前端面试题精选
1.用es5实现es6中类的继承
function Animal(){
this.name="动物";
this.sex="男孩";
}
Animal.prototype.eat = ()=>{console.log("吃食物")}
function Dog(){
Animal.call(this);
this.name="狗狗";
}
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;
Dog.prototype.bark = ()=>{console.log("狗在叫")}
/*
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;这两句代码其实可以使用 Dog.prototype.__proto__ = Animal.prototype代替.
*/结果:
2.你知道多少种数组去重的方法?
方法1:
function listUnique(list){
let arr = [];
list.forEach((item)=>{
if(!arr.includes(item)){
arr.push(item);
}
})
return arr;
}
方法2:
function listUnique(list){
let obj = {},arr = [];
list.forEach((item)=>{
if(!obj[item]){
obj[item] = true;
arr.push(item);
}
})
return arr;
}
方法3:
function listUnique(list){
let set = new Set(list); //Set与数组类似,但是它存储的值是唯一的
return [...set];
}
3.实现script的延迟加载有多少种方法
1.使用动态创建script标签的方式实现延迟加载
function lazyLoad(src){ //需要延迟加载的时候传入要加载的js路径
let script = document.createElement("SCRIPT");
script.src = src;
document.body.appendChild(script);
}
2.操作dom的方式实现延迟加载
3.async属性
HTML5为
4.call函数实现
Function.prototype._call = function (obj, ...rest) {
if (typeof obj === "object" && obj !== null) {
obj.fun = this;
obj.fun(...rest);
delete obj.fun;
} else {
this(...rest);
}
}
function test(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c, this.name);
}
test._call({ name: "kay" }, 1, 2, 3);5.apply函数实现
Function.prototype._apply = function (obj, arr = []) {
if (typeof obj === "object" && obj !== null) {
obj.fun = this;
obj.fun(...arr);
delete obj.fun;
} else {
this(...arr);
}
}
function test(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c, this.name);
}
test._apply({ name: "kay" }, [1, 3, 5]);6.bind函数实现
Function.prototype._bind = function (obj, ...rest) {
if (typeof obj === "object" && obj !== null) {
const obj_copy = { ...obj, fun: this };
return function (...rest2) {
return obj_copy.fun(...rest, ...rest2);
}
} else {
const fun = this;
return function (...rest2) {
return fun(...rest, ...rest2);
}
}
}
function fun1(a, b) {
return this.x + a + b;
}
const fun2 = fun1._bind({ x: 1 }, 2);
console.log(fun2(3));7.你能写出几种节流函数
//时间戳版本(立即执行)
function throttle(fun, delay = 250) {
let old_time = 0;
return function (...args) {
const now = new Date().getTime();
if (now - old_time >= delay) {
fun(...args);
old_time = now;
}
}
}
//定时器版本(延迟执行)
function throttle(fun, delay = 250) {
let running = false;
return function (...args) {
if (running) {
return false;
}
running = true;
let timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
fun(...args);
running = false;
}, delay)
}
}验证方法:
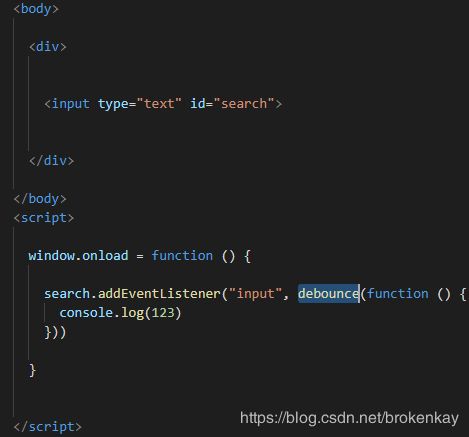
window.onload = function () {
window.onresize = throttle(function () {
console.log(123);
}, 1000)
}8.实现防抖函数
//延迟执行
function debounce(fn, delay = 300) {
let timer = null;
return function (...args) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
fn(...args);
}, delay)
}
}
//和上面函数相比多了一个初次进入函数时会立即执行
function debounce(fn, delay = 300) {
let timer = null;
return function (...args) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
}
if (timer === null) { //第一次执行
fn(...args);
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
fn(...args);
}, delay)
}
}验证方法:
9.模拟实现new(创建实例)
/**
* new主要做三件事情
*
* 1.创建一个空对象
* 2.构造函数的this指向该空对象
* 3.执行构造函数
* 4.返回该对象
*/
function _new(constructor) {
let obj = {};
return function (...args) {
constructor.apply(obj, args);
obj.__proto__ = constructor.prototype;
return obj;
}
}验证方法:
function test(a, b) {
this.name = `测试:${a},${b}`;
}
test.prototype.init = function () { console.log("测试原型对象上面的方法") }
const obj = _new(test)(1, 2);//创建的新对象
console.log(obj);
obj.init();10.你知道多少种浅拷贝和深拷贝的方法
/**
* 使用函数的嵌套实现深拷贝
*/
function deepCopy(data) {
if (Array.isArray(data)) { // 对数组的处理
let arr = [];
data.forEach((item) => {
arr.push(deepCopy(item));
})
return arr;
} else if (Object.prototype.toString === "[object Object]" && data !== null) { //对对象的处理
let obj = Object.create(null);
for (let key in data) {
obj[key] = deepCopy(data[key]);
}
return obj;
} else { //其他类型数据处理
return data;
}
}
/*
* 利用json方法实现深拷贝,但是缺点是不能拷贝函数
*/
function deepCopy(data) {
try {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(data));
} catch (error) {
return data;
}
}
/**
