OKHTTP分享二缓存策略
与缓存有关的Header
Expires
Expires: Thu, 12 Jan 2017 11:01:33 GMT
表示到期时间,一般用在response报文中,当超过此时间响应将被认为是无效的而需要网络连接,反之直接使用缓存条件GET
客户端发送条件get请求,如果缓存是有效的,则返回304 Not Modifiled,否则才返回body。ETag
ETag是对资源文件的一种摘要,当客户端第一次请求某个对象,服务器在响应头返回
ETag: “5694c7ef-24dc”
客户端再次请求时,通过发送
If-None-Match:”5694c7ef-24dc”
交给服务器进行判断,如果仍然可以缓存使用,服务器就直接返回304 Not ModifiledVary
Vary: *
告诉客户端和缓存服务器不要缓存任何信息
Vary: header-name, header-name, …
逗号分隔的一系列http头部名称,用于确定缓存是否可用
作用:动态服务,防止客户端误使用了用于pc端的缓存。即使请求的是相同资源,因Vary指定的首部字段不同,也必须从源服务器请求- Cache Control
客户端可以在HTTP**请求**中使用的标准 Cache-Control 指令
Cache-Control: max-age=
Cache-Control: max-stale[=]
Cache-Control: min-fresh=
Cache-control: no-cache
Cache-control: no-store
Cache-control: no-transform
Cache-control: only-if-cached
服务器可以在响应中使用的标准 Cache-Control 指令。
Cache-control: must-revalidate
Cache-control: no-cache
Cache-control: no-store
Cache-control: no-transform
Cache-control: public
Cache-control: private
Cache-control: proxy-revalidate
Cache-Control: max-age=
Cache-control: s-maxage=
1) 可缓存性
public
表明其他用户也可以利用缓存。
private
表明缓存只对单个用户有效,不能作为共享缓存。
no-cache
强制所有缓存了该响应的缓存用户,在使用已存储的缓存数据前,发送带验证的请求到原始服务器
no-store
缓存不应存储有关客户端请求或服务器响应的任何内容。
only-if-cached
表明客户端只接受已缓存的响应,并且不要向原始服务器检查是否有更新的拷贝(相当于禁止使用网络连接)
2) 到期
max-age=
设置缓存存储的最大周期,超过这个时间缓存被认为过期(单位秒)。与Expires相反,时间是相对于请求的时间。
s-maxage=
覆盖max-age 或者 Expires 头,但是仅适用于共享缓存(比如各个代理),并且私有缓存中它被忽略。
max-stale[=
表明客户端愿意接收一个已经过期的资源,且可选地指定响应不能超过的过时时间。
min-fresh=
表示客户端希望在指定的时间内获取最新的响应。
3) 有效性
must-revalidate
缓存必须在使用之前验证旧资源的状态,并且不可使用过期资源。
proxy-revalidate
与must-revalidate作用相同,但它仅适用于共享缓存(例如代理),并被私有缓存忽略。
immutable
表示响应正文不会随时间而改变。资源(如果未过期)在服务器上不发生改变,因此客户端不应发送重新验证请求头(例如If-None-Match或If-Modified-Since)来检查更新,即使用户显式地刷新页面。
缓存策略
CacheInterceptor
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null
? cache.get(chain.request())
: null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
...
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
}主要做三件事:
- 根据Request和之前缓存的Response得到CacheStrategy
- 根据CacheStrategy决定是请求网络还是直接返回缓存
- 如果2中决定请求网络,则在这一步将返回的网络响应和本地缓存对比,对本地缓存进行增删改操作
CacheStrategy
public final class CacheStrategy {
/** The request to send on the network, or null if this call doesn't use the network. */
public final @Nullable Request networkRequest;
/** The cached response to return or validate; or null if this call doesn't use a cache. */
public final @Nullable Response cacheResponse;
CacheStrategy(Request networkRequest, Response cacheResponse) {
this.networkRequest = networkRequest;
this.cacheResponse = cacheResponse;
}
...
