Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor,这两个接口,都是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点。两个接口名称看起来很相似,但作用及使用场景却不同,分析如下:
1、BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
该接口的定义如下:
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。接口方法的入参是ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,使用该参数,可以获取到相关bean的定义信息,例子:
1)spring bean的定义:
2)自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myJavaBean");
System.out.println("属性值============" + bd.getPropertyValues().toString());
MutablePropertyValues pv = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (pv.contains("remark")) {
pv.addPropertyValue("remark", "把备注信息修改一下");
}
bd.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
}
}
- org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
- org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyOverrideConfigurer
- org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer:用来注册自定义的属性编辑器
2、BeanPostProcessor接口
该接口的定义如下:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance before any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance after any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding bean instanceof FactoryBean checks.
*
This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
1)bean实现了InitializingBean接口,对应的方法为afterPropertiesSet
2)在bean定义的时候,通过init-method设置的方法
注意:BeanPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件并且实例化bean之后执行的。BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序是在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之后。
spring中,有内置的一些BeanPostProcessor实现类,例如:
- org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Resource注解的注入
- org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Required注解的注入
- org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Autowired注解的注入
- org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@PersistenceUnit和@PersistenceContext注解的注入
- org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:用来为bean注入ApplicationContext等容器对象
这些注解类的BeanPostProcessor,在spring配置文件中,可以通过这样的配置
3、下面通过完整的一个例子,来加深理解
1)定义一个JavaBean
public class MyJavaBean implements InitializingBean {
private String desc;
private String remark;
public MyJavaBean() {
System.out.println("MyJavaBean的构造函数被执行啦");
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
System.out.println("调用setDesc方法");
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
System.out.println("调用setRemark方法");
this.remark = remark;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用afterPropertiesSet方法");
this.desc = "在初始化方法中修改之后的描述信息";
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("调用initMethod方法");
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("[描述:").append(desc);
builder.append(", 备注:").append(remark).append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myJavaBean");
MutablePropertyValues pv = bd.getPropertyValues();
if (pv.contains("remark")) {
pv.addPropertyValue("remark", "在BeanFactoryPostProcessor中修改之后的备忘信息");
}
}
}
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor,对象" + beanName + "调用初始化方法之前的数据: " + bean.toString());
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor,对象" + beanName + "调用初始化方法之后的数据:" + bean.toString());
return bean;
}
}
5)测试类
public class PostProcessorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/postprocessor.xml");
MyJavaBean bean = (MyJavaBean) context.getBean("myJavaBean");
System.out.println("===============下面输出结果============");
System.out.println("描述:" + bean.getDesc());
System.out.println("备注:" + bean.getRemark());
}
}7)分析
从上面的结果可以看出,BeanFactoryPostProcessor在bean实例化之前执行,之后实例化bean(调用构造函数,并调用set方法注入属性值),然后在调用两个初始化方法前后,执行了BeanPostProcessor。初始化方法的执行顺序是,先执行afterPropertiesSet,再执行init-method。
4、进一步深入分析
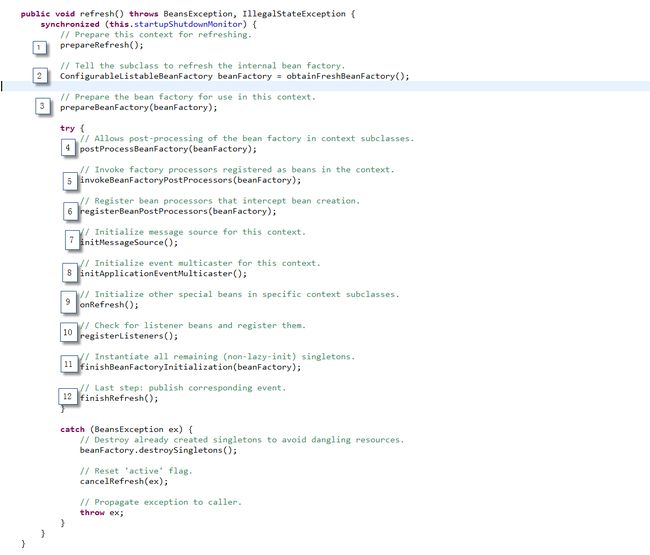
在使用ApplicationContext启动spring容器的时候,在AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()方法中,完成相关初始化工作:
1)BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory,是在第5步执行的,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法实现如下:
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* Must be called before singleton instantiation.
*/
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
for (Iterator it = getBeanFactoryPostProcessors().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
BeanFactoryPostProcessor factoryProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next();
factoryProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < postProcessorNames.length; i++) {
if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorNames[i]));
}
else if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
Collections.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator());
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
for (Iterator it = orderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String postProcessorName = (String) it.next();
orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName));
}
Collections.sort(orderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator());
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
for (Iterator it = nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String postProcessorName = (String) it.next();
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
}
/**
* Invoke the given BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List postProcessors) {
for (Iterator it = postProcessors.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next();
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
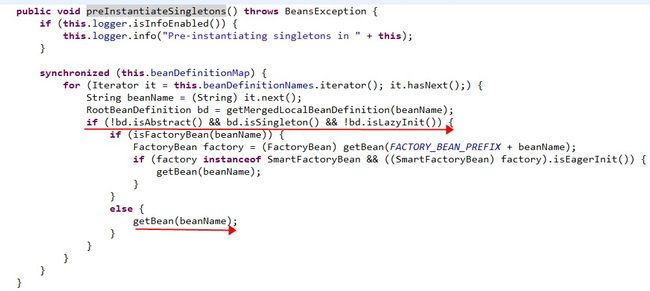
2)而BeanPostProcessor的执行,取决于配置文件中bean的定义,如果定义的bean是singleton并且不是抽象类,也不延迟初始化,则BeanPostProcessor是在第11步中执行;而对于prototype的bean,BeanPostProcessor是在程序getBean的时候执行的。在第6步中,调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法,注册所有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的bean,该方法的实现如下:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < postProcessorNames.length; i++) {
if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorNames[i]));
}
else if (isTypeMatch(postProcessorNames[i], Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(postProcessorNames[i]);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
Collections.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator());
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
for (Iterator it = orderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String postProcessorName = (String) it.next();
orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName));
}
Collections.sort(orderedPostProcessors, new OrderComparator());
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, register all other BeanPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList();
for (Iterator it = nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String postProcessorName = (String) it.next();
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName));
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
}在第11步中,调用finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法,该方法通过调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(),进行相关初始化工作:
从上面的代码可以看出,对于非抽象类、非延迟初始化的单例bean,在spring容器启动的时候调用getBean方法来实例化bean,并进行相关初始化工作,getBean方法最终调用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean方法,该方法的实现如下:
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = (BeanWrapper) this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet(dependentBeans.length);
for (int i = 0; i < dependentBeans.length; i++) {
String dependentBean = dependentBeans[i];
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
return exposedObject;
}protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(this);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
} public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (Iterator it = getBeanPostProcessors().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) it.next();
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
}
return result;
}
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (Iterator it = getBeanPostProcessors().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) it.next();
result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
}
return result;
}
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
String initMethodName = (mbd != null ? mbd.getInitMethodName() : null);
if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, initMethodName, mbd.isEnforceInitMethod());
}
}