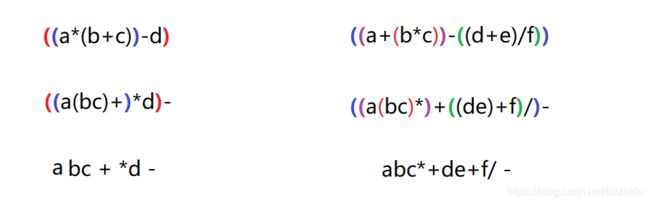数据结构面试题及答案+阿里云+腾讯+网易有道面试题+栈和队列专题(高频)
数据结构面试题及答案-栈和队列专题(高频)
- 本节目标
- 1、 栈特性相关选择题一:不可能的出栈序列
- 2、栈特性相关选择题二:中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰式)
- 3、判定字符串括号是否匹配(网易有道2018年面试题)
- 4、两个栈实现队列(腾讯2019年面试原题)
- 5、实现最小栈(阿里云2020年面试原题)
- 1、栈特性相关选择题一:不可能的出栈序列
- 高频考察的大厂云图:
- 解题思路:
- 2、栈特性相关选择题二:中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰式)
- 高频考察的大厂云图:
- 解题思路:
- 3、判定字符串括号是否匹配
- 高频考察的大厂云图:
- 解题思路:
- 代码实现:
- 4、两个栈实现队列
- 高频考察的大厂云图:
- 解题思路:
- 代码实现:
- 5、 实现最小栈
- 高频考察的大厂云图:
- 解题思路:
- 代码实现:
本节目标
-
1、 栈特性相关选择题一:不可能的出栈序列
-
2、栈特性相关选择题二:中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰式)
-
3、判定字符串括号是否匹配(网易有道2018年面试题)
-
4、两个栈实现队列(腾讯2019年面试原题)
-
5、实现最小栈(阿里云2020年面试原题)
1、栈特性相关选择题一:不可能的出栈序列
若进栈序列为 1,2,3,4 ,进栈过程中可以出栈,则下列不可能的一个出栈序列是(C)
A 1,4,3,2
B 2,3,4,1
C 3,1,4,2
D 3,4,2,1
高频考察的大厂云图:
解题思路:
该题主要是考察栈的特性,栈是后进先出的一种数据结构,只要记住该特性就可以,题目说了在入栈的过程中,可以出栈,因此该题目最近但的方式就是用每个选项来模拟入栈和出栈过程就可以,比如:
A: 1 4 3 2–> 1 入栈,然后出栈;2 3 4依次入栈,然后再一次出栈,可以得到该序列,说明A选项正确,后面选项以此类推。
2、栈特性相关选择题二:中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰式)
1.表达式 a*(b+c)-d 的后缀表达式是:(B)
A、abcd*+-
B、abc+*d-
C、abc*+d-
D、-+*abcd
2.表达式 a+b*c-(d+e)/f 的后缀表达式为( abc*+de+f/ -)。
高频考察的大厂云图:
解题思路:
- 先将中缀表达式,从左到右,先乘除后加减,对应位置加上括号。
- 将每个括号的运算符移到括号外面
- 去掉括号,即是后缀表达式。
3、判定字符串括号是否匹配
OJ链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/
高频考察的大厂云图:
解题思路:
该题是栈经典的应用。比如:{[]}就是匹配的
- 从前往后依次取每一个字符
- 如果该字符是左括号,则入栈
- 如果是右括号:
- 如果栈为空,则不匹配,当前右括号没有与之匹配的左括号,直接返回false
- 如果栈非空:取栈顶的左括号,检测是否与当前右括号匹配
- 匹配,当前左括号出栈,继续
- 不匹配,直接返回false
- 遍历完所有括号之后,如果栈非空,说明左括号比右括号多,则不匹配,如果栈空则完全匹配
代码实现:
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if(ch == '(' || ch == '[' || ch == '{') {
stack.push(ch);
}else {
//1、判断栈是否为空
if(stack.empty()) {
System.out.println("右括号多!");
return false;
}
//先拿到栈顶元素的括号
char ch2 = stack.peek();
if(ch2 == '(' && ch == ')' || ch2 == '[' && ch == ']'
|| ch2 == '{' && ch == '}') {
stack.pop();
}else {
System.out.println("左右括号不匹配");
return false;
}
}
}
if (!stack.empty()) {
System.out.println("左括号多!");
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
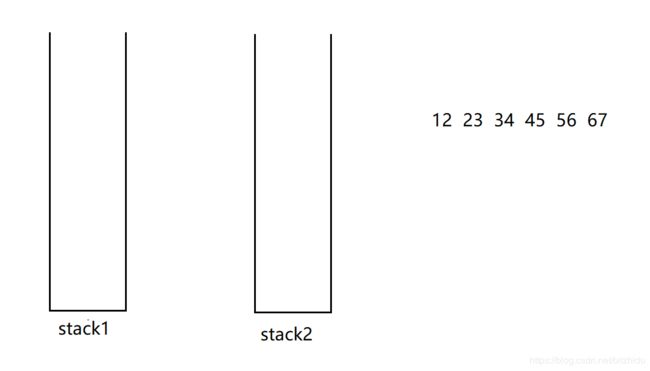