}- 作用:将“请求”和旧的缓存进行分析比较,决定是发起网络请求还是直接使用缓存。具体来说,根据networkRequest和cacheResponse是否为空执行不同的动作
| networkRequest | cacheResponse | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| null | null | 禁止进行网络请求,但缓存不存在或者过期,只能返回503错误 |
| null | non-null | 缓存可以使用,直接返回缓存,不用请求网络 |
| non-null | null | 缓存不存在或者过期,直接访问网络 |
| non-null | non-null | 条件get,请求网络 |
CacheStrategy的加工过程
主要是读取请求头和响应头中有关缓存的HTTP 字段生成CacheStrategy对象,可结合开头与缓存有关的Header查看源码,这里不再赘述
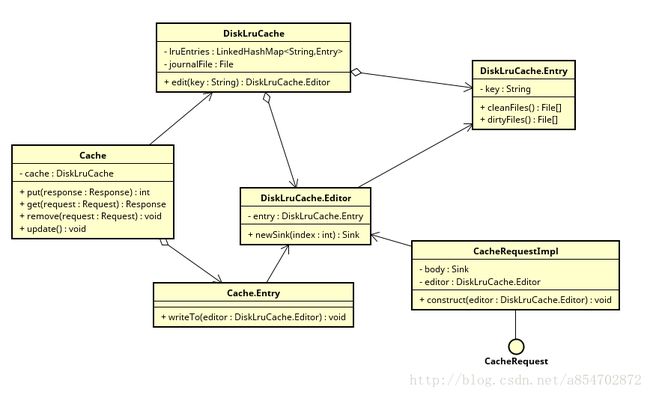
缓存UML类图
Cache
- OkHttp的缓存“门面”,对外提供增删改查方法
- 通过内部的DiskLruCache来管理缓存对象
- 每一条缓存记录的key是url的md5值
public Cache(File directory, long maxSize) {
this(directory, maxSize, FileSystem.SYSTEM);
} //OkHttpClient指定Cache
public Builder cache(@Nullable Cache cache) {
this.cache = cache;
this.internalCache = null;
return this;
}使用时需指定缓存目录和缓存大小上限
DiskLruCache
Cache内部通过DiskLruCache管理cache在文件系统层面的创建,读取,自动清理等工作
public final class DiskLruCache implements Closeable, Flushable {
static final String JOURNAL_FILE = "journal";
static final String JOURNAL_FILE_TEMP = "journal.tmp";
static final String JOURNAL_FILE_BACKUP = "journal.bkp";
static final String MAGIC = "libcore.io.DiskLruCache";
static final String VERSION_1 = "1";
static final long ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER = -1;
static final Pattern LEGAL_KEY_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("[a-z0-9_-]{1,120}");
private static final String CLEAN = "CLEAN";//缓存记录的4种状态
private static final String DIRTY = "DIRTY";
private static final String REMOVE = "REMOVE";
private static final String READ = "READ";
final FileSystem fileSystem;
final File directory;
private final File journalFile;//缓存日志
private final File journalFileTmp;
private final File journalFileBackup;
private final int appVersion;
private long maxSize;
final int valueCount;
private long size = 0;
BufferedSink journalWriter;
final LinkedHashMap lruEntries = new LinkedHashMap<>(0, 0.75f, true);//Entry是缓存文件的描述
...
