Python深度学习:基于TensorFlow - 第9章 TensorFlow基础 阅读笔记
读书笔记,垃圾内容
文章目录
- Client
- Distributed master
- Worker Service
- Kernel Implementations
- 本章主要内容
- 数据流图 `tf.Graph`
- TensorFlow基本概念
- 张量 tensor
- 算子 operations
- 计算图 computation graph
- Session
- 常量&变量
- 占位符
- TensorFlow数据流图实现与可视化
- TensorFlow分布式
这一章首先介绍了TensorFlow的整体架构图,给出一个大体的认识。
We designed TensorFlow for large-scale distributed training and inference, but it is also flexible enough to support experimentation with new machine learning models and system-level optimizations. TensorFlow Architecture
上面源自TensorFlow官方doc,下面三点需要特别关注:
- large scale distributed training,分布式是一个需要重点关注的点
- support experimentation with new machine learning models,具有一定的灵活性,能够对新模型的进行简单的实验
- system-level optimizations,系统级优化
Tensorflow的整体架构图如下所示:

注:上图源于TensorFlow Architecture
文档写的很详尽,我直接摘抄过来。
- Client:
- Defines the computation as a dataflow graph.
- Initiates graph execution using a session. - Distributed Master
- Prunes a specific subgraph from the graph, as defined by the arguments to Session.run().
- Partitions the subgraph into multiple pieces that run in different processes and devices.
- Distributes the graph pieces to worker services.
- Initiates graph piece execution by worker services. - Worker Services (one for each task)
- Schedule the execution of graph operations using kernel implementations appropriate to the available hardware (CPUs, GPUs, etc).
- Send and receive operation results to and from other worker services. - Kernel Implementations
- Perform the computation for individual graph operations.
Client
官方文档中指明Client是通过写TensorFlow program来创建计算图,用户可以通过独立的operations或者使用提供的API去构造特定的神经网络。TensorFlow比较倾向于python和C++,但骨子里还是倾向于C++的,用户使用python,但库的作者期望C++的高性能。
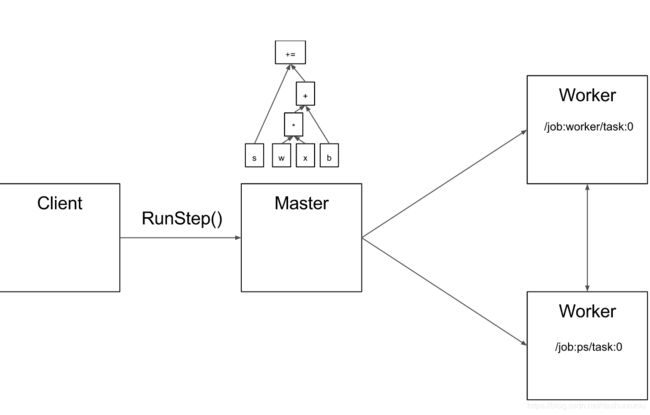
Client创建session,这个session会将graph definition通过tf.GraphDel协议buffer传递给distributed master。当Client evaluate图中的节点时,这个evaluation会触发distributed master来启动整个计算。
Distributed master
官方文档描述如下:
- 修剪graph来获得subgraph
- 根据不同的device对这些裁剪后得到的subgraph进行分类
- 缓存这些pieces,可能会在后续的步骤中用到(有点儿搞不懂什么意思?)
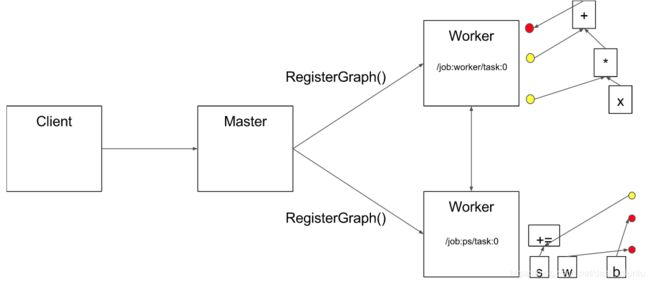
由于master能够看到整个computation,所以能够应用一些标准的优化,例如common subexpression elimination或者constant folding,然后优化这些子图的执行。
由于Master会将这些计算图进行分割,从而将它们放到不同的device上进行运行,一种可能的分割如下所示。既然是分割,肯定需要考虑到这些部分之间的通信。

一种信息的传递方式如下:

