- DASH Basics: MPD and Segments
- ISO Base Media File Format
- MPEG-2 TS
- Multiple Representations
- Osmo4 Playback
- Some guidelines
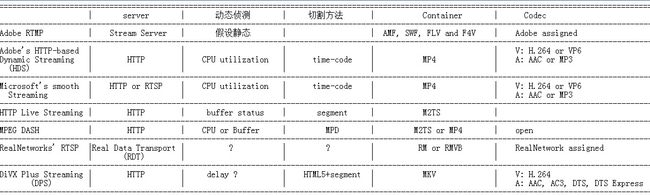
We have been updating the support for DASH Streaming (ISO/IEC 23009-1) in GPAC as of revision 3849. The update covers both content generation tools and player, and both DASH and HLS support.
For more details on what is DASH and HTTP streaming, please refer to this post.
DASH Basics: MPD and Segments
Let’s quickly summarize how a DASH content is made of:
- MPD: an XML document describing where the various media resources present in the content are located. The media resources can be single-media (for example, a video-only MP4 file) or a multiplexed set of streams (for example an AV MPEG-2 Transort Stream). Streams can be scalable (such as SVC) but we won’t go into such details as GPAC doesn’t support advanced description of scalable streams in DASH. Some media resources may exist in different versions, for example different bitrate or language or resolutions. In DASH, such a “version” of the stream is called a representation, and all representations are grouped together in an AdaptationSet.
- segment: a continuous part of a media resource. The segment is the smallest part of the media that can be located in the MPD. What a segment exactly contains depends on the underlying media format of the content.
- subsegment: a continuous part of a segment, or of a subsegment.
- sidx: short name for SegmentIndexBox, this is an ISOBMF (MP4/3GP container) structure describing a segment by giving its earliest presentation time, how the segment is further divided into subsegments, random access points locations (byte offset) and timing in the segment payload. The goal of the SIDX is to build an index of the segment at a given granularity to simplify trick modes (seeking, fast-forward, fast-rewind, …).
There are several ways to refer to a segment in an MPD. If the file is made of a single segment (-single-segment option for ISOBMF), one will likely use SegmentBase element. If a file is made of several segments, each segment will be identified by the SegmentList syntax in the MPD, using byte ranges. For other cases, we need to instruct MP4Box how to refer to segments (and how to store them as well). The following switches are defined:
- -segment-ext EXT: tells MP4Box to generate segments with EXT extension (by defaultm4s for ISOBMF and or ts for MPEG-2)
- -segment-name NAME: tells MP4Box to generate each segment in a dedicated file, called NAME%d.EXT. NAME can also have %s in it, in which case %s will be replaced by the name of the file being dashed without folder indication and extension. By default, such segments will be stored using the SegmentList syntax in the MPD.
- -url-template: if set when generating segements in different files, the segments will be refered to using the SegmentTemplate syntax in the MPD.
ISO Base Media File Format
For content based on ISOBMF (ISO/IEC 14496-12), MP4Box can be used to cut files into DASH segments. Before going any further, some definitions will be needed:
- segment: for ISOBMF, a segment is a consecutive set of movie fragments. Each movie fragment is composed of a moof box followed by mdat box(es), and all data adressing in the mdat(s) are done using relative offsets in the moof.
- subsegment: a part of a segment, made of a consecutive set of movie fragments. A subsegment can be further divided in subsegments, until only a single movie fragment per subsegment is present.
With that in mind, we can generate DASH content by playing with the following MP4Box parameters:
- -dash X: produce segments of roughly X milliseconds.
- -frag Y: use movie fragments of roughly Y milliseconds. By default, fragments duration is 500 milliseconds.
- -rap: attempts to cut segments so that they all start with an access point (IDR, I-frame or beginning of a gradual decoding refresh for example).
- -subsegs-per-sidx N: specifies how many subsegments per sidx we would like. This only covers the first level of segment spliting (MP4Box doesn’t handle subsegments subdivision into subsegments). Noticable values are:
- <0: disable: sidx will not be produced
- 0: a single sidx box is used for the entire segment, and each subsegment is made of a single movie fragment (i.e., there will be X/Y subsegments in sidx). This is the default value.
