数据结构_线性表_链式存储_单向循环链表的基本操作
1.概述:
对于一个循环链表来说,其首节点和末节点被连接在一起。这种方式在单向和双向链表中皆可实现。要转换一个循环链表,可以选择开始于任意一个节点然后沿着列表的任一方向直到返回开始的节点。再来看另一种方法,循环链表可以被视为“无头无尾”。这种列表很利于节约数据存储缓存, 假定你在一个列表中有一个对象并且希望所有其他对象迭代在一个非特殊的排列下。
指向整个列表的指针可以被称作访问指针。 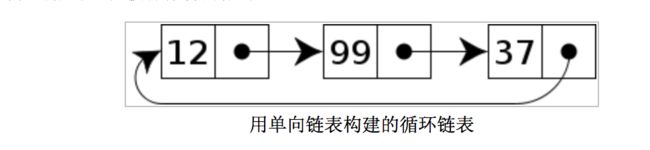
用单向链表构建的循环链表
循环链表中第一个节点之前就是最后一个节点,反之亦然。循环链表的无边界使得在这样的链表上设计算法会比普通链表更加容易。对于新加入的节点应该是在第一个节点之前还是最后一个节点之后可以根据实际要求灵活处理,区别不大(详见下面实例代码)。当然,如果只会在最后插入数据(或者只会在之前),处理也是很容易的。
另外有一种模拟的循环链表,就是在访问到最后一个节点之后的时候,手工的跳转到第一个节点。访问到第一个节点之前的时候也一样。这样也可以实现循环链表的功能,在直接用循环链表比较麻烦或者可能会出现问题的时候可以用。
#define OVERFLOW 1
typedef int ElemType;
typedef enum {
TRUE,
FALSE,
OK,
} Status;
struct LNode
{
ElemType data;
struct LNode *next;
};
typedef struct LNode *LinkList; /* 另一种定义LinkList的方法 */
/* bo2-4.c 设立尾指针的单循环链表(存储结构由c2-2.h定义)的12个基本操作 */
Status InitList_CL(LinkList *L)
{ /* 操作结果:构造一个空的线性表L */
*L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)); /* 产生头结点,并使L指向此头结点 */
if(!*L) /* 存储分配失败 */
exit(OVERFLOW);
(*L)->next=*L; /* 指针域指向头结点 */
return OK;
}
Status DestroyList_CL(LinkList *L)
{ /* 操作结果:销毁线性表L */
LinkList q,p=(*L)->next; /* p指向头结点 */
while(p!=*L) /* 没到表尾 */
{
q=p->next;
free(p);
p=q;
}
free(*L);
*L=NULL;
return OK;
}
Status ClearList_CL(LinkList *L) /* 改变L */
{ /* 初始条件:线性表L已存在。操作结果:将L重置为空表 */
LinkList p,q;
*L=(*L)->next; /* L指向头结点 */
p=(*L)->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */
while(p!=*L) /* 没到表尾 */
{
q=p->next;
free(p);
p=q;
}
(*L)->next=*L; /* 头结点指针域指向自身 */
return OK;
}
Status ListEmpty_CL(LinkList L)
{ /* 初始条件:线性表L已存在。操作结果:若L为空表,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
if(L->next==L) /* 空 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
int ListLength_CL(LinkList L)
{ /* 初始条件:L已存在。操作结果:返回L中数据元素个数 */
int i=0;
LinkList p=L->next; /* p指向头结点 */
while(p!=L) /* 没到表尾 */
{
i++;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
Status GetElem_CL(LinkList L,int i,ElemType *e)
{ /* 当第i个元素存在时,其值赋给e并返回OK,否则返回ERROR */
int j=1; /* 初始化,j为计数器 */
LinkList p=L->next->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */
if(i<=0||i>ListLength_CL(L)) /* 第i个元素不存在 */
return FALSE;
while(j<i)
{ /* 顺指针向后查找,直到p指向第i个元素 */
p=p->next;
j++;
}
*e=p->data; /* 取第i个元素 */
return OK;
}
int LocateElem_CL(LinkList L,ElemType e,Status(*compare)(ElemType,ElemType))
{ /* 初始条件:线性表L已存在,compare()是数据元素判定函数 */
/* 操作结果:返回L中第1个与e满足关系compare()的数据元素的位序。 */
/* 若这样的数据元素不存在,则返回值为0 */
int i=0;
LinkList p=L->next->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */
while(p!=L->next)
{
i++;
if(compare(p->data,e)) /* 满足关系 */
return i;
p=p->next;
}
return 0;
}
Status PriorElem_CL(LinkList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType *pre_e)
{ /* 初始条件:线性表L已存在 */
/* 操作结果:若cur_e是L的数据元素,且不是第一个,则用pre_e返回它的前驱, */
/* 否则操作失败,pre_e无定义 */
LinkList q,p=L->next->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */
q=p->next;
while(q!=L->next) /* p没到表尾 */
{
if(q->data==cur_e)
{
*pre_e=p->data;
return TRUE;
}
p=q;
q=q->next;
}
return FALSE;
}
Status NextElem_CL(LinkList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType *next_e)
{ /* 初始条件:线性表L已存在 */
/* 操作结果:若cur_e是L的数据元素,且不是最后一个,则用next_e返回它的后继, */
/* 否则操作失败,next_e无定义 */
LinkList p=L->next->next; /* p指向第一个结点 */
while(p!=L) /* p没到表尾 */
{
if(p->data==cur_e)
{
*next_e=p->next->data;
return TRUE;
}
p=p->next;
}
return FALSE;
}
Status ListInsert_CL(LinkList *L,int i,ElemType e) /* 改变L */
{ /* 在L的第i个位置之前插入元素e */
LinkList p=(*L)->next,s; /* p指向头结点 */
int j=0;
if(i<=0||i>ListLength_CL(*L)+1) /* 无法在第i个元素之前插入 */