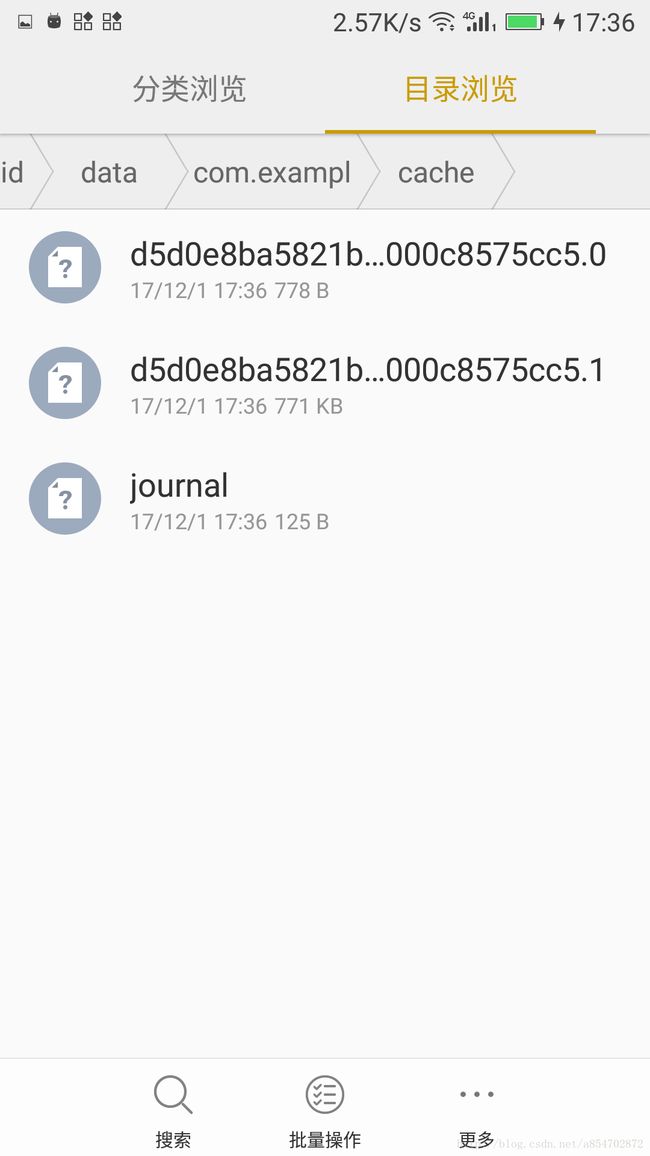
} DiskLruCache通过journal文件和lruEntries(LinkedHashMap)共同管理缓存文件
journal
作用:
- 在进程启动时重建DiskLruCache(lruEntries),将磁盘中的缓存文件和url对应关系加载到内存中
- 记录和跟踪缓存文件的状态
- 保证对缓存文件读写操作的原子性
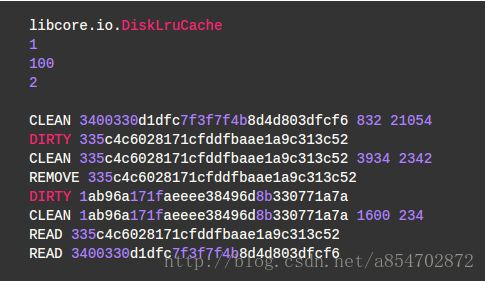
- 前5行固定不变,分别为:常量:libcore.io.DiskLruCache;diskLruCache版本;应用程序版本;valueCount(表示一个Entry对应的文件数量,在Cache中为2),空行
- 接下来每一行对应一个cache entry的一次状态记录,其格式为:[状态(DIRTY,CLEAN,READ,REMOVE),key(url的md5值),文件大小(两个文件:响应头和响应体)]。中间以空格隔开。
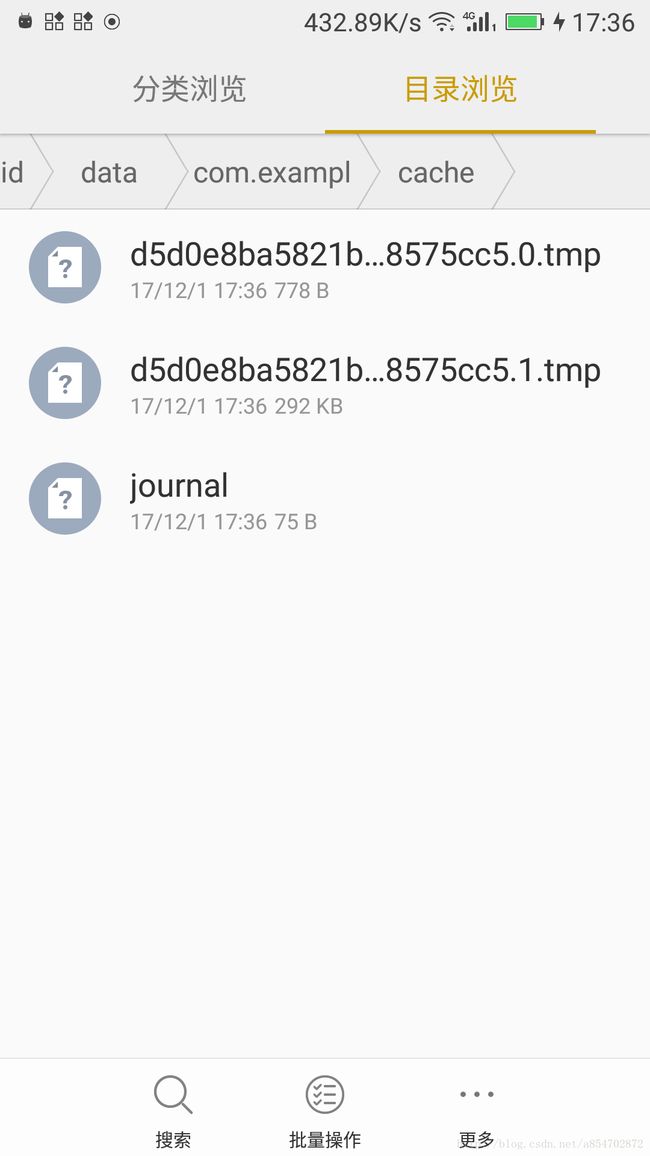
- DIRTY 表示缓存正在被插入、更新或删除,在磁盘中操作成功后会有一条对应的CLEAN或REMOVE记录。否则该DIRTY记录无效(操作未成功,被异常中断过)。相当于DIRTY对应的只是临时文件。
- CLEAN 表示该条缓存是一个有效的记录,可以正常读取(get)。
- READ 表示该条缓存最近被读取过
- REMOVE 表示该条记录对应的缓存文件已经被删除了
DiskLruCache.Entry
private final class Entry {
final String key;
/** Lengths of this entry's files. */
final long[] lengths;
final File[] cleanFiles;
final File[] dirtyFiles;
/** True if this entry has ever been published. */
boolean readable;
/** The ongoing edit or null if this entry is not being edited. */
Editor currentEditor;- Entry是缓存文件在文件系统层面的引用
- key是url的md5值
- 每个Entry可以对应多个文件,具体由DiskLruCache的valueCount决定,默认是2(响应头和响应体)
- cleanFiles代表正常有效的可读缓存,dirtyFiles表示缓存文件正在被创建或更新(但还没完成,只是临时文件),操作完成后会将dirtyFiles重命名为cleanFiles,并将旧的cleanFiles删除
Entry(String key) {
this.key = key;
lengths = new long[valueCount];
cleanFiles = new File[valueCount];
dirtyFiles = new File[valueCount];
