最小二乘法多项式拟合的Java实现
背景
由于项目中需要根据磁盘的历史使用情况预测未来一段时间的使用情况,决定采用最小二乘法做多项式拟合,这里简单描述下:
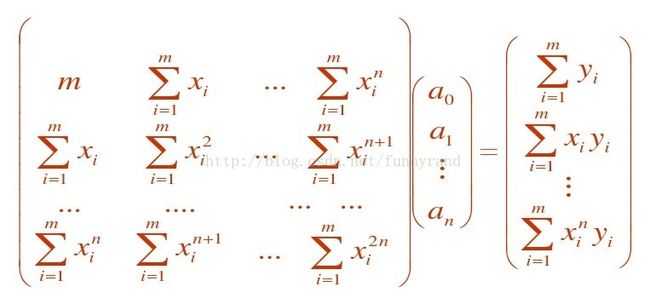
假设给定的数据点和其对应的函数值为 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym),需要做的就是得到一个多项式函数
f(x) = a0 * x + a1 * pow(x, 2) + .. + an * pow(x, n),使其对所有给定x所计算出的f(x)与实际对应的y值的差的平方和最小,
也就是计算多项式的各项系数 a0, a1, ... an.
所以从编程的角度来说需要做两件事情,1,确定线性方程组的各个系数,2,解线性方程组
确定系数比较简单,对给定的 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym) 做相应的计算即可,相关代码:
private void compute() {
...
}
解线性方程组稍微复杂,这里用到了高斯消元法,基本思想是通过递归做矩阵转换,逐渐减少求解的多项式系数的个数,相关代码:
private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) {
...
}
Java代码
package com.my.study.algorithm.leastSquareMethod;
/**
* Least square method class.
*/
public class LeastSquareMethod {
private double[] x;
private double[] y;
private double[] weight;
private int n;
private double[] coefficient;
/**
* Constructor method.
*
* @param x
* Array of x
* @param y
* Array of y
* @param n
* The order of polynomial
*/
public LeastSquareMethod(double[] x, double[] y, int n) {
if (x == null || y == null || x.length < 2 || x.length != y.length
|| n < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"IllegalArgumentException occurred.");
}
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.n = n;
weight = new double[x.length];
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
weight[i] = 1;
}
compute();
}
/**
* Constructor method.
*
* @param x
* Array of x
* @param y
* Array of y
* @param weight
* Array of weight
* @param n
* The order of polynomial
*/
public LeastSquareMethod(double[] x, double[] y, double[] weight, int n) {
if (x == null || y == null || weight == null || x.length < 2
|| x.length != y.length || x.length != weight.length || n < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"IllegalArgumentException occurred.");
}
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.n = n;
this.weight = weight;
compute();
}
/**
* Get coefficient of polynomial.
*
* @return coefficient of polynomial
*/
public double[] getCoefficient() {
return coefficient;
}
/**
* Used to calculate value by given x.
*
* @param x
* x
* @return y
*/
public double fit(double x) {
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coefficient.length; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(x, i) * coefficient[i];
}
return sum;
}
/**
* Use Newton's method to solve equation.
*
* @param y
* y
* @return x
*/
public double solve(double y) {
return solve(y, 1.0d);
}
/**
* Use Newton's method to solve equation.
*
* @param y
* y
* @param startX
* The start point of x
* @return x
*/
public double solve(double y, double startX) {
final double EPS = 0.0000001d;
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double x1 = 0.0d;
double x2 = startX;
do {
x1 = x2;
x2 = x1 - (fit(x1) - y) / calcReciprocal(x1);
} while (Math.abs((x1 - x2)) > EPS);
return x2;
}
/*
* Calculate the reciprocal of x.
*
* @param x x
*
* @return the reciprocal of x
*/
private double calcReciprocal(double x) {
if (coefficient == null) {
return 0;
}
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < coefficient.length; i++) {
sum += i * Math.pow(x, i - 1) * coefficient[i];
}
return sum;
}
/*
* This method is used to calculate each elements of augmented matrix.
*/
private void compute() {
if (x == null || y == null || x.length <= 1 || x.length != y.length
|| x.length < n || n < 2) {
return;
}
double[] s = new double[(n - 1) * 2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) {
s[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * weight[j];
}
}
double[] b = new double[n];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) {
b[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * y[j] * weight[j];
}
}
double[][] a = new double[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
a[i][j] = s[i + j];
}
}
// Now we need to calculate each coefficients of augmented matrix
coefficient = calcLinearEquation(a, b);
}
/*
* Calculate linear equation.
*
* The matrix equation is like this: Ax=B
*
* @param a two-dimensional array
*
* @param b one-dimensional array
*
* @return x, one-dimensional array
*/
private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) {
if (a == null || b == null || a.length == 0 || a.length != b.length) {
return null;
}
for (double[] x : a) {
if (x == null || x.length != a.length)
return null;
}
int len = a.length - 1;
double[] result = new double[a.length];
if (len == 0) {
result[0] = b[0] / a[0][0];
return result;
}
double[][] aa = new double[len][len];
double[] bb = new double[len];
int posx = -1, posy = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++)
if (a[i][j] != 0.0d) {
posy = j;
break;
}
if (posy != -1) {
posx = i;
break;
}
}
if (posx == -1) {
return null;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
if (i == posx) {
continue;
}
bb[count] = b[i] * a[posx][posy] - b[posx] * a[i][posy];
int count2 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++) {
if (j == posy) {
continue;
}
aa[count][count2] = a[i][j] * a[posx][posy] - a[posx][j]
* a[i][posy];
count2++;
}
count++;
}
// Calculate sub linear equation
double[] result2 = calcLinearEquation(aa, bb);
// After sub linear calculation, calculate the current coefficient
double sum = b[posx];
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
if (i == posy) {
continue;
}
sum -= a[posx][i] * result2[count];
result[i] = result2[count];
count++;
}
result[posy] = sum / a[posx][posy];
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LeastSquareMethod eastSquareMethod = new LeastSquareMethod(
new double[] { 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 }, new double[] {
1.75, 2.45, 3.81, 4.8, 7.0, 8.6 }, 3);
/*double[] coefficients = eastSquareMethod.getCoefficient();
for (double c : coefficients) {
System.out.println(c);
}*/
System.out.println(eastSquareMethod.fit(4));
LeastSquareMethod eastSquareMethod2 = new LeastSquareMethod(
new double[] { 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 }, new double[] {
1.75, 2.45, 3.81, 4.8, 7.0, 8.6 }, 2);
System.out.println(eastSquareMethod2.solve(100));
}
}
使用开源库
也可使用Apache开源库commons math,提供的功能更强大,
http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-math/userguide/fitting.html
org.apache.commons
commons-math3
3.5
private static void testLeastSquareMethodFromApache() {
final WeightedObservedPoints obs = new WeightedObservedPoints();
obs.add(-3, 4);
obs.add(-2, 2);
obs.add(-1, 3);
obs.add(0, 0);
obs.add(1, -1);
obs.add(2, -2);
obs.add(3, -5);
// Instantiate a third-degree polynomial fitter.
final PolynomialCurveFitter fitter = PolynomialCurveFitter.create(3);
// Retrieve fitted parameters (coefficients of the polynomial function).
final double[] coeff = fitter.fit(obs.toList());
for (double c : coeff) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}