Linux FUSE开发
参考
github libfuse
FUSE简介(译)
用户态文件系统fuse学习
使用 FUSE 开发自己的文件系统
fuse接口用法说明
linux的readdir和readdir_r函数
基于fuse文件系统优化方法总结[附带详细说明]
介绍
FUSE指的是用户态文件系统,FUSE在内核中存在一个驱动,用户态对文件系统的操作,通过FUSE驱动转发到用户态程序,这样就可以在用户态实现文件系统操作,传统的Linux文件系统存在于内核中,比如Linux下对NTFS提供读写支持的NTFS-3G软件包就是利用FUSE实现的,
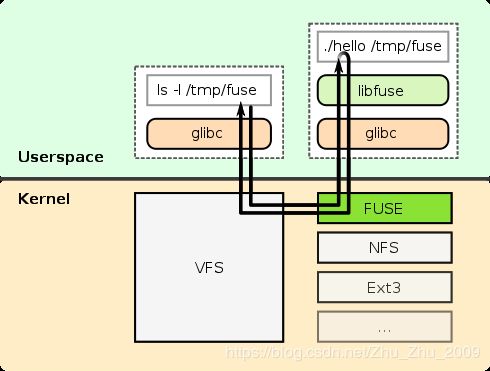
实现
实现FUSE也就是实现FUSE定义的一套函数集,通过这组函数虚拟出一个文件系统,不管这个文件系统存在什么地方,以一种什么样的形式,
struct fuse_operations {
int (*getattr) (const char *, struct stat *);
int (*readlink) (const char *, char *, size_t);
int (*getdir) (const char *, fuse_dirh_t, fuse_dirfil_t);
int (*mknod) (const char *, mode_t, dev_t);
int (*mkdir) (const char *, mode_t);
int (*unlink) (const char *);
int (*rmdir) (const char *);
int (*symlink) (const char *, const char *);
int (*rename) (const char *, const char *);
int (*link) (const char *, const char *);
int (*chmod) (const char *, mode_t);
int (*chown) (const char *, uid_t, gid_t);
int (*truncate) (const char *, off_t);
int (*utime) (const char *, struct utimbuf *);
int (*open) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*read) (const char *, char *, size_t, off_t, struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*write) (const char *, const char *, size_t, off_t,struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*statfs) (const char *, struct statfs *);
int (*flush) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*release) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*fsync) (const char *, int, struct fuse_file_info *);
int (*setxattr) (const char *, const char *, const char *, size_t, int);
int (*getxattr) (const char *, const char *, char *, size_t);
int (*listxattr) (const char *, char *, size_t);
int (*removexattr) (const char *, const char *);
};
- getattr: int (*getattr) (const char *, struct stat *);
这个函数与 stat() 类似。st_dev 和 st_blksize 域都可以忽略。st_ino 域也会被忽略,除非在执行 mount 时指定了 use_ino 选项。 - readlink: int (*readlink) (const char *, char *, size_t);
这个函数会读取一个符号链接的目标。缓冲区应该是一个以 null 结束的字符串。缓冲区的大小参数包括这个 null 结束字符的空间。如果链接名太长,不能保存到缓冲区中,就应该被截断。成功时的返回值应该是 “0”。 - getdir: int (*getdir) (const char *, fuse_dirh_t, fuse_dirfil_t);
这个函数会读取一个目录中的内容。这个操作实际上是在一次调用中执行 opendir()、readdir()、…、closedir() 序列。对于每个目录项来说,都应该调用 filldir() 函数。 - mknod: int (*mknod) (const char *, mode_t, dev_t);
这个函数会创建一个文件节点。此处没有 create() 操作;mknod() 会在创建非目录、非符号链接的节点时调用。 - mkdir: int (*mkdir) (const char *, mode_t);
创建一个目录。 - rmdir: int (*rmdir) (const char *);
删除一个目录。 - unlink: int (*unlink) (const char *);
删除一个文件。 - rename: int (*rename) (const char *, const char *);
重命名一个文件。 - symlink: int (*symlink) (const char *, const char *);
这个函数用来创建一个符号链接。 - link: int (*link) (const char *, const char *);
这个函数创建一个到文件的硬链接。 - chmod: int (*chmod) (const char *, mode_t);
- chown: int (*chown) (const char *, uid_t, gid_t);
- truncate: int (*truncate) (const char *, off_t);
- utime: int (*utime) (const char *, struct utimbuf *);
这 4 个函数分别用来修改文件的权限位、属主和用户、大小以及文件的访问/修改时间。 - open: int (*open) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
这是文件的打开操作。对 open() 函数不能传递创建或截断标记(O_CREAT、O_EXCL、O_TRUNC)。这个函数应该检查是否允许执行给定的标记的操作。另外,open() 也可能在 fuse_file_info 结构中返回任意的文件句柄,这会传递给所有的文件操作。 - read: int (*read) (const char *, char *, size_t, off_t, struct fuse_file_info *);
这个函数从一个打开文件中读取数据。除非碰到 EOF 或出现错误,否则 read() 应该返回所请求的字节数的数据;否则,其余数据都会被替换成 0。一个例外是在执行 mount 命令时指定了 direct_io 选项,在这种情况中 read() 系统调用的返回值会影响这个操作的返回值。 - write: int (*write) (const char *, const char *, size_t, off_t, struct fuse_file_info *);