// The names are repetitive so re-use the same builder to avoid allocations.
StringBuilder fileBuilder = new StringBuilder(key).append('.');
int truncateTo = fileBuilder.length();
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
fileBuilder.append(i);
cleanFiles[i] = new File(directory, fileBuilder.toString());
fileBuilder.append(".tmp");
dirtyFiles[i] = new File(directory, fileBuilder.toString());
fileBuilder.setLength(truncateTo);
}
}public synchronized void initialize() throws IOException {
assert Thread.holdsLock(this);
if (initialized) {
return; // Already initialized.
}
// If a bkp file exists, use it instead.
if (fileSystem.exists(journalFileBackup)) {
// If journal file also exists just delete backup file.
if (fileSystem.exists(journalFile)) {
fileSystem.delete(journalFileBackup);
} else {
fileSystem.rename(journalFileBackup, journalFile);
}
}
// Prefer to pick up where we left off.
if (fileSystem.exists(journalFile)) {
try {
readJournal();
processJournal();
initialized = true;
return;
} catch (IOException journalIsCorrupt) {
Platform.get().log(WARN, "DiskLruCache " + directory + " is corrupt: "
+ journalIsCorrupt.getMessage() + ", removing", journalIsCorrupt);
}
// The cache is corrupted, attempt to delete the contents of the directory. This can throw and
// we'll let that propagate out as it likely means there is a severe filesystem problem.
