一:简介
一、什么Heat
1. Heat 是一套业务流程平台,旨在帮助用户更轻松地配置以 OpenStack 为基础的云体系。利用Heat应用程序,开发人员能够在程序中使用模板以实现资源的自动化部署。Heat能够启动应用、创建虚拟机并自动处理整个流程。它还拥有出色的跨平台兼容性,能够与 Amazon Web Services 业务流程平台 CloudFormation 相对接——这意味着用户完全可以将 AWS 模板引入 OpenStack 环境当中。
2. Heat 是 OpenStack 提供的自动编排功能的组件,基于描述性的模板,来编排复合云应用程序。
二、为什么需要Heat
1. 更快更有效的管理 OpenStack 的资源:云平台系统在相对比较稳定的情况下,管理成本逐渐变成首要的解决问题。云上自动化能力是一个云平台的刚需,可以有效降低维护难度。Heat 采用了模板方式来设计或者定义编排,为方便用户使用,Heat 还提供了大量的模板例子,使用户能够方便地得到想要的编排。
2. 更小的研发成本:引入 Heat,对于不了解 OpenStack 的研发者来说,可以更快的接入现有的业务系统。开发者更关心的是授权认证和对虚拟资源的增删改,而对于底层的状态并不用太多了解。
三、概念
1. 堆栈(stack):管理资源的集合。单个模板中定义的实例化资源的集合,是 Heat 管理应用程序的逻辑单元,往往对应一个应用程序。
2. 模板(template):如何使用代码定义和描述堆栈。描述了所有组件资源以及组件资源之间的关系,是 Heat 的核心。
3. 资源(resource):将在编排期间创建或修改的对象。资源可以是网络、路由器、子网、实例、卷、浮动IP、安全组等。
4. 参数(parameters):heat模板中的顶级key,定义在创建或更新 stack 时可以传递哪些数据来定制模板。
5. 参数组(parameter_groups):用于指定如何对输入参数进行分组,以及提供参数的顺序。
6. 输出(outputs):heat模板中的顶级key,定义实例化后 stack 将返回的数据。
二:架构
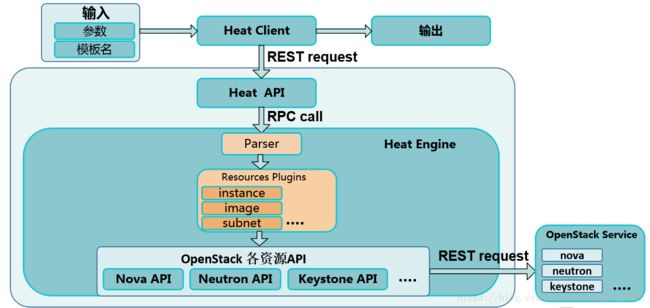
一、核心架构
1. heat command-line client:CLI通过与 heat-api 通信,来调用 API 实现相关功能。终端开发者可以直接使用编排 REST API。
2. heat-api:实现 OpenStack 原生支持的 REST API。该组件通过把 API 请求经由 AMQP 传送给 Heat engine 来处理 API 请求。
3. heat-api-cfn:提供与 AWS CloudFormation 兼容的、AWS 风格的查询 API,处理请求并通过 AMQP 将它们发送到 heat-engine。
4. heat-engine:执行模板内容,最终完成应用系统的创建和部署,并把执行结果返回给 API 调用者。
5. heat-cfntools:完成虚拟机实例内部的操作配置任务,需要单独下载。
二、工作流程
1. 用户在 Horizon 中或者命令行中提交包含模板和参数输入的请求
2. Horizon 或者命令行工具会将接收到的请求转化为 REST 格式的 API 调用 Heat-api 或者是 Heat-api-cfn。
3. Heat-api 和 Heat-api-cfn 会验证模板的正确性,然后通过 AMQP 异步传递给 Heat Engine 来处理请求。
4. Heat Engine 接收到请求后,会把请求解析为各种类型的资源,每种资源都对应 OpenStack 其它的服务客户端,然后通过发送 REST 的请求给其它服务。
5. Heat Engine 在这里的作用分为三层: 第一层处理 Heat 层面的请求,就是根据模板和输入参数来创建 Stack,这里的 Stack 是由各种资源组合而成。 第二层解析 Stack 里各种资源的依赖关系,Stack 和嵌套 Stack 的关系。第三层就是根据解析出来的关系,依次调用各种服务客户段来创建各种资源。
三、模板
一、 概念:Heat 模板全称为heat orchestration template,简称为HOT。
二、模板详解
1. 典型 Heat 模板结构
1 heat_template_version: 2015-04-30 ### HOT版本 2 description: ### 说明 3 # a description of the template 4 5 parameter_groups: ### 指定参数顺序 6 - label:7 description: 8 parameters: 9 - 10 - 11 12 parameters: ### 传递的参数 13 : ### 参数名 14 type: <string | number | json | comma_delimited_list | boolean> ### 参数类型 15 label: ### 标签 16 description: 17 default: for parameter> 18 hidden: <true | false> ### 是否隐藏 19 constraints: ### 已有的内置参数:OS::stack_name、OS::stack_id、OS::project_id 20 21 immutable: <true | false> 22 23 resources: ### 资源对象 24 : ### 资源的ID 25 type: ### 资源的类型 26 properties: ### 资源的属性 27 : 28 metadata: ### 资源的元数据 29 30 depends_on: 31 update_policy: 32 deletion_policy: 33 34 outputs: ### 返回值 35 : ### 参数名 36 description: ### 说明 37 value: ### 输出值
