opencv中的BackgroundSubtractorKNN源码解读
1.前言
最近看opencv的源码时发现opencv3.1版本和2.4.13版本在背景提取方面的一点区别:相对于2.4.13,3.1版本代码删去了GMG算法,增加了KNN算法,这篇文章主要记录自己对BackgroundSubtractorKNN算法源码的解读。实际上自己是先看了对应的论文,但是没有完全看懂,之后通过读源码加上做了一点实验后反向推想算法的一些思想。所以这篇文章的论述顺序是:算法的基本原理——>源码的基本流程——>个人验证——>源码解读。
2.算法原理
根据源码中注释,该算法来自于论文《Efficient Adaptive Density Estimation per Image Pixel for the Task of Background Subtraction》。是不是有点眼熟?没错,就是那篇同时提出改进的GMM,被opencv收录为BackgroundSubtractorMOG2算法的文章!大神就是大神。。。论文我简单看了下,但是没看懂。。本着实用的思想我把BackgroundSubtractorKNN读了一遍,结合着自己的一些实验,基本从实现层面看懂了算法的意思。按照自己的理解,该算法结合了无参数概率密度估计+KNN分类思想。首先是无参数概率密度估计,是指在不方便建立样本分布模型的情况下(与之相反的就是有参数概率密度估计,像BackgroundSubtractorMOG2就是明确的建立了混合高斯模型然后根据一定的优化目标求取模型参数)估计其概率密度分布。文中选取的是核函数密度估计方法,有关该方法的理解可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/yuanxing14/article/details/41948485,有点类似于直方图分布的意思。之后就是KNN算法,是一种简单的聚类方法,百度百科对其解释的都比较清楚了,基本概念截图如下:
3.算法流程
源码的算法流程可以总结如下,对于图像某个位置的新像素值:
(1)与该像素值历史信息(包括前几帧的像素值和像素点是前景还是背景的判断)比较,如果像素值之间的差别在指定阈值内,则认为新像素值与该历史信息是匹配的,是“潜在的”一类;所有历史信息比较完毕后,如果与历史信息匹配的次数超过了设定阈值,那么:(1)新像素点被归为“潜在背景点”(2)如果被匹配的历史信息中属于背景的点个数超过设定阈值,那么新的像素点就被归为背景点
(2)将新像素点根据一定规则保存到历史信息中(这个保存规则还挺复杂的)
看源码的过程中算法的第一步流程清晰明了,很容易理解,但是第二步过程的保存规则着实搞晕了,主要的疑问是为什么搞这么复杂的保存规则?好吧,为了验证其作用和目的,我先把算法流程简化为:实时保存每个像素点的历史7帧信息,之后新的像素点与历史7帧像素点比较,然后按照上面的流程进行前景/背景的判断。上代码
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/videoio.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const int HISTORY_NUM = 7;// 14;// 历史信息帧数
const int nKNN = 3;// KNN聚类后判断为背景的阈值
const float defaultDist2Threshold = 20.0f;// 灰度聚类阈值
struct PixelHistory
{
unsigned char *gray;// 历史灰度值
unsigned char *IsBG;// 对应灰度值的前景/背景判断,1代表判断为背景,0代表判断为前景
};
int main()
{
PixelHistory* framePixelHistory = NULL;// 记录一帧图像中每个像素点的历史信息
cv::Mat frame, FGMask, FGMask_KNN;
int keyboard = 0;
int rows, cols;
rows = cols = 0;
bool InitFlag = false;
int frameCnt = 0;
int gray = 0;
VideoCapture capture("768X576.avi");
Ptr pBackgroundKnn =
createBackgroundSubtractorKNN();
pBackgroundKnn->setHistory(200);
pBackgroundKnn->setDist2Threshold(600);
pBackgroundKnn->setShadowThreshold(0.5);
while ((char)keyboard != 'q' && (char)keyboard != 27)
{
// 读取当前帧
if (!capture.read(frame))
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
cvtColor(frame, frame, CV_BGR2GRAY);
if (!InitFlag)
{
// 初始化一些变量
rows = frame.rows;
cols = frame.cols;