try {
delete();
} finally {
closed = false;
}
}
rebuildJournal();
initialized = true;
}- 根据journal文件重建lruEntries,并删除dirty缓存
- 如果journal文件初始化失败会重建journal文件
private void readJournal() throws IOException {
BufferedSource source = Okio.buffer(fileSystem.source(journalFile));
try {
String magic = source.readUtf8LineStrict();
String version = source.readUtf8LineStrict();
String appVersionString = source.readUtf8LineStrict();
String valueCountString = source.readUtf8LineStrict();
String blank = source.readUtf8LineStrict();
if (!MAGIC.equals(magic)
|| !VERSION_1.equals(version)
|| !Integer.toString(appVersion).equals(appVersionString)
|| !Integer.toString(valueCount).equals(valueCountString)
|| !"".equals(blank)) {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal header: [" + magic + ", " + version + ", "
+ valueCountString + ", " + blank + "]");
}
int lineCount = 0;
while (true) {
try {
readJournalLine(source.readUtf8LineStrict());
lineCount++;
} catch (EOFException endOfJournal) {
break;
}
}
redundantOpCount = lineCount - lruEntries.size();
// If we ended on a truncated line, rebuild the journal before appending to it.
if (!source.exhausted()) {
rebuildJournal();
} else {
journalWriter = newJournalWriter();
}
} finally {
Util.closeQuietly(source);
}
}readJournal方法开头校验Journal文件的前面5行是否正确,如果不正确抛出异常,并在之后重建Journal文件。然后通过readJournalLine方法,逐行读取Journal文件的每条缓存记录,并更新对应Entry
private void processJournal() throws IOException {
fileSystem.delete(journalFileTmp);
for (Iterator i = lruEntries.values().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Entry entry = i.next();
if (entry.currentEditor == null) {
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
size += entry.lengths[t];
}
} else {
entry.currentEditor = null;
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
fileSystem.delete(entry.cleanFiles[t]);
fileSystem.delete(entry.dirtyFiles[t]);
}
i.remove();
}
}
} processJournal方法将DIRTY(且无对应CLEAN)的entry从内存和磁盘中一并删除
Response缓存的添加
//CacheInterceptor中intercept方法
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);//缓存响应头
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);//缓存响应体
}响应头的缓存
@Nullable CacheRequest put(Response response) {
String requestMethod = response.request().method();
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(response.request().method())) {
try {
remove(response.request());
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
return null;
}
if (!requestMethod.equals("GET")) {
// Don't cache non-GET responses. We're technically allowed to cache
// HEAD requests and some POST requests, but the complexity of doing
// so is high and the benefit is low.
return null;
}
if (HttpHeaders.hasVaryAll(response)) {
return null;
}
Entry entry = new Entry(response);
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = null;
try {
editor = cache.edit(key(response.request().url()));
if (editor == null) {
return null;
}
entry.writeTo(editor);
return new CacheRequestImpl(editor);
} catch (IOException e) {
abortQuietly(editor);
return null;
}
}- 检查请求头的方法,非”get”的响应不缓存
- 响应头中包含“Vary:*”的不缓存
- 通过DiskLruCache.Editor将响应头信息缓存到磁盘中
- 生成CacheRequest对象为下一步将响应体信息缓存到磁盘中做准备
public @Nullable Editor edit(String key) throws IOException {
return edit(key, ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER);
}synchronized Editor edit(String key, long expectedSequenceNumber) throws IOException {
initialize();
checkNotClosed();
validateKey(key);
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (expectedSequenceNumber != ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER && (entry == null
|| entry.sequenceNumber != expectedSequenceNumber)) {
return null; // Snapshot is stale.
}
if (entry != null && entry.currentEditor != null) {
return null; // Another edit is in progress.
}
if (mostRecentTrimFailed || mostRecentRebuildFailed) {
// The OS has become our enemy! If the trim job failed, it means we are storing more data than
// requested by the user. Do not allow edits so we do not go over that limit any further. If
// the journal rebuild failed, the journal writer will not be active, meaning we will not be
// able to record the edit, causing file leaks. In both cases, we want to retry the clean up
// so we can get out of this state!