注: “PS” stands for “parameter server”: a task responsible for storing and updating the model’s parameters.
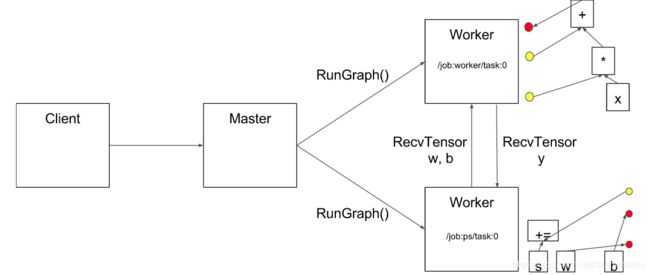
最终distributed master将这些分割后的子图传递给不同的分布式任务。
Worker Service
官方文档 The worker service in each task:
- handles requests from the master
- schedules the execution of the kernels for the operations that comprise a local subgraph, and
- mediates direct communication between tasks.
我们可以看到worker是真正干活儿的人,目的是把这些computation干完而且干好。如果distributed master比较重视较顶层逻辑层面的分派调度,而worker则较为重视实现层面的优化,直接与CPU和GPU打交道。
The worker service dispatches kernels to local devices and runs kernels in parallel when possible, for example by using multiple CPU and GPU streams.
注:The implementation of an op is known as a kernel, and it is the concrete implementation of the specification
一个整体的computation,拆分成不同的子部分,丢给不同的device进行处理,中间肯定需要进行通信,CPU与CPU之间的,CPU和GPU之间的,例如通过DMA。
For transfers between tasks, TensorFlow uses multiple protocols, including:
- gRPC over TCP
- RDMA over Converged Ethernet.
注:什么是gRPC?与json-RPC有什么异同?什么是RDMA?
另外TensorFlow还支持NVIDIA的NCCL来进行多GPU之间的通信。一种可能的方式如下:
Kernel Implementations
The implementation of an op is known as a kernel, and it is the concrete implementation of the specification you registered in Step 1. Create an op
就像上面说的那样,一个operation的implementation称之为kernel。据官方文档指出的那样,TensorFlow的runtime已经包含了超过200个标准的实现,数学,数组处理,控制流和状态管理等operations。这些operations有多种针对不同device进行优化后的kernel implementation。
许多operation kernels通过Eigen::Tensor实现,它使用C++模板生成高效的能够在多核GPU和CPU上并行处理的代码。但是TensorFlow推荐使用更加高效的cuDNN。
注:什么是Eigen::Tensor?什么是cuDNN?
注:cuDNN是用于深度神经网络的GPU加速库
本章主要内容
通过官方的介绍,对TensorFlow有了一个比较顶层的认识,但是细节还有些不清楚,未来进行填充。下面罗列本章的一些初识TensorFlow的代码片段。
数据流图 tf.Graph
TensorFlow中的数据流图由一组算子tf.Operation和一组张量tf.Tensor构成,其中tf.Operation代表了一组运算,张量tf.Tensor表示了算子之间流动的数据。
TensorFlow基本概念
张量 tensor
按照官方文档,Tensor表示了Operation的输出, Tensor可以作为输入传递给Operation。
算子 operations
一个Oepration是Graph中的一个节点,接收0个或者多个Tensor作为输入,然后产生0个或多个Tensor对象。Operation可以通过一个算子构造器tf.matmul或者tf.Graph.create_op来创建。
例如c = tf.matmul创建了一个Operation,接收a和b作为输入,c作为输出。
计算图 computation graph
Session
A class for running TensorFlow operations.
A Session object encapsulates the environment in which Operation objects are executed, and Tensor objects are evaluated.
Graph仅仅定义了所有op与Tensor流向,但是并没有进行任何计算。一个Session拥有一些资源,例如tf.Variable或者tf.queue.QueueBase等等,最好在使用完成之后释放这些资源。例如通过sess.close()等方法。
g = tf.Graph()
with g.as_default():
# Build a graph.
a = tf.constant(5.0)
b = tf.constant(6.0)
c = a * b
# Launch the graph in a session.
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
# Evaluate the tensor `c`.
print(sess.run(c))
Session的构造参数包含下面三个:
__init__(
target='',
graph=None.
config=None
)
target,可选。需要连接的执行引擎graph,可选。加载的Graph对象config,可选。例如CPU,GPU或者图中的优化参数,日志等选项。
Session中一个比较重要的方法是run,
run(
fetches,
feed_dict = None,
options = None,
run_metadata = None
)
This method runs one “step” of TensorFlow computation, by running the necessary graph fragment to execute every
Operationand evaluate everyTensorinfetches, substituting the values infeed_dictfor the corresponding input values.
fetches接收的是一个single graph element,一个single graph element可以是tf.Operation,可以是tf.Tensor,或者string等等。
常量&变量
创建一个常量Tensor,
tf.compat.v1.constant(
value,
dtype=None,
shape=None,
name='Const',
verify_shape=False
)
与常量对应的就是变量Variable,变量是TensorFlow中非常重要的概念,一个变量维护了TensorFlow graph的状态。Variable()构造函数可以接收任何类型和形状的Tensor作为输入。不像常量,变量的值是可以被修改的。
像张量一样,变量也可以作为算子的输入。但是当你装在graph时,变量必须被显示初始化过了。
The most common initialization pattern is to use the convenience function global_variables_initializer() to add an Op to the graph that initializes all the variables.
然后你就可以地运行这个算子。
占位符
我们可以在张量中插入一个占位符,未来再填充。
tf.compat.v1.placeholder(
dtype,
shape=None,
name=None
)
上面的tensor在evaluate的时候一定会产生error,我们必须使用feed_dict喂给它数据,例如在Session.run(),Tensor.eval()或者Operation.run()。
TensorFlow数据流图实现与可视化
TensorFlow一个比较酷功能是可视化数据流图,对于普通的程序,也有CallGraph的功能,但是这个功能对于TensorFlow更为紧要。
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
in_1 = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[], name="input_a")
in_2 = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[], name="input_b")
const = tf.constant(3, dtype=tf.float32, name="static_value")
with tf.name_scope("Transformation"):
with tf.name_scope("A"):
A_mul = tf.multiply(in_1, const)
A_out = tf.subtract(A_mul, in_1)
with tf.name_scope("B"):
B_mul = tf.multiply(in_2, const)
B_out = tf.subtract(B_mul, in_2)
with tf.name_scope("C"):
C_div = tf.math.divide(A_out, B_out)
C_out = tf.add(C_div, const)
with tf.name_scope("D"):
D_div = tf.math.divide(B_out, A_out)
D_out = tf.add(D_div, const)
out = tf.maximum(C_out, D_out)
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
print(sess.run(D_out, feed_dict={in_1: 4.0, in_2: 3.0}))
writer = tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter('/Users/henrywong/test/tmp', sess.graph)
writer.close()
对于上面的代码来说,整个graph如下图所示,我们可以有选择性的展开某个子部分。TensorFlow能够这样做的目的在于,TensorFlow的代码是基于数据流图的模型,逻辑性更强。
TensorFlow分布式
none