* 使用es6解析结构实现浅拷贝
*/
function lightCopy(data) {
if (Array.isArray(data)) {
return [...data];
} else if (Object.prototype.toString === "[object Object]" && data !== null) {
return { ...data };
} else {
return data;
}
}
/**
* 使用Object.assign实现浅拷贝
*/
function lightCopy(data) {
if (typeof data !== "object" || typeof data === null) {
return data;
}
return Object.assign(data);
}11.实现instanceof
/**
* @param {*对象} left
* @param {*构造函数} right
*/
function _instanceof(left, right) {
let _left = left.__proto__;
const _right = right.prototype;
while (true) {
if (_left === _right) {
return true;
} else if (_left === null || _left === undefined) {
return false;
} else {
_left = _left.__proto__;
}
}
}
console.log(_instanceof({}, Object));
console.log(_instanceof([], Array));
console.log(_instanceof(new Number(123), Number));
console.log(_instanceof(new String("String"), String)); //instanceof只能验证对象是否是特定类的一个实例.例如 var test = "string";_instanceof(test,String)结果为false
console.log(_instanceof([], Object));
12.实现Object.create
Object._create = function (obj) {
function F() { }
F.prototype = obj;
return new F();
}
const obj = Object._create(null);
console.log(obj);13.实现Array.isArray
Array._isArray = function (origin) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(origin) === "[object Array]";
}
console.log(Array._isArray({}));14.实现reduce
Array.prototype._reduce = function(fn,data){
const array = this;
let start_index = 0;
if(data === null || data === undefined){
data = array[0];
start_index = 1;
}
for(let i = start_index;i{
prev[index] = current;
return prev;
},obj)
console.log(result); 15.获取对象上所有的可枚举的属性(不包括原型链上的属性)
Object._getOwnPropertyNames = function(data){
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(data)!== "[object Object]"){
return null;
}
let arr = [];
for(let key in data){
if(data.hasOwnProperty(key)){
arr.push(key);
}
}
return arr;
}
let obj = {
a:1,
b:2,
c:function(){}
}
console.log(Object._getOwnPropertyNames(obj));16.请分别使用Object.defineProperty和Proxy实现双向数据绑定
//使用Object.defineProperty实现
const data = {};
const data_bak = {
text:""
}
const inputText = document.getElementById("inputText");
const showText = document.getElementById("showText");
Object.defineProperty(data,"text",{
set(value){
inputText.value = value;
showText.innerText = value;
data_bak.text = value;
},
get(){
return data_bak.text;
}
})
inputText.oninput = function(e){
data.text = e.target.value;
}
//使用Proxy实现
const data = {
text:""
};
const inputText = document.getElementById("inputText");
const showText = document.getElementById("showText");
const proxyItem = new Proxy(data,{
set(target,key,value){
inputText.value = value;
showText.innerText = value;
target[key] = value;
},
get(target,key){
return target[key];
}
})
inputText.oninput = function(e){
proxyItem.text = e.target.value;
}17.实现forEach
Array.prototype._forEach = function(fn){
const array = this;
for(let i=0;i{
item.value++;
})
console.log(arr); 18.模拟实现async await
function async(fn){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
const gennerator = fn();
function next(data){
const result = gennerator.next(data);
if(result.done){ //运行完成了
resolve(result.value);
}else{
if(result.value instanceof Promise){
result.value.then((value)=>{
next(value)
}).catch((e)=>{
reject(e);
})
}else{
next(result.value);
}
}
}
next();
})
}验证方法
function delay(){
return new Promise((resolve)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(100);
},1000)
})
}
function* getData(){
let data = yield delay();
data++;
data = data + (yield 100);
data = data + (yield delay());
return data;
}
async(getData).then((value)=>{
console.log(value); //结果为301
})19.题目如下
题目:有如下的求和函数
function sum(a,b,c,d,e){
return a+b+c+d+e;
}
请用函数柯里化的方式编写一个增强函数currying,如果当传入增强后的函数的参数个数等于sum的参数个数时才执行sum函数
例如:
const newFn = currying(sum);
console.log(newFn(1,2,3,4)); //结果为[Function]
console.log(newFn(1)(2)(3,4,5)); //结果为15
console.log(newFn(1)(2)(3)(4)(5)); //结果为15/**
* 函数珂里化
*/
function currying(fn){
const length = fn.length;//调用函数的length属性可以得到该函数拥有几个参数
return function child(...args){
if(args.length>=length){
return fn(...args);
}else{
return (...new_args)=>{
return child(...args,...new_args);
}
}
}
}20.箭头函数能new吗?为什么?