FGMask.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC1);// 输出图像初始化
// framePixelHistory分配空间
framePixelHistory = (PixelHistory*)malloc(rows*cols * sizeof(PixelHistory));
for (int i = 0; i < rows*cols; i++)
{
framePixelHistory[i].gray = (unsigned char*)malloc(HISTORY_NUM * sizeof(unsigned char));
framePixelHistory[i].IsBG = (unsigned char*)malloc(HISTORY_NUM * sizeof(unsigned char));
memset(framePixelHistory[i].gray, 0, HISTORY_NUM * sizeof(unsigned char));
memset(framePixelHistory[i].IsBG, 0, HISTORY_NUM * sizeof(unsigned char));
}
InitFlag = true;
}
if (InitFlag)
{
FGMask.setTo(Scalar(255));
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
gray = frame.at(i, j);
int fit = 0;
int fit_bg = 0;
// 比较确定前景/背景
for (int n = 0; n < HISTORY_NUM; n++)
{
if (fabs(gray - framePixelHistory[i*cols + j].gray[n]) < defaultDist2Threshold)// 灰度差别是否位于设定阈值内
{
fit++;
if (framePixelHistory[i*cols + j].IsBG[n])// 历史信息对应点之前被判断为背景
{
fit_bg++;
}
}
}
if (fit_bg >= nKNN)// 当前点判断为背景
{
FGMask.at(i, j) = 0;
}
// 更新历史值
int index = frameCnt % HISTORY_NUM;
framePixelHistory[i*cols + j].gray[index] = gray;
framePixelHistory[i*cols + j].IsBG[index] = fit >=nKNN ? 1:0;// 当前点作为背景点存入历史信息
}
}
}
pBackgroundKnn->apply(frame, FGMask_KNN);
imshow("Frame", frame);
imshow("FGMask", FGMask);
imshow("FGMask_KNN", FGMask_KNN);
keyboard = waitKey(30);
frameCnt++;
}
capture.release();
return 0;
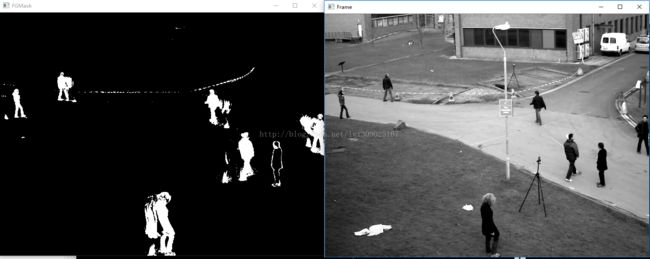
} 算法效果如上图所示:左图是检测的背景(黑色)/前景(白色)效果,右图是原图。可以看到行人能够有效的检测得到,但是同时行人背后出现了局部认为是前景的区域。这是为啥?因为我们的历史信息就是前7帧像素值,由于行人具有一定宽高,存在身后区域的之前几帧都被行人身体覆盖的情况。所以即便行人已经走过,被行人覆盖的背景像素得以露出,但是它对比的像素点大多是行人的历史像素点,所以又被划分为前景。
那如何解决这个问题?一种思路就是历史信息不仅包含一部分“最近的历史信息”,譬如前7帧,还要包含一部分“遥远的历史信息”,譬如前面的第10帧,第15帧之类的。这样即使行人经过的区域“最近的历史信息”都是行人区域的像素值,但是“遥远的历史信息”中就是行人未经过时的背景点像素值。行人已经走过,被行人覆盖的背景像素得以露出,它与该点“遥远的历史信息”比较相似,那也会被判断为背景点。
想法很美好,但是实际操作中还是遇到很多问题的,譬如历史帧数和一些阈值如何做到相互匹配且鲁棒?如何定义“最近的历史信息”和“遥远的历史信息”,它们的更新规则是什么?自己虽然做了一些尝试,但是短时间内无法对这个给出比较普适的结果。但是BackgroundSubtractorKNN给出了,且其背后有一定的数学理论支撑(尴尬,就是这部分数学理论楼主没看懂。。),下面就直接对BackgroundSubtractorKNN源码进行讲解。
4.源码讲解
BackgroundSubtractorKNN不仅能够判断像素的前景/背景,还包含阴影检测功能,其作用和原理与BackgroundSubtractorMOG2相似,可以参考点击打开链接,这里不再重复。下面给出带有自己注释的BackgroundSubtractorKNN源码,源码位于opencv3.1\opencv\sources\modules\video\src\bgfg_KNN.cpp内
/*M///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// IMPORTANT: READ BEFORE DOWNLOADING, COPYING, INSTALLING OR USING.