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
return null;
}
// Flush the journal before creating files to prevent file leaks.
journalWriter.writeUtf8(DIRTY).writeByte(' ').writeUtf8(key).writeByte('\n');
journalWriter.flush();//在jounar文件上添加DIRTY记录,表示该文件正在被加入缓存
if (hasJournalErrors) {
return null; // Don't edit; the journal can't be written.
}
if (entry == null) {
entry = new Entry(key);//建立和url对应的Entry对象
lruEntries.put(key, entry);//将Entry保存到LinkedHashMap中
}
Editor editor = new Editor(entry);
entry.currentEditor = editor;
return editor;
}- 在journal文件上写入DIRTY记录,表示该条缓存正在被写入
- 新建和url对应的Entry对象,将Entry保存到LinkedHashMap中
- 返回Editor对象,方便下一步真正写入文件流
DiskLruCache.Editor
public final class Editor {
final Entry entry;
final boolean[] written;
private boolean done;
Editor(Entry entry) {
this.entry = entry;
this.written = (entry.readable) ? null : new boolean[valueCount];
}- 每一个DiskLruCache.Editor对象对应一个DiskLruCache.Entry对象
- 负责返回和DIRTY FILE对应的output stream(new sink(int index))及commit修改
Cache.Entry
Entry(Response response) {
this.url = response.request().url().toString();
this.varyHeaders = HttpHeaders.varyHeaders(response);
this.requestMethod = response.request().method();
this.protocol = response.protocol();
this.code = response.code();
this.message = response.message();
this.responseHeaders = response.headers();
this.handshake = response.handshake();
this.sentRequestMillis = response.sentRequestAtMillis();
this.receivedResponseMillis = response.receivedResponseAtMillis();
}- 将Response中除了Responsebody外的信息提取出来
public void writeTo(DiskLruCache.Editor editor) throws IOException {
BufferedSink sink = Okio.buffer(editor.newSink(ENTRY_METADATA));//获取输出流
sink.writeUtf8(url)
.writeByte('\n');
sink.writeUtf8(requestMethod)
.writeByte('\n');
sink.writeDecimalLong(varyHeaders.size())
.writeByte('\n');
for (int i = 0, size = varyHeaders.size(); i < size; i++) {
sink.writeUtf8(varyHeaders.name(i))
.writeUtf8(": ")
.writeUtf8(varyHeaders.value(i))
.writeByte('\n');
}
sink.writeUtf8(new StatusLine(protocol, code, message).toString())
.writeByte('\n');
sink.writeDecimalLong(responseHeaders.size() + 2)
.writeByte('\n');
for (int i = 0, size = responseHeaders.size(); i < size; i++) {
sink.writeUtf8(responseHeaders.name(i))
.writeUtf8(": ")
.writeUtf8(responseHeaders.value(i))
.writeByte('\n');
}
sink.writeUtf8(SENT_MILLIS)
.writeUtf8(": ")
.writeDecimalLong(sentRequestMillis)
.writeByte('\n');
sink.writeUtf8(RECEIVED_MILLIS)
.writeUtf8(": ")
.writeDecimalLong(receivedResponseMillis)
.writeByte('\n');
if (isHttps()) {
sink.writeByte('\n');
sink.writeUtf8(handshake.cipherSuite().javaName())
.writeByte('\n');
writeCertList(sink, handshake.peerCertificates());
writeCertList(sink, handshake.localCertificates());
sink.writeUtf8(handshake.tlsVersion().javaName()).writeByte('\n');
}
sink.close();
}- 将除了响应体外的信息通过输出流写入到磁盘中
private static final int ENTRY_METADATA = 0;//对应响应头
private static final int ENTRY_BODY = 1;//对应响应体public Sink newSink(int index) {//在valuecount为2时,index为0或1
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
if (done) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
if (entry.currentEditor != this) {
return Okio.blackhole();
}
if (!entry.readable) {
written[index] = true;
}
File dirtyFile = entry.dirtyFiles[index];
Sink sink;
try {
sink = fileSystem.sink(dirtyFile);//获取临时文件xxx.0.tmp对应的输出流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
return Okio.blackhole();
}
return new FaultHidingSink(sink) {
@Override protected void onException(IOException e) {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
detach();
}
}
};
}
}获取和指定File对应的输出流
Blockquote
Sink是okio对OutputStream的封装,可简单理解为OutputStream,与之对应的还有source,是okio对InputStream的封装
CacheRequestImpl(final DiskLruCache.Editor editor) {
this.editor = editor;
this.cacheOut = editor.newSink(ENTRY_BODY);//拿到xxx.1.tmp
this.body = new ForwardingSink(cacheOut) {
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (Cache.this) {
if (done) {
return;
}
done = true;
writeSuccessCount++;
}
super.close();
editor.commit();
}
};
}private Response cacheWritingResponse(final CacheRequest cacheRequest, Response response)
throws IOException {
// Some apps return a null body; for compatibility we treat that like a null cache request.