这个函数将数据写入一个打开的文件中。除非碰到 EOF 或出现错误,否则 write() 应该返回所请求的字节数的数据。一个例外是在执行 mount 命令时指定了 direct_io 选项(这于 read() 操作的情况类似)。 - statfs: int (*statfs) (const char *, struct statfs *);
这个函数获取文件系统的统计信息。f_type 和 f_fsid 域都会被忽略。 - flush: int (*flush) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
这表示要刷新缓存数据。它并不等于 fsync() 函数 —— 也不是请求同步脏数据。每次对一个文件描述符执行 close() 函数时,都会调用 flush();因此如果文件系统希望在 close() 中返回写错误,并且这个文件已经缓存了脏数据,那么此处就是回写数据并返回错误的好地方。由于很多应用程序都会忽略 close() 错误,因此这通常用处不大。
注意:我们也可以对一个 open() 多次调用 flush() 方法。如果由于调用了 dup()、dup2() 或 fork() 而产生多个文件描述符指向一个打开文件的情况,就可能会需要这种用法。我们无法确定哪个 flush 操作是最后一次操作,因此每个 flush 都应该同等地对待。多个写刷新序列相当罕见,因此这并不是什么问题。 - release: int (*release) (const char *, struct fuse_file_info *);
这个函数释放一个打开文件。release() 是在对一个打开文件没有其他引用时调用的 —— 此时所有的文件描述符都会被关闭,所有的内存映射都会被取消。对于每个 open() 调用来说,都必须有一个使用完全相同标记和文件描述符的 release() 调用。对一个文件打开多次是可能的,在这种情况中只会考虑最后一次 release,然后就不能再对这个文件执行更多的读/写操作了。release 的返回值会被忽略。 - fsync: int (*fsync) (const char *, int, struct fuse_file_info *);
这个函数用来同步文件内容。如果 datasync 参数为非 0,那么就只会刷新用户数据,而不会刷新元数据。 - setxattr: int (*setxattr) (const char *, const char *, const char *, size_t, int);
- getxattr: int (*getxattr) (const char *, const char *, char *, size_t);
- listxattr: int (*listxattr) (const char *, char *, size_t);
- removexattr: int (*removexattr) (const char *, const char *);
这些函数分别用来设置、获取、列出和删除扩展属性。
性能优化
根据我们自研的文件系统特性,采取下面三个措施,提高顺序读写性能,
- 延长元数据有效时间,–o entry_timeout=T –o attr_timeout=T
- 扩大每次写入页面数,–o big_write –o max_write=N
- 使用DirectIO取代BufferIO,-o direct_io
示例
libfuse自带的hello,构造了一个只有一个可读文件的文件系统,文件名和文件内容来自于main的输入参数,
/*
FUSE: Filesystem in Userspace
Copyright (C) 2001-2007 Miklos Szeredi
This program can be distributed under the terms of the GNU GPL.
See the file COPYING.
*/
/** @file
*
* minimal example filesystem using high-level API
*
* Compile with:
*
* gcc -Wall hello.c `pkg-config fuse3 --cflags --libs` -o hello
*
* ## Source code ##
* \include hello.c
*/
#define FUSE_USE_VERSION 31
#include \n\n" , progname);
printf("File-system specific options:\n"
" --name= Name of the \"hello\" file\n"
" (default: \"hello\")\n"
" --contents= Contents \"hello\" file\n"
" (default \"Hello, World!\\n\")\n"
"\n");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
struct fuse_args args = FUSE_ARGS_INIT(argc, argv);
/* Set defaults -- we have to use strdup so that
fuse_opt_parse can free the defaults if other
values are specified */
options.filename = strdup("hello");
options.contents = strdup("Hello World!\n");
/* Parse options */
if (fuse_opt_parse(&args, &options, option_spec, NULL) == -1)
return 1;
/* When --help is specified, first print our own file-system
specific help text, then signal fuse_main to show
additional help (by adding `--help` to the options again)
without usage: line (by setting argv[0] to the empty
string) */
if (options.show_help) {
show_help(argv[0]);
assert(fuse_opt_add_arg(&args, "--help") == 0);
args.argv[0][0] = '\0';
}
ret = fuse_main(args.argc, args.argv, &hello_oper, NULL);
fuse_opt_free_args(&args);
return ret;
}
参考fusexmp.c,全面的实现,
/*
FUSE: Filesystem in Userspace
Copyright (C) 2001-2007 Miklos Szeredi
Copyright (C) 2011 Sebastian Pipping
This program can be distributed under the terms of the GNU GPL.
See the file COPYING.
gcc -Wall fusexmp.c `pkg-config fuse --cflags --libs` -o fusexmp
*/
#define FUSE_USE_VERSION 26
#ifdef HAVE_CONFIG_H
#include