2. 例子
1 heat_temp_version:2016-04-30 2 Description: AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm using Ceilometer. 3 parameters: 4 user_name: 5 type: string 6 label: User Name 7 description: User name to be configured for the application 8 port_number: 9 type: number 10 label: Port Number 11 description: Port number to be configured for the web server 12 13 resources: 14 my_instance: 15 type: OS::Nova::Server 16 properties: 17 flavor: m1.small 18 image: F18-x86_64-cfntools 19 20 outputs: 21 instance_ip: 22 description: IP address of the deployed compute instance 23 value: { get_attr: [my_instance, first_address] }
三、模板内部函数
1. get_attr:获取所创建资源的属性
1 语法 2 get_attr: 3 -### 必须是模板 resouce 段中指定的资源。 4 - ### 要获取的属性,如果属性对应的值是list 或map, 则可以指定key/index来获取具体的值。 5 - 1> (optional) 6 - 2> (optional) 7 - ... 8 9 示例 10 resources: 11 my_instance: 12 type: OS::Nova::Server 13 # ... 14 15 outputs: 16 instance_ip: 17 description: IP address of the deployed compute instance 18 value: { get_attr: [my_instance, first_address] } 19 instance_private_ip: 20 description: Private IP address of the deployed compute instance 21 value: { get_attr: [my_instance, networks, private, 0] }
2. get_file:获取文件的内容
1 语法 2 get_file:3 4 示例 5 resources: 6 my_instance: 7 type: OS::Nova::Server 8 properties: 9 # general properties ... 10 user_data: 11 get_file: my_instance_user_data.sh 12 my_other_instance: 13 type: OS::Nova::Server 14 properties: 15 # general properties ... 16 user_data: 17 get_file: http://example.com/my_other_instance_user_data.sh
3. get_param:引用模板中指定的参数
1 语法 2 get_param: 3 -4 - (optional) 5 - (optional) 6 - ... 7 8 示例 9 parameters: 10 instance_type: 11 type: string 12 label: Instance Type 13 description: Instance type to be used. 14 server_data: 15 type: json 16 17 resources: 18 my_instance: 19 type: OS::Nova::Server 20 properties: 21 flavor: { get_param: instance_type} 22 metadata: { get_param: [ server_data, metadata ] } 23 key_name: { get_param: [ server_data, keys, 0 ] }