//
// By downloading, copying, installing or using the software you agree to this license.
// If you do not agree to this license, do not download, install,
// copy or use the software.
//
//
// License Agreement
// For Open Source Computer Vision Library
//
// Copyright (C) 2000, Intel Corporation, all rights reserved.
// Copyright (C) 2013, OpenCV Foundation, all rights reserved.
// Third party copyrights are property of their respective owners.
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
// are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
//
// * Redistribution's of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// * Redistribution's in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
// this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
// and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
//
// * The name of the copyright holders may not be used to endorse or promote products
// derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// This software is provided by the copyright holders and contributors "as is" and
// any express or implied warranties, including, but not limited to, the implied
// warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose are disclaimed.
// In no event shall the Intel Corporation or contributors be liable for any direct,
// indirect, incidental, special, exemplary, or consequential damages
// (including, but not limited to, procurement of substitute goods or services;
// loss of use, data, or profits; or business interruption) however caused
// and on any theory of liability, whether in contract, strict liability,
// or tort (including negligence or otherwise) arising in any way out of
// the use of this software, even if advised of the possibility of such damage.
//
//M*/
//#include
#include "precomp.hpp"
namespace cv
{
/*!
The class implements the following algorithm:
"Efficient Adaptive Density Estimation per Image Pixel for the Task of Background Subtraction"
Z.Zivkovic, F. van der Heijden
Pattern Recognition Letters, vol. 27, no. 7, pages 773-780, 2006
http://www.zoranz.net/Publications/zivkovicPRL2006.pdf
*/
// default parameters of gaussian background detection algorithm
static const int defaultHistory2 = 500; // Learning rate; alpha = 1/defaultHistory2
static const int defaultNsamples = 7; // number of samples saved in memory// 实际上保存了7X3=21个历史值
static const float defaultDist2Threshold = 20.0f*20.0f;//threshold on distance from the sample
// additional parameters
static const unsigned char defaultnShadowDetection2 = (unsigned char)127; // value to use in the segmentation mask for shadows, set 0 not to do shadow detection// 检测到的阴影值赋值127,用于区分前景255
static const float defaultfTau = 0.5f; // Tau - shadow threshold, see the paper for explanation
class BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl : public BackgroundSubtractorKNN
{
public:
//! the default constructor
BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl()
{
frameSize = Size(0,0);
frameType = 0;
nframes = 0;
history = defaultHistory2;
//set parameters
// N - the number of samples stored in memory per model
nN = defaultNsamples;
//kNN - k nearest neighbour - number on NN for detecting background - default K=[0.1*nN]
nkNN=MAX(1,cvRound(0.1*nN*3+0.40));// 根据采样点数计算聚类阈值
//Tb - Threshold Tb*kernelwidth
fTb = defaultDist2Threshold;
// Shadow detection
bShadowDetection = 1;//turn on
nShadowDetection = defaultnShadowDetection2;
fTau = defaultfTau;// Tau - shadow threshold
name_ = "BackgroundSubtractor.KNN";