- >0: produces X/Y/N subsegments referenced in the first sidx.
- -daisy-chain: this is only used when producing multiple subsegments per segment (-subsegs-per-sidx). If specified, subsegments will be described in SIDX in which the last entry (subsegment) points to the next SIDX. Otherwise, multiple SIDXs will be stored in a hierarchical way, with the first SIDX pointing to each SIDX of the subsegments.
- -single-segment: special mode indicating that the file should be segmented as one single segment. In that case, the dash duration X becomes the subsegment duration, and a single sidx is produced before any movie fragment.
Now let’s see an example.
Dashing a file with 10 seconds, rap-aligned segments with a fragment duration (i.e. subsegment duration since we don’t subdivide the SIDX) of 1 sec:
MP4Box -dash 10000 -frag 1000 -rap test.mp4
The same with a separated segment using template addressing, and 5 subsegments per segments:
MP4Box -dash 10000 -frag 1000 -rap -segment-name myDash
-subsegs-per-sidx 5 -url-template test.mp4
Generating an onDemand profile DASH file (single segment) is just as simple:
MP4Box -dash 10000 -frag 1000 -rap -single-segment test.mp4
MPEG-2 TS
MP4Box can also be used to segment MPEG-2 TS files. The same options as the ISOBMF case are used, with the following restrictions:
- -single-segment, -frag, -subsegs-per-sidx and -daisy-chain are ignored
- -rap splits at the PAT preceeding the RAP found, but does not repacketize the TS to make sure it begins with the RAP
For example, spliting a TS in 10 seconds segments can be done with
MP4Box -dash 10000 -url-template -segment-name segments test.ts
Also note that it is possible to use MP4Box to translate an existing m3u8 (Apple HLS) to a conformant MPD, using the -mpd switch:
MP4Box -mpd test.mpd [-url-template] [http://...]myfile.m3u8
Multiple Representations
You now know how to create a conformant DASH content from a given file, but what about the ‘A for Adaptive’ in DASH ? At first thought it would just be enough to let you with a bunch of MPD and a good XSLT, to produce your final MPD (which you will have to do anyway I believe). However, there are some tricks in the segment generation itself that cannot be easily done.
The most problematic thing is that, when building ISOBMF files designed for bitstream switching, the initial bootstrap of the DASH session (i.e. moov and co) must contain all sample descriptions used in all representations of the media. Therefore, we will need MP4Box here to generate files with correct sample descriptions, and segments with correct sampleDescriptionIndex
Although this might look a bit complex, the process is itself quite simple; assuming you have encoded file1, .., fileN version of your movie, you can generate a nice adaptive MPD as follows:
MP4Box -dash 10000 [other options as seen above] -out final.mpd file1.mp4 … fileN.mp4
This works for both ISOBMF and TS files. Additionnaly, you don’t want segments to be overriden when generating segments in dedicated files for each representation. MP4Box gives you the possibility to format the name of the segment using -segment-name:
MP4Box -dash 10000 -segment-name mysegs_%s -url-template
-out final.mpd file1.mp4 ... fileN.mp
Osmo4 Playback
You can test DASH playback in GPAC using Osmo4/MP4Client. The player supports a good part of the technology:
- playback from an HTTP server or from local storage for test purposes.
- Media segments based on TS and ISOBMF
- independent component download (one adaptation set for audio, one for video)
- most MPD syntax is supported
- (some) bitstream switching. ISOBMF is not complete, multiple SampleDescription are not supported yet
- manual quality switching by using ctrl+h and ctrl+l
- basic automatic quality switching when playing HTTP urls
Some guidelines
DASH is still quite new, and few players support it. The main problematic, especially with ISOBMF, is to address the bitstream switching scenario while not breaking existing implementations. We would therefore recommend:
- do NOT mix codecs in your various representations of the media streams (whether multiplexed or not). This is not supported by existing players and will break seemless switching in most cases. And there is no point doing so, so don’t do it
- for AVC video, use dedicated SPS and PPS IDs for your different streams. This can even be done with x264 using –sps-id option. This will ensure that the produced files can still be played by most implementations supporting movie fragments.
- Obey the specification: use the same codec for each media in an adaptation set.