基于linux下的线程池复制多级目录及文件
1. 设计目标
拷贝指定文件夹下的所有子文件夹和文件,利用多线程加快拷贝速度。
2.设计方案
./xxx /源文件夹 /目标文件夹
递归遍历文件夹下所有文件,为文件夹便创建,为文件便复制
总是先创建文件夹,再复制文件,将复制文件投入线程池任务列队
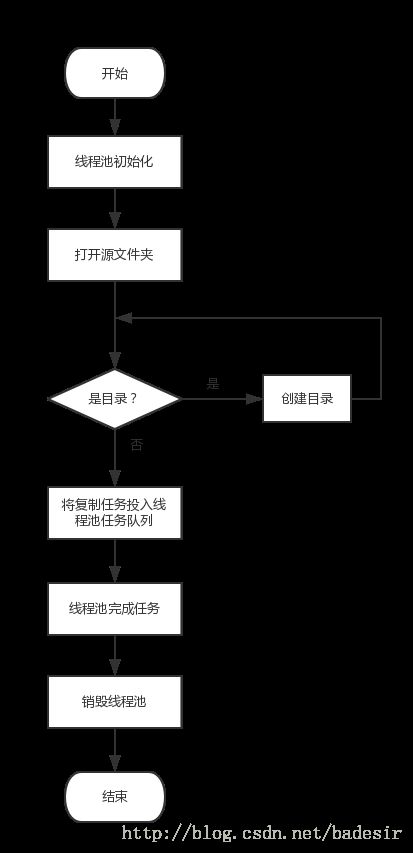
3.系统框架
4.源码分析
4.1 线程池接口函数
#define MAX_WAITING_TASKS 20000
#define MAX_ACTIVE_THREADS 20
struct task
{
void *(*do_task)(void *arg);
void *arg;
struct task *next;
};
typedef struct thread_pool
{ //互斥量和条件变量
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
//停止标志位
bool shutdown;
//任务链表
struct task *task_list;
//线程号数组
pthread_t *tids;
unsigned max_waiting_tasks;
unsigned waiting_tasks;
unsigned active_threads;
}thread_pool;
//线程池初始化 threads_number->初始线程数
bool init_pool(thread_pool *pool, unsigned int threads_number);
//添加任务进线程池 do_task->功能函数(实际使用只需将此函数改为自己需要的功能函数即可)
bool add_task(thread_pool *pool, void *(*do_task)(void *arg), void *arg);
//添加线程
int add_thread(thread_pool *pool, unsigned int additional_threads_number);
//移除线程
int remove_thread(thread_pool *pool, unsigned int removing_threads_number);
//销毁线程池
bool destroy_pool(thread_pool *pool);
void *routine(void *arg);4.2文件操作函数框架
#define SIZE 512
char filecwd[SIZE];
char dircwd[SIZE];
//定义文件的结构体
struct filepath
{
char filesp[SIZE];
char filedp[SIZE];
};
void rootdir(char sp[SIZE],char dp[SIZE]);
void printdir(char *dir,char sp[SIZE],char dp[SIZE],thread_pool *pool);
void replace_string(char * source_str,char * targ_str,char *val);
void mk_dir(char dpath[]);
void* copy_file(void *arg);
#endif4.3遍历目录函数
void printdir(char *dir,char sp[SIZE],char dp[SIZE],thread_pool *pool)
{
//打开目录指针
DIR *Dp;
//文件目录结构体
struct dirent *enty;
//详细文件信息结构体
struct stat statbuf;
//打开指定的目录,获得目录指针
if(NULL == (Dp = opendir(dir)))
{
fprintf(stderr,"can not open dir:%s\n",dir);
return;
}
//切换到这个目录
chdir(dir);
//遍历这个目录下的所有文件
while(NULL != (enty = readdir(Dp) ))
{
//通过文件名,得到详细文件信息
lstat(enty->d_name,&statbuf);
//判断是不是目录
if(S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode))
{
if(0 == strcmp(".",enty->d_name) ||
0 == strcmp("..",enty->d_name)) //当前目录和上一目录过滤掉
{
continue;
}
getcwd(dircwd,SIZE);
strcat(dircwd,"/");
strcat(dircwd,enty->d_name); //工作路径+目录名
replace_string(dircwd,sp,rindex(sp,'/'));
char dirdp[SIZE];
sprintf(dirdp,"%s%s",dp,dircwd); //目录最终绝对路径
mk_dir(dirdp); //创建目录
//递归调用
printdir(enty->d_name,sp,dp,pool);
}
else
{
struct filepath fpath; //定义文件路径结构体
char temp_path[SIZE];
getcwd(filecwd,SIZE);