}
//! the full constructor that takes the length of the history,
// the number of gaussian mixtures, the background ratio parameter and the noise strength
BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl(int _history, float _dist2Threshold, bool _bShadowDetection=true)
{
frameSize = Size(0,0);
frameType = 0;
nframes = 0;
history = _history > 0 ? _history : defaultHistory2;
//set parameters
// N - the number of samples stored in memory per model
nN = defaultNsamples;
//kNN - k nearest neighbour - number on NN for detcting background - default K=[0.1*nN]
nkNN=MAX(1,cvRound(0.1*nN*3+0.40));
//Tb - Threshold Tb*kernelwidth
fTb = _dist2Threshold>0? _dist2Threshold : defaultDist2Threshold;
bShadowDetection = _bShadowDetection;
nShadowDetection = defaultnShadowDetection2;
fTau = defaultfTau;
name_ = "BackgroundSubtractor.KNN";
}
//! the destructor
~BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl() {}
//! the update operator
void apply(InputArray image, OutputArray fgmask, double learningRate=-1);
//! computes a background image which are the mean of all background gaussians
virtual void getBackgroundImage(OutputArray backgroundImage) const;
//! re-initiaization method
void initialize(Size _frameSize, int _frameType)
{
frameSize = _frameSize;
frameType = _frameType;
nframes = 0;
int nchannels = CV_MAT_CN(frameType);
CV_Assert( nchannels <= CV_CN_MAX );
// Reserve memory for the model
int size=frameSize.height*frameSize.width;
// for each sample of 3 speed pixel models each pixel bg model we store ...
// values + flag (nchannels+1 values)
bgmodel.create( 1,(nN * 3) * (nchannels+1)* size,CV_8U);// 每一个像素点,预留了7X3=21个位置,每个位置包含像素值(nchannels个字节)+前景/背景判断标志(一个字节)
//index through the three circular lists
aModelIndexShort.create(1,size,CV_8U);
aModelIndexMid.create(1,size,CV_8U);
aModelIndexLong.create(1,size,CV_8U);
//when to update next
nNextShortUpdate.create(1,size,CV_8U);
nNextMidUpdate.create(1,size,CV_8U);
nNextLongUpdate.create(1,size,CV_8U);
//Reset counters
nShortCounter = 0;
nMidCounter = 0;
nLongCounter = 0;
aModelIndexShort = Scalar::all(0);//random? //((m_nN)*rand())/(RAND_MAX+1);//0...m_nN-1
aModelIndexMid = Scalar::all(0);
aModelIndexLong = Scalar::all(0);
nNextShortUpdate = Scalar::all(0);
nNextMidUpdate = Scalar::all(0);
nNextLongUpdate = Scalar::all(0);
}
virtual int getHistory() const { return history; }
virtual void setHistory(int _nframes) { history = _nframes; }
virtual int getNSamples() const { return nN; }
virtual void setNSamples(int _nN) { nN = _nN; }//needs reinitialization!
virtual int getkNNSamples() const { return nkNN; }
virtual void setkNNSamples(int _nkNN) { nkNN = _nkNN; }
virtual double getDist2Threshold() const { return fTb; }
virtual void setDist2Threshold(double _dist2Threshold) { fTb = (float)_dist2Threshold; }
virtual bool getDetectShadows() const { return bShadowDetection; }
virtual void setDetectShadows(bool detectshadows) { bShadowDetection = detectshadows; }
virtual int getShadowValue() const { return nShadowDetection; }
virtual void setShadowValue(int value) { nShadowDetection = (uchar)value; }
virtual double getShadowThreshold() const { return fTau; }
virtual void setShadowThreshold(double value) { fTau = (float)value; }
virtual void write(FileStorage& fs) const
{
fs << "name" << name_
<< "history" << history
<< "nsamples" << nN
<< "nKNN" << nkNN
<< "dist2Threshold" << fTb
<< "detectShadows" << (int)bShadowDetection
<< "shadowValue" << (int)nShadowDetection
<< "shadowThreshold" << fTau;
}