return FALSE;
while(j<i-1) /* 寻找第i-1个结点 */
{
p=p->next;
j++;
}
s=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)); /* 生成新结点 */
s->data=e; /* 插入L中 */
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s;
if(p==*L) /* 改变尾结点 */
*L=s;
return OK;
}
Status ListDelete_CL(LinkList *L,int i,ElemType *e) /* 改变L */
{ /* 删除L的第i个元素,并由e返回其值 */
LinkList p=(*L)->next,q; /* p指向头结点 */
int j=0;
if(i<=0||i>ListLength_CL(*L)) /* 第i个元素不存在 */
return FALSE;
while(j<i-1) /* 寻找第i-1个结点 */
{
p=p->next;
j++;
}
q=p->next; /* q指向待删除结点 */
p->next=q->next;
*e=q->data;
if(*L==q) /* 删除的是表尾元素 */
*L=p;
free(q); /* 释放待删除结点 */
return OK;
}
Status ListTraverse_CL(LinkList L,void(*vi)(ElemType))
{ /* 初始条件:L已存在。操作结果:依次对L的每个数据元素调用函数vi()。一旦vi()失败,则操作失败 */
LinkList p=L->next->next;
while(p!=L->next)
{
vi(p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
Status compare(ElemType c1,ElemType c2)
{
if(c1==c2)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void visit(ElemType c)
{
printf("%d ",c);
}
void main()
{
LinkList L;
ElemType e;
int j;
Status i;
i=InitList_CL(&L); /* 初始化单循环链表L */
printf("初始化单循环链表L i=%d (1:初始化成功)\n",i);
i=ListEmpty_CL(L);
printf("L是否空 i=%d(1:空 0:否)\n",i);
ListInsert_CL(&L,1,3); /* 在L中依次插入3,5 */
ListInsert_CL(&L,2,5);
i=GetElem_CL(L,1,&e);
j=ListLength_CL(L);
printf("L中数据元素个数=%d,第1个元素的值为%d。\n",j,e);
printf("L中的数据元素依次为:");
ListTraverse_CL(L,visit);
PriorElem_CL(L,5,&e); /* 求元素5的前驱 */
printf("5前面的元素的值为%d。\n",e);
NextElem_CL(L,3,&e); /* 求元素3的后继 */
printf("3后面的元素的值为%d。\n",e);
printf("L是否空 %d(1:空 0:否)\n",ListEmpty_CL(L));
j=LocateElem_CL(L,5,compare);
if(j)
printf("L的第%d个元素为5。\n",j);
else
printf("不存在值为5的元素\n");
i=ListDelete_CL(&L,2,&e);
printf("删除L的第2个元素:\n");
if(i)
{
printf("删除的元素值为%d,现在L中的数据元素依次为:",e);
ListTraverse_CL(L,visit);
}
else
printf("删除不成功!\n");
printf("清空L:%d(1: 成功)\n",ClearList_CL(&L));
printf("清空L后,L是否空:%d(1:空 0:否)\n",ListEmpty_CL(L));
printf("销毁L:%d(1: 成功)\n",DestroyList_CL(&L));
}
运行结果:
#include 第三种方法
//循环链表是一种手尾相接的链表,在单链表中,如果最后一个结点的指针域不指向空,而是指向头结点,整个链表就形成一个环,这是另一种的链式存储结构,成为单循环链表,类似的还有多重循环链表
//为了使空表和非空表的处理一致,同样设置了一个头结点
//创建头结点后,应有h->next=h语句
//特点1.从任意结点出发可以很容易的找到其他的结点,在某些算法上易于实现
//特点2.单循环链表的操作和实现和单链表的上基本一致,但注意的是算法的循环条件p或p->next 是否为空改为是否等于头指针
#include malloc(sizeof(cNode));
if (cNew==NULL) {
printf("errpr\n");
exit(0);
}
cNew->data=i;
if (cHead->next==cHead) {//此时为空链表
cHead->next=cNew;
cTail=cNew; //cTail指向新添加的结点
}else { //不是空链表的时候
cTail->next=cNew;
cTail=cNew;
}
}
cTail->next=cHead;//添加完毕后,把尾指针的指针域指向头结点
return cTail;
}
#pragma mark --单循环链表的遍历
void traverse(cNode*c) {
cNode* tempNode;
tempNode=c;
printf("------链表中的元素--------\n");
printf("%4d ",tempNode->data) ;
do {
printf("%4d ",tempNode->data) ;
}while((tempNode = tempNode->next) != c);
printf("\n") ;
printf("\n") ;
}
#pragma mark --在单循环列表查找值为x的结点
cNode* get(cNode*h,elemetType x) {
cNode*p;
p=h->next;
while (p!=h&&p->data!=x)
p=p->next;
if (p==h) {
printf("----不好意思,您转了一圈还是没有找到----\n");
return NULL;
}
printf("--找到了--\n");
return p;
}
#pragma mark 返回结点所处的位置
int searchPosition(cNode * pNode,int elem) {
cNode * target ;
int i = 1 ;
for(target = pNode ; target->data != elem && target->next != pNode ; ++i , target = target->next) ;
if(target->next == pNode) /*表中不存在该元素*/
return 0 ;
else
return i ;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
cNode*c=create(20);
traverse(c);
get(c, 40);
get(c, 10);
int position=searchPosition(c, 6);
printf("position====%d\n",position);///????为什么等于9
return 0;
} 
