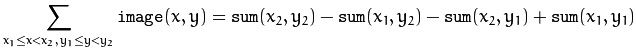OpenCV—使用积分图像统计像素
OpenCV—使用积分图像统计像素
本文为对《OpenCV计算机视觉编程攻略(第二版)》4.8节积分图像部分的学习笔记。
1.积分图像的基本概念
(1)为什么要用积分图像?
直方图的计算方法为遍历图像的全部像素并累计每个强度值在图像中出现的次数。有时仅需要计算图像中某个特定区域的直方图,而如果需要计算图像中多个区域的直方图,这些计算过程将变得非常耗时。在这种情况下使用积分图像将极大地提高统计图像子区域像素的效率。积分图像在程序中应用非常广泛。
(2)什么是积分图像?
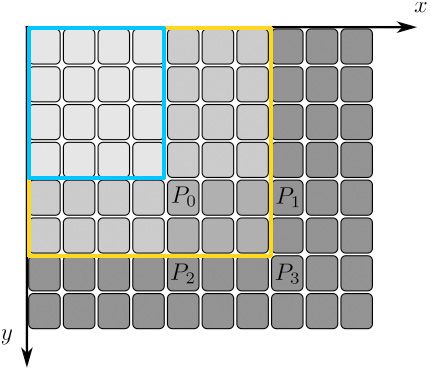
积分图像的定义:取图像左上侧的全部像素计算累加和,并用这个累加和替换图像中的每一个像素,使用这种方式得到的图像称为积分图像。
(3)如何计算积分图像?
计算积分图像的函数:C++接口
- void integral(InputArray image,OutputArray sum, int sdepth=-1 )
- void integral(InputArray image,OutputArray sum, OutputArray sqsum, int sdepth=-1 )
- void integral(InputArray image,OutputArray sum, OutputArray sqsum, OutputArray tilted,int sdepth=-1 )
函数参数:
- image 输入W×H源图像,8bit字符型,或32bit、64bit浮点型矩阵
- sum 输出(W+1)×(H +1)积分图像,32bit整型或32bit、64bit浮点型矩阵
- sqsum 输出(W+1)×(H +1)平方积分图像,双精度浮点型矩阵。
- tilted 输出旋转45°的(W+1)×(H +1)积分图像,数据类型同sum
- sdepth 积分图像sum或titled的位深度:CV_32S、CV_32F或CV_64F
根据定义,计算源图像的积分图像的函数执行如下操作:
按照上面的公式,P0点的积分值为蓝色方框中像素的强度累加和,P3点的积分像素为黄色方框内像素点的强度累加和。从上图可知,想要从原始图像获得积分图像,只需要对整幅图像扫描一次。这是因为对同一行(列)的相邻两像素,当前像素的积分值等于上一像素的积分值加上当前像素所在列(行)的左上侧累计值。可见,积分图像是一个包含像素累加和的新图像。为了防止累加和过大溢出,积分图像的值通常都使用int类型变量(CV_32S)或float类型变量(CV_32F)。
对于多通道图像,每个通道都将独立累积计算积分图像。
(4)如何使用积分图像?
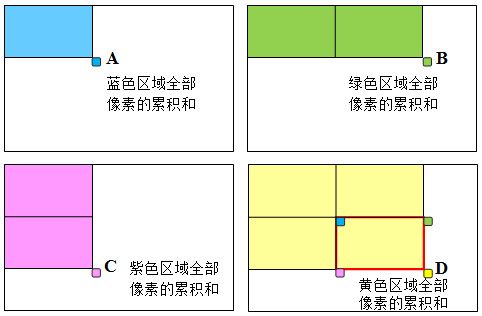
假设一幅图像中4个点ABCD,其积分图像中A(x1,y1)点的值为其左上侧所有像素的值的累加和,也就是蓝色区域中所有像素点的值累加和。同理积分图像中的B(x2,y1)、C(x1,y2)、D(x2,y2)点值分别是绿色、紫色和黄色区域像素值的累加和。ABCD四点的位置关系在右下角图所示。
那么如果需要计算由ABCD组成的ROI的累加值就只需要使用如下公式:
即:D-C-B+A。显然,计算量不受区域尺寸的影响。所以,如果需要在多个尺寸的区域上计算像素累加和,最好采用积分图像。
2.利用积分图像进行自适应阈值分割
局部阈值,即根据每个像素的邻域计算阈值。这种策略叫做自适应阈值化,包括将每个像素的值与邻域的平均值进行比较。如果某像素的值与它的局部平均值差别很大,就会被当做异常值在阈值化过程中剔除。因此,自适应阈值化需要计算每个像素周围的局部平均值。这需要多次计算图像窗口的累计值,可以通过积分图像来提高计算效率。
(1)自适应阈值分割函数AdaptiveThreshold()
首先,读取一幅图片
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("f:\\images\\book.jpg",0);
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// rotate the image for easier display
cv::transpose(image, image);
cv::flip(image, image, 0);
// display original image
cv::namedWindow("Original Image");
cv::imshow("Original Image",image);原始图像
观察一下使用固定阈值分割得到的结果
// using a fixed threshold
cv::Mat binaryFixed;
cv::Mat binaryAdaptive;
cv::threshold(image,binaryFixed,180,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);//固定阈值分割
cv::namedWindow("Fixed Threshold");
cv::imshow("Fixed Threshold",binaryFixed);使用固定阈值分割的结果
显然,固定阈值难以完成这个任务,难以给出不同光照区域的最佳分割。对于这类问题,可以使用自适应阈值分割。实现自适应阈值分割有很多方法,最简单的就是直接使用opencv中的自适应阈值分割函数。
// using as adaptive threshold
int blockSize= 21; // size of the neighborhood
int threshold=10; // pixel will be compared to (mean-threshold)
cv::adaptiveThreshold(image, // input image
binaryAdaptive, // output binary image
255, // max value for output
cv::ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, // adaptive method方法
