cv2霍夫圆环检测(HoughCircle)
本篇博客主要介绍利用霍夫变换来进行圆环检测。一个圆环需要3个参数来确定,所以进行圆环检测的累加器必须是三维的,这样效率就会很低,因此OpenCV使用了霍夫梯度法这个巧妙的方法,来使用边界的梯度信息,从而提升计算的效率。
cv2中进行霍夫圆环检测的函数:
cv2.HoughCircles(image, method, dp, minDist, circles=None, param1=None, param2=None, minRadius=None, maxRadius=None)
其中:
image:8位,单通道图像。如果使用彩色图像,需要先转换为灰度图像。
method:定义检测图像中圆的方法。目前唯一实现的方法是cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT。
dp:累加器分辨率与图像分辨率的反比。dp获取越大,累加器数组越小。
minDist:检测到的圆的中心,(x,y)坐标之间的最小距离。如果minDist太小,则可能导致检测到多个相邻的圆。如果minDist太大,则可能导致很多圆检测不到。
param1:用于处理边缘检测的梯度值方法。
param2:cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT方法的累加器阈值。阈值越小,检测到的圈子越多。
minRadius:半径的最小大小(以像素为单位)。
maxRadius:半径的最大大小(以像素为单位)。
示例:
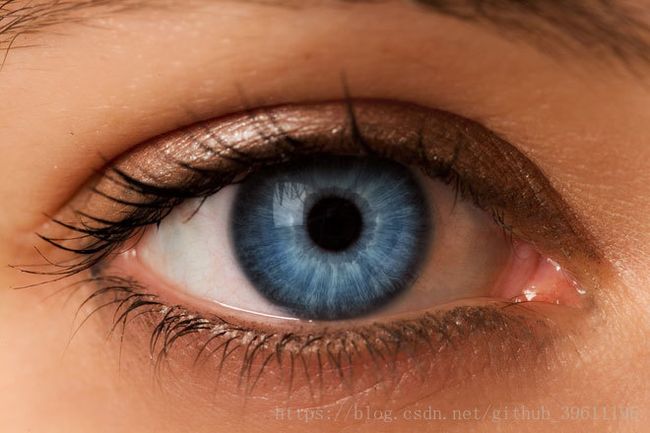
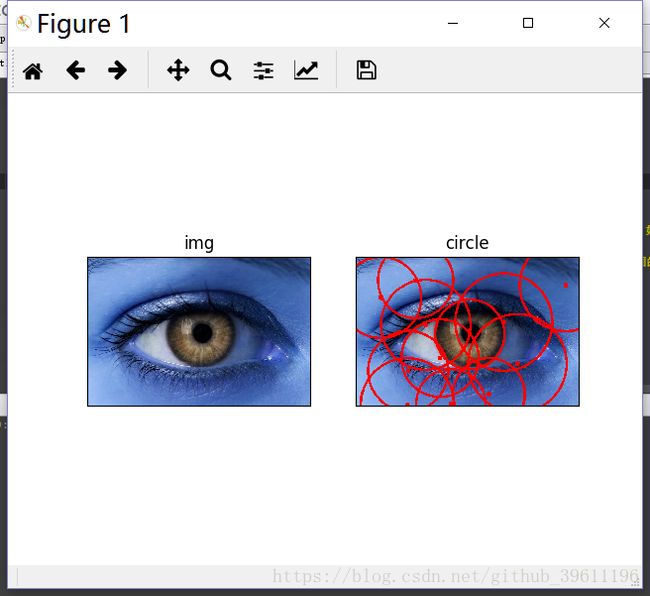
原始图像:
示例代码:
# encoding:utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('eye-color-blue-z-c-660x440.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度图像
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('img'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
# hough transform 规定检测的圆的最大最小半径,不能盲目的检测,否则浪费时间空间
# circle1 = cv2.HoughCircles(gray, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 100, param1=100, param2=30, minRadius=200, maxRadius=300)
circle1 = cv2.HoughCircles(gray, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 100, param1=100, param2=30, minRadius=100, maxRadius=200) #把半径范围缩小点,检测内圆,瞳孔
circles = circle1[0, :, :] # 提取为二维
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles)) # 四舍五入,取整
for i in circles[:]:
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (255, 0, 0), 5) # 画圆
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), 2, (255, 0, 0), 10) # 画圆心
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(img)
plt.title('circle'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
检测结果:
围棋颜色识别:
示例代码:
# encoding:utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
from collections import Counter
# 检测棋子的颜色
def detect_weiqi(img):
txt = 'black'
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, threshold = cv2.threshold(gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
c = Counter(list(threshold.flatten()))
print(c.most_common())
if c.most_common()[0][0] != 0:
txt = 'white'
return txt, threshold
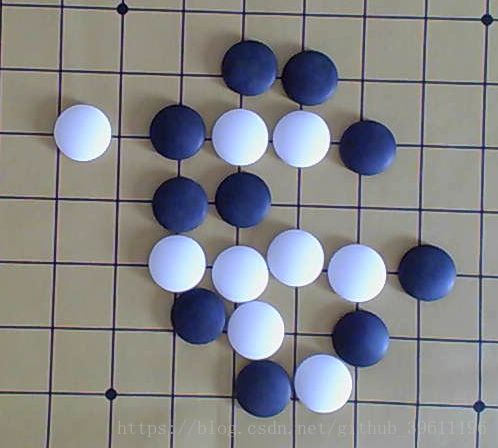
img = cv2.imread('../data/weiqi.png')
img = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(gray, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1=100, param2=30, minRadius=10, maxRadius=50)
if circles is None:
exit(-1)
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
print(circles)
cv2.waitKey(0)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
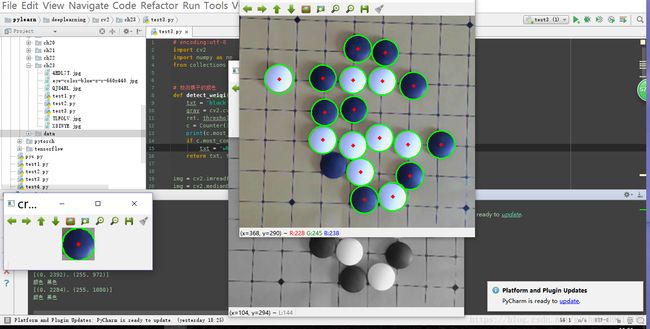
for i in circles[0, :]:
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), 2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
x, y, r = i
crop_img = img[y - r: y + r, x - r: x + r]
# 检测围棋
txt, threshold = detect_weiqi(crop_img)
print('颜色', '黑色' if txt == 'black' else '白色')
cv2.putText(threshold, text=txt, org=(0, 0), fontFace=font, fontScale=0.5, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.imshow('threshold', threshold)
cv2.imshow('crop_img', crop_img)
cv2.moveWindow('crop_img', x=0, y=img.shape[0])
cv2.imshow('detected chess', img)
cv2.moveWindow('detected chess', y=0, x=img.shape[1])
cv2.waitKey(1500)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
原图:
结果图片:
欢迎关注我的公众号:
编程技术与生活(ID:hw_cchang)