pjsip音频流传递过程和混音算法
对于实现voip,pjsip是一个非常优秀的开源项目。其实现了复杂的sip信令交互和音频的传输建立。
1、媒体流的传递过程
我们来结合代码分析下媒体流的传递。
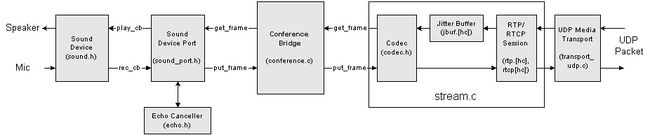
conference.c模块是用来做音频设备和媒体数据流之间的桥接作用,它与媒体流和音频设备之间的数据传递都是通过pjmedia_port接口来实现的。pjmedia_port定义如下(省略了其他字段):
typedef struct pjmedia_port
{
pj_status_t (*put_frame)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port,
pjmedia_frame *frame);
pj_status_t (*get_frame)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port,
pjmedia_frame *frame);
} pjmedia_port;媒体stream对象要实现pjmedia_port的方法,作为接口交给conference管理,被动的被conference调用。conference通过get_frame得到stream中解码后的pcm数据,通过put_frame将pcm传递给stream来编码、传输。
conferece内部需要实现一个index为0的port,其对应的pjmedia_port叫master_port。master_port作为与音频设备之间的接口,被动的被sound device调用。音频设备采集的pcm通过put_frame传递给conference,conference接下来传递给所有监听他的音频流。音频设备播放是会通过get_frame从conference获取pcm数据,这些pcm数据是所有被conference监听流mix后的pcm数据。
conference还要充当混音合流的角色。它会将多个输入的stream流的PCM数据混音后,再交给音频设备播放。也能将音频采集的pcm和某路流A混音后,传递个streamB编码发送。
2、音频混音分析
上述提到的master_port需要实现put_frame和get_frame接口。
/*
* Recorder (or passive port) callback.
*/
static pj_status_t put_frame(pjmedia_port *this_port,
pjmedia_frame *frame)
{
pj_status_t status;
status = pjmedia_delay_buf_put(port->delay_buf, (pj_int16_t*)frame->buf);
return status;
}删除我们分析不比较的代码。
我们看到put_frame方法是将数据保存进了一个delay_buf。由1我们知道这个接口是被sound device调用的,但是这里仅仅做了数据的保存,没有将数据发送给监听的stream。这是为何呢?
其实媒体数据的发送过程是在了get_frame里实现的,为何这么做我们在后面分析。
/*
* Player callback.
*/
static pj_status_t get_frame(pjmedia_port *this_port,
pjmedia_frame *frame)
{
pjmedia_conf *conf = (pjmedia_conf*) this_port->port_data.pdata;
pjmedia_frame_type speaker_frame_type = PJMEDIA_FRAME_TYPE_NONE;
unsigned ci, cj, i, j;
pj_int16_t *p_in;
TRACE_((THIS_FILE, "- clock -"));
/* Check that correct size is specified. */
pj_assert(frame->size == conf->samples_per_frame *
conf->bits_per_sample / 8);
/* Must lock mutex */
pj_mutex_lock(conf->mutex);
/* Reset port source count. We will only reset port's mix
* buffer when we have someone transmitting to it.
*/
for (i=0, ci=0; imax_ports && ci < conf->port_cnt; ++i) {
struct conf_port *conf_port = conf->ports[i];
/* Skip empty port. */
if (!conf_port)
continue;
/* Var "ci" is to count how many ports have been visited so far. */
++ci;
/* Reset buffer (only necessary if the port has transmitter) and
* reset auto adjustment level for mixed signal.
*/
conf_port->mix_adj = NORMAL_LEVEL;
if (conf_port->transmitter_cnt) {
pj_bzero(conf_port->mix_buf,
conf->samples_per_frame*sizeof(conf_port->mix_buf[0]));
}
} 上述代码初始化了每个port的合流调整值mix_adj为NORMAL_LEVEL,NORMAL_LEVEL的值为128。当mix_adj值为NORMAL_LEVEL时,合流后的音频数据不做调整。若mix_adj为200,需要对mix_buf的每个采样做处理:
mix_buf[i] = mix_buf[i] * 200 / 128
这里要注意的是,mix_buf保存的不是这个port本身的数据,而是其监听流的数据。
假如有三个流对象streamA、streamB和streamC,若streamA监听了streamB和streamC,那么streamA的transmitter_cnt值为2,streamB和streamC的listener_cnt为1。streamB和streamC的数据会被conference 混合进streamA的mix_buf中,最终通过streamA发送出去。
/* Get frames from all ports, and "mix" the signal
* to mix_buf of all listeners of the port.