virtual void read(const FileNode& fn)
{
CV_Assert( (String)fn["name"] == name_ );
history = (int)fn["history"];
nN = (int)fn["nsamples"];
nkNN = (int)fn["nKNN"];
fTb = (float)fn["dist2Threshold"];
bShadowDetection = (int)fn["detectShadows"] != 0;
nShadowDetection = saturate_cast((int)fn["shadowValue"]);
fTau = (float)fn["shadowThreshold"];
}
protected:
Size frameSize;
int frameType;
int nframes;
/////////////////////////
//very important parameters - things you will change
////////////////////////
int history;
//alpha=1/history - speed of update - if the time interval you want to average over is T
//set alpha=1/history. It is also usefull at start to make T slowly increase
//from 1 until the desired T
float fTb;
//Tb - threshold on the squared distance from the sample used to decide if it is well described
//by the background model or not. A typical value could be 2 sigma
//and that is Tb=2*2*10*10 =400; where we take typical pixel level sigma=10
/////////////////////////
//less important parameters - things you might change but be carefull
////////////////////////
int nN;//totlal number of samples
int nkNN;//number on NN for detcting background - default K=[0.1*nN]
//shadow detection parameters
bool bShadowDetection;//default 1 - do shadow detection
unsigned char nShadowDetection;//do shadow detection - insert this value as the detection result - 127 default value
float fTau;
// Tau - shadow threshold. The shadow is detected if the pixel is darker
//version of the background. Tau is a threshold on how much darker the shadow can be.
//Tau= 0.5 means that if pixel is more than 2 times darker then it is not shadow
//See: Prati,Mikic,Trivedi,Cucchiarra,"Detecting Moving Shadows...",IEEE PAMI,2003.
//model data
int nLongCounter;//circular counter
int nMidCounter;
int nShortCounter;
Mat bgmodel; // model data pixel values
Mat aModelIndexShort;// index into the models
Mat aModelIndexMid;
Mat aModelIndexLong;
Mat nNextShortUpdate;//random update points per model
Mat nNextMidUpdate;
Mat nNextLongUpdate;
String name_;
};
//{ to do - paralelization ...
//struct KNNInvoker....
CV_INLINE void
_cvUpdatePixelBackgroundNP( long pixel,const uchar* data, int nchannels, int m_nN,
uchar* m_aModel,
uchar* m_nNextLongUpdate,
uchar* m_nNextMidUpdate,
uchar* m_nNextShortUpdate,
uchar* m_aModelIndexLong,
uchar* m_aModelIndexMid,
uchar* m_aModelIndexShort,
int m_nLongCounter,
int m_nMidCounter,
int m_nShortCounter,
int m_nLongUpdate,
int m_nMidUpdate,
int m_nShortUpdate,
uchar include
)
{
// hold the offset
int ndata=1+nchannels;
// 计算存储当前点的空间地址
long offsetLong = ndata * (pixel * m_nN * 3 + m_aModelIndexLong[pixel] + m_nN * 2);
long offsetMid = ndata * (pixel * m_nN * 3 + m_aModelIndexMid[pixel] + m_nN * 1);
long offsetShort = ndata * (pixel * m_nN * 3 + m_aModelIndexShort[pixel]);
// 每隔m_nLongUpdate帧保存一帧图像到m_aModel[offsetLong]中,最“古老”的历史信息
// Long update?
if (m_nNextLongUpdate[pixel] == m_nLongCounter)
{
// add the oldest pixel from Mid to the list of values (for each color)
memcpy(&m_aModel[offsetLong],&m_aModel[offsetMid],ndata*sizeof(unsigned char));
// increase the index
m_aModelIndexLong[pixel] = (m_aModelIndexLong[pixel] >= (m_nN-1)) ? 0 : (m_aModelIndexLong[pixel] + 1);
};
if (m_nLongCounter == (m_nLongUpdate-1))
{
//m_nNextLongUpdate[pixel] = (uchar)(((m_nLongUpdate)*(rand()-1))/RAND_MAX);//0,...m_nLongUpdate-1;
m_nNextLongUpdate[pixel] = (uchar)( rand() % m_nLongUpdate );//0,...m_nLongUpdate-1;
};
// 每隔m_nMidUpdate帧保存一帧图像到m_aModel[offsetMid]中,相对“古老”的历史信息
// Mid update?