sprintf(fpath.filesp,"%s/%s",filecwd,enty->d_name); //源文件绝对路径
strcpy(temp_path,fpath.filesp); //暂存源文件绝对路径
replace_string(temp_path,sp,rindex(sp,'/'));
sprintf(fpath.filedp,"%s%s",dp,temp_path); //目标文件绝对路径
add_task(pool, copy_file, (void *)(&fpath)); //添加复制文件任务
usleep(9000); //线程休息时间
}
}
//切换到上一及目录
chdir("..");
//关闭文件指针
closedir(Dp);
}
/*
据说线程池的线程也需要一定时间休息, 因而我在实际操作中在添加任务add_task()后加了休眠函数usleep(), 否则会导致遗漏任务,休眠的时间根据自己执行的功能函数时间而具体决定
*//*将字符串中指定子字符串用指定字符串代替,targ_str 是被替换的,val是替换的字符串*/
void replace_string(char * source_str,char * targ_str,char *val)
{
char temp_sstr[SIZE],result[SIZE];
char *p=NULL,*q=NULL;
int len=0;
memset(result,0,sizeof(result));
memset(temp_sstr,0,sizeof(temp_sstr));
strcpy(temp_sstr,source_str);
p=temp_sstr;
q=temp_sstr;
len=strlen(targ_str);
while(q!=NULL)
{
if((q=strstr(p,targ_str))!=NULL)
{
strncat(result,p,q-p);
strcat(result,val);
strcat(result,"\0");
q+=len;
p=q;
}
else
strcat(result,p);
}
strcpy(source_str,result);
}4.4创建目录及复制文件函数
//创建目录函数
void mk_dir(char dpath[])
{
mkdir(dpath,S_IRWXU|S_IRGRP|S_IROTH);
}
//复制文件函数
void* copy_file(void *arg)
{
struct filepath *p = (struct filepath *)arg; //转换
FILE *fb_from,*fb_to;
int rd_cnt;
char rd_buf[1024];
char path1[SIZE];
char dp1[SIZE];
fb_from = fopen(p->filesp,"r");
if(fb_from == NULL)
{
printf("read open file failure:%s \n",p->filesp);
return NULL;
}
fb_to = fopen(p->filedp,"w+");
if(fb_to == NULL)
{
printf("write open file failure: %s \n",p->filedp);
return NULL;
}
while((rd_cnt = fread(rd_buf,sizeof(char),1024,fb_from)) > 0)
{
fwrite(rd_buf,sizeof(char),rd_cnt,fb_to);
fflush(fb_to);
}
i++;
printf("%d copy success : %s\n",i,p->filedp);
fclose(fb_from);
fclose(fb_to);
return NULL;
}void rootdir(char sp[SIZE],char dp[SIZE])
{
mkdir(dp,S_IRWXU|S_IRGRP|S_IROTH); //创建目标根目录
char dp1[SIZE];
strcpy(dp1,dp);
strcat(dp1,rindex(sp,'/'));
mkdir(dp1,S_IRWXU|S_IRGRP|S_IROTH); //创建源根目录
}4.5main函数
#include "thread_pool.h"
#include "file.h"
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 3)
{
printf("path error\n");
return -1;
}
thread_pool *pool = malloc(sizeof(thread_pool));
//线程池初始化
init_pool(pool, 15);
rootdir(argv[1],argv[2]);
printdir(argv[1],argv[1],argv[2],pool);
destroy_pool(pool);
return 0;
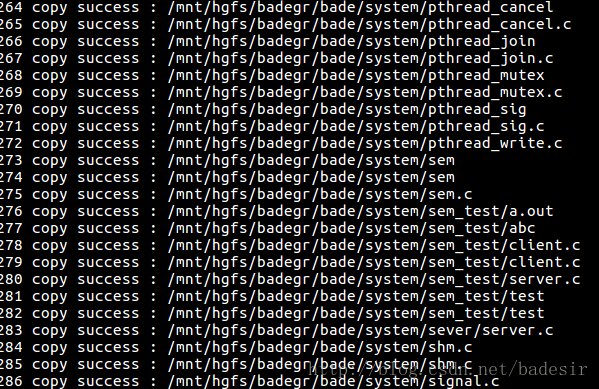
}5.最终效果
6.心得笔录
这个小程序主要是靠文件夹递归查找文件为核心实现的,局限在于只能识别目录与一般文件,对管道等文件类型无法识别;
对线程池的理解还不够深,对互锁和条件变量使用不够清楚;
出现过复制丢失文件的情况,原因应该为添加任务后的休息时间,太短容易造成丢失,原因还需研究。
先这样了…加油
2017.8.18
bade