4、两个栈实现队列
OJ链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
高频考察的大厂云图:
解题思路:
队列的特性:先进先出 栈的特性:后进先出
本解法主要是使用两个栈来模拟实现队列的特性,一个栈用来模拟入队列,一个栈用来模拟出队列
-
入队列
假设栈1模拟入队列,即每次入队列时都将元素插入到栈1中
-
出队列
用栈2模拟出队列,如果栈2中没有数据时,将栈1中所有的数据导入到栈2再出栈,因为栈是后进先出,将栈1中数据导入到栈2后,先队列的元素刚好在栈2的栈顶,就可以先出了
-
获取队头元素
直接获取栈2的栈顶元素,当栈2没有元素时,将栈1中元素移动到栈2中,再取栈顶元素,但是该操作与出队列有点重复,因此:先出队列,然后保存元素作为返回值,再将该元素入队列即可
-
判空
如果队列底层的两个栈都是空的,则队列为空
代码实现:
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
this.stack1 = new Stack<>();
this.stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()) {
//导入第一个栈的元素
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()) {
//导入第一个栈的元素
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
//stack2.empty()
return stack2.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
if(stack1.empty() && stack2.empty()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
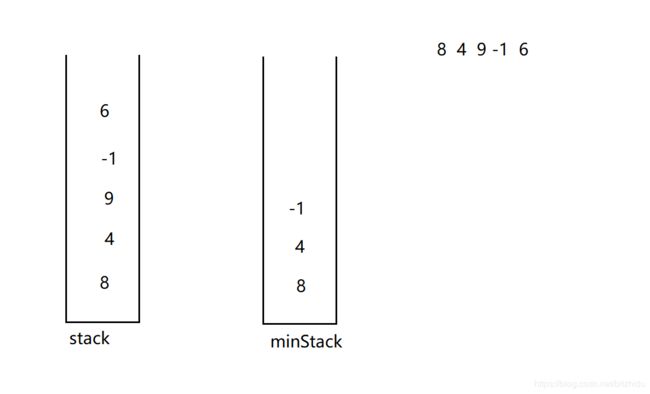
5、 实现最小栈
OJ链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-stack/
高频考察的大厂云图:
解题思路:
本方法采用两个栈来模拟实现:minStack 栈主要用来保存最小值,stack 栈主要用来保存入栈的数据
-
入栈
入栈时每次都将元素向stack 数据栈中放一个,注意该元素入栈后可能会是栈中的最小值,因此可能需要更新最小栈,当minStack 栈为空,或者入栈元素小于等于当前栈中最小值(即minStack 的栈顶元素)时,将该元素在minStack 栈中也放置一份
-
出栈:
当stack 和minStack 栈顶元素相等时候,minStack 栈要出一个元素
stack 每次出栈都要出一个元素
-
获取栈顶元素
取stack 数据栈栈顶即可
-
获取栈中的最小值
获取minStack 栈顶元素即可
代码实现:
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
this.stack = new Stack<>();
this.minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(minStack.empty()) {
//最小栈内没有元素
minStack.push(x);
}else {
//最小栈内有元素 拿到栈顶元素 和 x比较
int top = minStack.peek();// -2
if(x <= top) {
minStack.push(x);
}
}
}
public void pop() {
if(!stack.empty()) {
int tmp = stack.pop();
if(tmp == minStack.peek()) {
minStack.pop();
}
}
}
public int top() {
if(stack.empty()) {
return -1;
}
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
if(minStack.empty()) {
return -1;
}
return minStack.peek();
}
}
如果你看了以后不是很明白,你可以点击看下面的视频讲解:
鼠标点击这里
或者观看:
数据结构高频面试题之栈和队列(JAVA实现)
如果视频中遇到问题,请咨询:1092687209(QQ群)
下一篇:https://blog.csdn.net/bitzhidu/article/details/106645101
文章还不错,请点赞
想看什么内容,请留言
持续更新有价值的内容~~