箭头函数不能使用new创建实例.new操作符其实做了四件事.1.创建一个空对象,将this指向该对象2.执行构造函数3.将空对象的__proto__指向构造函数的原型对象4.最后返回该对象.箭头函数为什么不能new呢?首先它没有自己的this指向,其次箭头函数没有原型对象.
21.有形似如下树形结构任意层级的数据static,请编写一个函数findName通过传入数据源static和type_id返回相应的type_name.例如:
const static = {
type_id:1,
children:[
{
type_id:2,
type_name:"2号",
children:[{
type_id:5,
type_name:"5号",
children:[
{type_id:6, type_name:"6号",},
{type_id:88, type_name:"88号",}
]
}]
},
{
type_id:3,
type_name:"3号",
}, {
type_id:4,
type_name:"4号",
children:[{
type_id:7,
type_name:"7号",
},{
type_id:8,
type_name:"8号",
}]
}
]
}
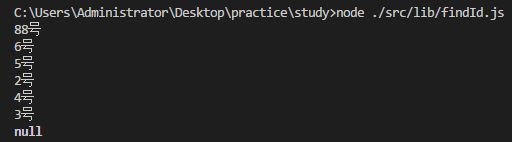
console.log(findName(static,88)); //返回88号
console.log(findName(static,6)); //返回6号
console.log(findName(static,5)); //返回5号
console.log(findName(static,2)); //返回2号
console.log(findName(static,100)); //返回null参考编码:
const toString = Object.prototype.toString;
const static = {
type_id:1,
children:[
{
type_id:2,
type_name:"2号",
children:[{
type_id:5,
type_name:"5号",
children:[
{type_id:6, type_name:"6号",},
{type_id:88, type_name:"88号",}
]
}]
},
{
type_id:3,
type_name:"3号",
}, {
type_id:4,
type_name:"4号",
children:[{
type_id:7,
type_name:"7号",
},{
type_id:8,
type_name:"8号",
}]
}
]
}
function findName(data,id){
if(typeof data !== "object" || data === null){
return false;
}
if(toString.call(data) === "[object Object]"){
data = [data];
}
const result = clac(data,id,[]);
if(result){
let value;
Array.from(Array(result.length)).forEach((v,index)=>{
if(index == 0){
value = data[result[index]];
}else{
value = value.children[result[index]];
}
})
if(value){
return value.type_name;
}
}else{
return null;
}
}
function clac(data,id,array){
for(let i = 0;i运行结果:
22.请实现迭代器函数Iterator,如下所示:
const it = Iterator([1,2,3,4]);
console.log(it.next()); //输出{ done: false, value: 1 }
console.log(it.next()); //输出{ done: false, value: 2 }
console.log(it.next()); //输出{ done: false, value: 3 }
console.log(it.next()); //输出{ done: false, value: 4 }
console.log(it.next()); //输出{ done: true, value: undefined }Iterator函数代码实现:
function Iterator(array){
let i = 0;
return {
next:function(){
return {
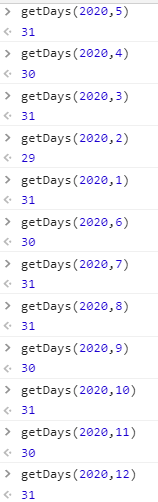
done:i23.请实现一个函数getDays,通过传入年份和月份作为函数的参数,返回该月的天数.
(提示:闰年的二月有29天,平年的二月只有28天.如果一个年份能被4整除但不能被100整除或者能被400整除则该年份为闰年)
例如:
实现代码:
function getDays(year, month) {
//根据年和月得到当月的天数
month = parseInt(month);
if (!month || month <= 0 || month > 12) {
return null;
}
if (month === 2) {
// 2月份的时候根据闰年和平年计算
if ((year % 4 === 0 && year % 100 !== 0) || year % 400 == 0) {
//闰年
return 29;
} else {
return 28;
}
} else {
const result = month % 2;
if (month <= 7) {
return result > 0 ? 31 : 30;
} else {
return result > 0 ? 30 : 31;
}
}
}