24
25 输出
{"instance_type": "m1.tiny",
{"server_data": {"metadata": {"foo": "bar"},"keys": ["a_key","other_key"]}}}
4. get_resource:获取模板中指定的资源
1 语法 2 get_resource:3 4 示例 5 resources: 6 instance_port: 7 type: OS::Neutron::Port 8 properties: ... 9 10 instance: 11 type: OS::Nova::Server 12 properties: 13 ... 14 networks: 15 port: { get_resource: instance_port }
5. list_join:使用指定的分隔符将一个list中的字符串合成一个字符串
1 语法 2 list_join: 3 -4 - join> 5 6 示例输出:one,two,three 7 list_join: [', ', ['one', 'two', 'and three']]
6. digest:在指定的值上使用algorithm
1 语法 2 digest: 3 -### 可用的值是hashlib(md5, sha1, sha224, sha256, sha384, and sha512) 或openssl的相关值 4 - 5 6 示例 7 # from a user supplied parameter 8 pwd_hash: { digest: ['sha512', { get_param: raw_password }] }
7. repeat:迭代fore_each中的列表,按照template的格式生成一个list
1 语法 2 repeat: 3 template: 4 5 for_each: 6 :7 8 示例 9 parameters: 10 ports: 11 type: comma_delimited_list 12 label: ports 13 default: "80,443,8080" 14 protocols: 15 type: comma_delimited_list 16 label: protocols 17 default: "tcp,udp" 18 19 resources: 20 security_group: 21 type: OS::Neutron::SecurityGroup 22 properties: 23 name: web_server_security_group 24 rules: 25 repeat: 26 for_each: 27 <%port%>: { get_param: ports } 28 <%protocol%>: { get_param: protocols } 29 template: 30 protocol: <%protocol%> 31 port_range_min: <%port%> 32 33 结果 34 [{‘protocal’:tpc, ‘prot_range_min’:80}, 35 36 {‘protocal’:tpc, ‘prot_range_min’:443}, 37 38 {‘protocal’:tpc, ‘prot_range_min’:8080}, 39 40 {‘protocal’:udp, ‘prot_range_min’:80}, 41 42 {‘protocal’:udp, ‘prot_range_min’:443}, 43 44 {‘protocal’:udp, ‘prot_range_min’:8080}]
8. resource_facade:检索资源的数据
9. str_replace:使用params中的值替换template中的占位符,从而构造一个新的字符串
1 语法 2 str_replace: 3 template: string> 4 params:5 6 示例 7 resources: 8 my_instance: 9 type: OS::Nova::Server 10 # general metadata and properties ... 11 12 outputs: 13 Login_URL: 14 description: The URL to log into the deployed application 15 value: 16 str_replace: 17 template: http://host/MyApplication 18 params: 19 host: { get_attr: [ my_instance, first_address ] }
10. str_split:将一个字符串按照分隔符分隔成一个list
1 语法 2 str_split: 3 - ',' 4 - string,to,split 5 6 示例 7 str_split: [',', 'string,to,split'] 8 9 结果 10 ['string', 'to', 'split']
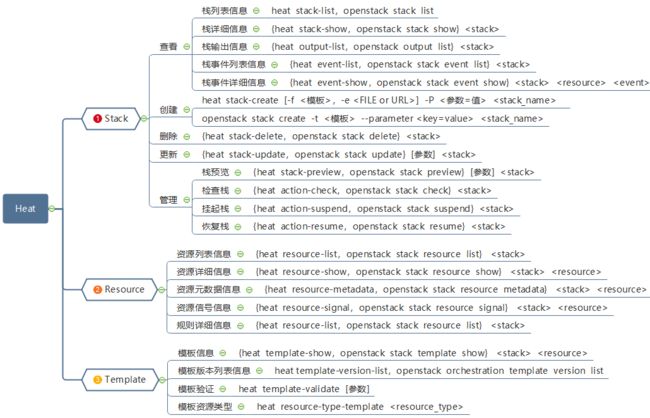
四:常用操作
一、栈、资源、模板管理
二、软件、快照管理