*/
for (i=0, ci=0; i < conf->max_ports && ci < conf->port_cnt; ++i) {
struct conf_port *conf_port = conf->ports[i];
pj_int32_t level = 0;
/* Skip empty port. */
if (!conf_port)
continue;
/* Var "ci" is to count how many ports have been visited so far. */
++ci;
/* Skip if we're not allowed to receive from this port. */
if (conf_port->rx_setting == PJMEDIA_PORT_DISABLE) {
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
/* Also skip if this port doesn't have listeners. */
if (conf_port->listener_cnt == 0) {
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
/* Get frame from this port.
* For passive ports, get the frame from the delay_buf.
* For other ports, get the frame from the port.
*/
if (conf_port->delay_buf != NULL) {
pj_status_t status;
status = pjmedia_delay_buf_get(conf_port->delay_buf,
(pj_int16_t*)frame->buf);
if (status != PJ_SUCCESS) {
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
} else {
pj_status_t status;
pjmedia_frame_type frame_type;
status = read_port(conf, conf_port, (pj_int16_t*)frame->buf,
conf->samples_per_frame, &frame_type);
if (status != PJ_SUCCESS) {
/* bennylp: why do we need this????
* Also see comments on similar issue with write_port().
PJ_LOG(4,(THIS_FILE, "Port %.*s get_frame() returned %d. "
"Port is now disabled",
(int)conf_port->name.slen,
conf_port->name.ptr,
status));
conf_port->rx_setting = PJMEDIA_PORT_DISABLE;
*/
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
/* Check that the port is not removed when we call get_frame() */
if (conf->ports[i] == NULL) {
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
/* Ignore if we didn't get any frame */
if (frame_type != PJMEDIA_FRAME_TYPE_AUDIO) {
conf_port->rx_level = 0;
continue;
}
}遍历所有port,查看其是否被其他port监听,若listener_cnt为0,直接continue,若有,从这个port中读取pcm数据。
这里读取pcm数据有两个方式,一直是从delay_buf,正好就是我们我们在第1节中提到的录音回调,这个port是一个特殊的media_port,叫master_port,index为0,;其他普通的port都是通过read_port调用各stream对象的get_frame得到。
p_in = (pj_int16_t*) frame->buf;
/* Adjust the RX level from this port
* and calculate the average level at the same time.
*/
if (conf_port->rx_adj_level != NORMAL_LEVEL) {
for (j=0; jsamples_per_frame; ++j) {
/* For the level adjustment, we need to store the sample to
* a temporary 32bit integer value to avoid overflowing the
* 16bit sample storage.
*/
pj_int32_t itemp;
itemp = p_in[j];
/*itemp = itemp * adj / NORMAL_LEVEL;*/
/* bad code (signed/unsigned badness):
* itemp = (itemp * conf_port->rx_adj_level) >> 7;
*/
itemp *= conf_port->rx_adj_level;
itemp >>= 7;
/* Clip the signal if it's too loud */
if (itemp > MAX_LEVEL) itemp = MAX_LEVEL;
else if (itemp < MIN_LEVEL) itemp = MIN_LEVEL;
p_in[j] = (pj_int16_t) itemp;
level += (p_in[j]>=0? p_in[j] : -p_in[j]);
}
} else {
for (j=0; jsamples_per_frame; ++j) {
level += (p_in[j]>=0? p_in[j] : -p_in[j]);
}
}
level /= conf->samples_per_frame;
/* Convert level to 8bit complement ulaw */
level = pjmedia_linear2ulaw(level) ^ 0xff;
/* Put this level to port's last RX level. */
conf_port->rx_level = level; 上述代码根据设置的rx_adj_level,调整每个sample的值。根据调整后的sample值的绝对值累加值,计算出平均sample的值level。将level转换成8bit的u律,保存进rx_level。
// Ticket #671: Skipping very low audio signal may cause noise
// to be generated in the remote end by some hardphones.
