng.pc;
public class Customer {
private Person person;
public Customer(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [person=" + person + "]";
}
}
Person
package com.peng.pc;
public class Person {
private String name;
private String address;
private int age;
//setter and getter
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}Customer 构造函数默认要传入Person类的对象,原因是 Customer没有默认的无参构造函数。而你的bean定义,没有传入构造参数,可以使用下面的构造注入设置或者写一个无参构造函数
<bean id="CustomerBean" class="com.peng.pc.Customer">
<constructor-arg name="person" ref="PersonBean">constructor-arg>
bean>内部bean的方式:
<bean id="CustomerBean" class=com.peng.pc.Customer">
<property name="person">
<bean class="com.peng.pc.Person">
<property name="name" value="yiibai" />
<property name="address" value="address1" />
<property name="age" value="28" />
bean>
property>
bean>在Spring框架中,一个bean仅用于一个特定的属性,这是提醒其声明为一个内部bean