if (cacheRequest == null) return response;
Sink cacheBodyUnbuffered = cacheRequest.body();
if (cacheBodyUnbuffered == null) return response;
final BufferedSource source = response.body().source();//从Response中取出body
final BufferedSink cacheBody = Okio.buffer(cacheBodyUnbuffered);//通过cacheBody将文件写入存储设备中
Source cacheWritingSource = new Source() {
boolean cacheRequestClosed;
@Override public long read(Buffer sink, long byteCount) throws IOException {
long bytesRead;
try {
bytesRead = source.read(sink, byteCount);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true;
cacheRequest.abort(); // Failed to write a complete cache response.
}
throw e;
}
if (bytesRead == -1) {
if (!cacheRequestClosed) {
cacheRequestClosed = true;
cacheBody.close(); // The cache response is complete!
}
return -1;
}
sink.copyTo(cacheBody.buffer(), sink.size() - bytesRead, bytesRead);
cacheBody.emitCompleteSegments();
return bytesRead;
}
@Override public Timeout timeout() {
return source.timeout();
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
if (!cacheRequestClosed
&& !discard(this, HttpCodec.DISCARD_STREAM_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS)) {
cacheRequestClosed = true;
cacheRequest.abort();
}
source.close();
}
};
String contentType = response.header("Content-Type");
long contentLength = response.body().contentLength();
return response.newBuilder()
.body(new RealResponseBody(contentType, contentLength, Okio.buffer(cacheWritingSource)))
.build();
}这一步涉及较多okio的知识,但主要意思是将ResponseBody通过写io缓存到磁盘中
提交更改
public void commit() throws IOException {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
if (done) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
if (entry.currentEditor == this) {
completeEdit(this, true);
}
done = true;
}
}synchronized void completeEdit(Editor editor, boolean success) throws IOException {
Entry entry = editor.entry;
if (entry.currentEditor != editor) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
// If this edit is creating the entry for the first time, every index must have a value.