/* Skip processing frame if level is zero */
//if (level == 0)
// continue;
/* Add the signal to all listeners. */
for (cj=0; cj < conf_port->listener_cnt; ++cj)
{
struct conf_port *listener;
pj_int32_t *mix_buf;
listener = conf->ports[conf_port->listener_slots[cj]];
/* Skip if this listener doesn't want to receive audio */
if (listener->tx_setting != PJMEDIA_PORT_ENABLE)
continue;
mix_buf = listener->mix_buf;
if (listener->transmitter_cnt > 1) {
/* Mixing signals,
* and calculate appropriate level adjustment if there is
* any overflowed level in the mixed signal.
*/
unsigned k, samples_per_frame = conf->samples_per_frame;
pj_int32_t mix_buf_min = 0;
pj_int32_t mix_buf_max = 0;
for (k = 0; k < samples_per_frame; ++k) {
mix_buf[k] += p_in[k];
if (mix_buf[k] < mix_buf_min)
mix_buf_min = mix_buf[k];
if (mix_buf[k] > mix_buf_max)
mix_buf_max = mix_buf[k];
}
/* Check if normalization adjustment needed. */
if (mix_buf_min < MIN_LEVEL || mix_buf_max > MAX_LEVEL) {
int tmp_adj;
if (-mix_buf_min > mix_buf_max)
mix_buf_max = -mix_buf_min;
/* NORMAL_LEVEL * MAX_LEVEL / mix_buf_max; */
tmp_adj = (MAX_LEVEL<<7) / mix_buf_max;
if (tmp_adj < listener->mix_adj)
listener->mix_adj = tmp_adj;
}
} else {
/* Only 1 transmitter:
* just copy the samples to the mix buffer
* no mixing and level adjustment needed
*/
unsigned k, samples_per_frame = conf->samples_per_frame;
for (k = 0; k < samples_per_frame; ++k) {
mix_buf[k] = p_in[k];
}
}
} /* loop the listeners of conf port */
} /* loop of all conf ports */上述代码将此port的pcm数据拷贝进它listener port的mix_buf里。
1、若listener port仅监听一个port,即当前的port,只要将pcm数据简单拷贝进mix_buf里即可;
2、若listener port监听多个port,需将当前port的数据累加到mix_buf,计算累加后的最大值mix_buf_max和最小值mix_buf_min。当MAX(-mix_buf_min, mix_buf_max)大于MAX_LEVEL时,计算tmp_adj值:MAX_LEVEL * 128 / mix_buf_max。更新port->mix_adj为tmp_adj,若tmp_adj变小。
/* Time for all ports to transmit whetever they have in their
* buffer.
*/
for (i=0, ci=0; imax_ports && ciport_cnt; ++i) {
struct conf_port *conf_port = conf->ports[i];
pjmedia_frame_type frm_type;
pj_status_t status;
if (!conf_port)
continue;
/* Var "ci" is to count how many ports have been visited. */
++ci;
status = write_port( conf, conf_port, &frame->timestamp,
&frm_type);
if (status != PJ_SUCCESS) {
/* bennylp: why do we need this????
One thing for sure, put_frame()/write_port() may return
non-successfull status on Win32 if there's temporary glitch
on network interface, so disabling the port here does not
sound like a good idea.
PJ_LOG(4,(THIS_FILE, "Port %.*s put_frame() returned %d. "
"Port is now disabled",
(int)conf_port->name.slen,
conf_port->name.ptr,
status));
conf_port->tx_setting = PJMEDIA_PORT_DISABLE;
*/
continue;
}
/* Set the type of frame to be returned to sound playback
* device.
*/
if (i == 0)
speaker_frame_type = frm_type;
} 遍历所有port,通过write_port往stream里put_frame数据。后面会分析write_port()。
/* Return sound playback frame. */
if (conf->ports[0]->tx_level) {
TRACE_((THIS_FILE, "write to audio, count=%d",
conf->samples_per_frame));
pjmedia_copy_samples( (pj_int16_t*)frame->buf,
(const pj_int16_t*)conf->ports[0]->mix_buf,
conf->samples_per_frame);
} else {
/* Force frame type NONE */
speaker_frame_type = PJMEDIA_FRAME_TYPE_NONE;
}
/* MUST set frame type */
frame->type = speaker_frame_type;
pj_mutex_unlock(conf->mutex);
#ifdef REC_FILE
if (fhnd_rec == NULL)
fhnd_rec = fopen(REC_FILE, "wb");
if (fhnd_rec)
fwrite(frame->buf, frame->size, 1, fhnd_rec);
#endif
return PJ_SUCCESS;
} 数据返回。前面我们知道get_frame方法是被音频设备调用的,conference的index为0的port用来给音频设备提供数据。直接从此port的mix_buf拷贝数据。