cv::THRESH_BINARY, // threshold type
blockSize, // size of the block
threshold); // threshold used
cv::namedWindow("Adaptive Threshold");
cv::imshow("Adaptive Threshold",binaryAdaptive);自适应阈值函数cv::AdaptiveThreshold的分割结果
(2)使用积分图像integral()实现自适应阈值分割
当然,也可以自己写程序实现自适应阈值分割// compute integral image
IntegralImage integral(image);//IntegralImage为计算积分图像的方法封装的模板类,实例化一个变量
cv::Mat binary= image.clone();//深度复制图像
// 使用指针遍历图像来计算积分图像
int nl= binary.rows; // number of lines
int nc= binary.cols; // total number of elements per line
// compute integral image
cv::Mat iimage;
cv::integral(image,iimage,CV_32S);//计算积分图像
// for each row
int halfSize= blockSize/2;
for (int j=halfSize; j(j);
int* idata1= iimage.ptr(j-halfSize);
int* idata2= iimage.ptr(j+halfSize+1);
// for pixel of a line
for (int i=halfSize; i 在积分图像上实现自适应阈值分割
用积分图像实现自适应阈值分割的结果与使用自适应阈值分割函数AdaptiveThreshold()完全一样。上段代码中的IntegralImage类,在integral.h头文件中定义,该步骤将积分计算的过程封装进了模板类中。
#if !defined IINTEGRAL
#define IINTEGRAL
#include
#include
#include
#include
template //将积分计算过程封装进模板类为向量数据类型,为向量数量
class IntegralImage {
cv::Mat integralImage;
public:
IntegralImage(cv::Mat image) {
// (costly) computation of the integral image
cv::integral(image,integralImage,cv::DataType::type);
}
// compute sum over sub-regions of any size from 4 pixel access
cv::Vec operator()(int xo, int yo, int width, int height) {
// window at (xo,yo) of size width by height
return (integralImage.at >(yo+height,xo+width)//Vec ,T为类型,N为向量元素数量
-integralImage.at >(yo+height,xo)
-integralImage.at >(yo,xo+width)
+integralImage.at >(yo,xo));
}
// compute sum over sub-regions of any size from 4 pixel access
cv::Vec operator()(int x, int y, int radius) {
// square window centered at (x,y) of size 2*radius+1
return (integralImage.at >(y+radius+1,x+radius+1)
-integralImage.at >(y+radius+1,x-radius)
-integralImage.at >(y-radius,x+radius+1)
+integralImage.at >(y-radius,x-radius));
}
};
// convert to a multi-channel image made of binary planes
// nPlanes must be a power of 2
void convertToBinaryPlanes(const cv::Mat& input, cv::Mat& output, int nPlanes) {
// number of bits to mask out
int n= 8-static_cast(log(static_cast(nPlanes))/log(2.0));
// mask used to eliminate least significant bits
uchar mask= 0xFF< planes;
// reduce to nBins bins by eliminating least significant bits
cv::Mat reduced= input&mask;
// compute each binary image plane
for (int i=0; i (3)使用图像运算符来实现自适应阈值分割
还可以使用OpenCV的图像运算符来实现自适应阈值分割的过程。// adaptive threshold using image operators
cv::Mat filtered;
cv::Mat binaryFiltered;
cv::boxFilter(image,filtered,CV_8U,cv::Size(blockSize,blockSize));
filtered= filtered-threshold;
binaryFiltered= image>= filtered;通过实验,上述3中方法中,使用第一种自适应阈值化函数花费的时间较少。
转载请注明:iracer的CSDN博客 http://blog.csdn.net/iracer/article/details/49029239