if (success && !entry.readable) {
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
if (!editor.written[i]) {
editor.abort();
throw new IllegalStateException("Newly created entry didn't create value for index " + i);
}
if (!fileSystem.exists(entry.dirtyFiles[i])) {
editor.abort();
return;
}
}
}//保证两个Dirty File都“写完”才提交
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
File dirty = entry.dirtyFiles[i];
if (success) {
if (fileSystem.exists(dirty)) {
File clean = entry.cleanFiles[i];
fileSystem.rename(dirty, clean);
long oldLength = entry.lengths[i];
long newLength = fileSystem.size(clean);
entry.lengths[i] = newLength;
size = size - oldLength + newLength;
}//将写完的Dirty File(xxx.0.tmp)重命名为Clean File的名字(xxx.0),并删除Dirty File
} else {
fileSystem.delete(dirty);
}
}
redundantOpCount++;
entry.currentEditor = null;
if (entry.readable | success) {//更新journar文件
entry.readable = true;
journalWriter.writeUtf8(CLEAN).writeByte(' ');
journalWriter.writeUtf8(entry.key);
entry.writeLengths(journalWriter);
journalWriter.writeByte('\n');
if (success) {
entry.sequenceNumber = nextSequenceNumber++;
}
} else {
lruEntries.remove(entry.key);
journalWriter.writeUtf8(REMOVE).writeByte(' ');
journalWriter.writeUtf8(entry.key);
journalWriter.writeByte('\n');
}
journalWriter.flush();
if (size > maxSize || journalRebuildRequired()) {
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
}commit成功代表写入缓存完成
缓存的清理
boolean journalRebuildRequired() {
final int redundantOpCompactThreshold = 2000;
return redundantOpCount >= redundantOpCompactThreshold
&& redundantOpCount >= lruEntries.size();
}journal文件的缓存条目数量同时超出阈值(2000)和Entry的数量,说明journal需要重建
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
if (!initialized | closed) {
return; // Nothing to do
}
try {
trimToSize();
} catch (IOException ignored) {
mostRecentTrimFailed = true;
}
try {
if (journalRebuildRequired()) {
rebuildJournal();
redundantOpCount = 0;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
mostRecentRebuildFailed = true;
journalWriter = Okio.buffer(Okio.blackhole());
}
}
}
};void trimToSize() throws IOException {
while (size > maxSize) {
Entry toEvict = lruEntries.values().iterator().next();
removeEntry(toEvict);
}
mostRecentTrimFailed = false;
}在循环中不断删除“旧”文件,直到剩余缓存文件的大小总和小于DiskLruCache初始化时传入的maxSize
boolean removeEntry(Entry entry) throws IOException {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
entry.currentEditor.detach(); // Prevent the edit from completing normally.
}
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
fileSystem.delete(entry.cleanFiles[i]);//删除缓存文件
size -= entry.lengths[i];
entry.lengths[i] = 0;
}
redundantOpCount++;
journalWriter.writeUtf8(REMOVE).writeByte(' ').writeUtf8(entry.key).writeByte('\n');//更新journal
lruEntries.remove(entry.key);//移除entry
if (journalRebuildRequired()) {
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
return true;
}重建journal
synchronized void rebuildJournal() throws IOException {
if (journalWriter != null) {
journalWriter.close();
}
BufferedSink writer = Okio.buffer(fileSystem.sink(journalFileTmp));
try {
writer.writeUtf8(MAGIC).writeByte('\n');
writer.writeUtf8(VERSION_1).writeByte('\n');
writer.writeDecimalLong(appVersion).writeByte('\n');
writer.writeDecimalLong(valueCount).writeByte('\n');
writer.writeByte('\n');
for (Entry entry : lruEntries.values()) {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
writer.writeUtf8(DIRTY).writeByte(' ');
writer.writeUtf8(entry.key);
writer.writeByte('\n');
} else {
writer.writeUtf8(CLEAN).writeByte(' ');
writer.writeUtf8(entry.key);
entry.writeLengths(writer);
writer.writeByte('\n');
}
}
} finally {
writer.close();
}
if (fileSystem.exists(journalFile)) {
fileSystem.rename(journalFile, journalFileBackup);
}
fileSystem.rename(journalFileTmp, journalFile);
fileSystem.delete(journalFileBackup);
journalWriter = newJournalWriter();
hasJournalErrors = false;
mostRecentRebuildFailed = false;
}- 在journalFileTmp中新建journal,且只保留 DIRTY和CLEAN的记录
journalFileTmp新建完成后重命名为journalFile,并将旧的journalFile重命名为journalFileBackup
DiskLruCache总结
- 通过LinkedHashMap实现LRU替换
- 通过journal保证Cache操作的原子性及可用性
- 每一条缓存对应两个状态副本:DIRTY,CLEAN。CLEAN表示当前可用的Cache。DIRTY为编辑状态的cache。由于更新和创建都只操作DIRTY状态的副本,实现了读和写的分离。
- 每一个url对应四个文件,两个状态(DIRY,CLEAN),每个状态对应两个文件:0文件对应存储meta数据,1文件存储body数据。