if (m_nNextMidUpdate[pixel] == m_nMidCounter)
{
// add this pixel to the list of values (for each color)
memcpy(&m_aModel[offsetMid],&m_aModel[offsetShort],ndata*sizeof(unsigned char));
// increase the index
m_aModelIndexMid[pixel] = (m_aModelIndexMid[pixel] >= (m_nN-1)) ? 0 : (m_aModelIndexMid[pixel] + 1);
};
if (m_nMidCounter == (m_nMidUpdate-1))
{
m_nNextMidUpdate[pixel] = (uchar)( rand() % m_nMidUpdate );
};
// 每隔m_nShortUpdate帧保存一帧图像到m_aModel[offsetShort]中,最“近期”的历史信息
// Short update?
if (m_nNextShortUpdate[pixel] == m_nShortCounter)
{
// add this pixel to the list of values (for each color)
memcpy(&m_aModel[offsetShort],data,ndata*sizeof(unsigned char));
//set the include flag
m_aModel[offsetShort+nchannels]=include;
// increase the index
m_aModelIndexShort[pixel] = (m_aModelIndexShort[pixel] >= (m_nN-1)) ? 0 : (m_aModelIndexShort[pixel] + 1);
};
if (m_nShortCounter == (m_nShortUpdate-1))
{
m_nNextShortUpdate[pixel] = (uchar)( rand() % m_nShortUpdate );
};
};
CV_INLINE int
_cvCheckPixelBackgroundNP(long pixel,
const uchar* data, int nchannels,
int m_nN,
uchar* m_aModel,
float m_fTb,
int m_nkNN,
float tau,
int m_nShadowDetection,
uchar& include)
{
int Pbf = 0; // the total probability that this pixel is background
int Pb = 0; //background model probability
float dData[CV_CN_MAX];
//uchar& include=data[nchannels];
include=0;//do we include this pixel into background model?
int ndata=nchannels+1;
long posPixel = pixel * ndata * m_nN * 3;
// float k;
// now increase the probability for each pixel
for (int n = 0; n < m_nN*3; n++)// 与7X3=21个历史点信息对比
{
uchar* mean_m = &m_aModel[posPixel + n*ndata];
//calculate difference and distance
// 计算像素值之间的差异大小
float dist2;
if( nchannels == 3 )
{
dData[0] = (float)mean_m[0] - data[0];
dData[1] = (float)mean_m[1] - data[1];
dData[2] = (float)mean_m[2] - data[2];
dist2 = dData[0]*dData[0] + dData[1]*dData[1] + dData[2]*dData[2];
}
else
{
dist2 = 0.f;
for( int c = 0; c < nchannels; c++ )
{
dData[c] = (float)mean_m[c] - data[c];
dist2 += dData[c]*dData[c];
}
}
if (dist2= m_nkNN)//Tb
{
include=1;//include
return 1;//background ->exit// 当前点为背景点
};
}
};
};
//include?
if (Pbf>=m_nkNN)//m_nTbf)
{
include=1;// 当前点虽然不是背景点,但是作为潜在背景点保存到历史信息中
}
int Ps = 0; // the total probability that this pixel is background shadow
// Detected as moving object, perform shadow detection
// 阴影检测流程
if (m_nShadowDetection)
{
for (int n = 0; n < m_nN*3; n++)
{
//long subPosPixel = posPixel + n*ndata;
uchar* mean_m = &m_aModel[posPixel + n*ndata];
if(mean_m[nchannels])//check only background
{
float numerator = 0.0f;
float denominator = 0.0f;
for( int c = 0; c < nchannels; c++ )
{
numerator += (float)data[c] * mean_m[c];
denominator += (float)mean_m[c] * mean_m[c];
}
// no division by zero allowed
if( denominator == 0 )
return 0;
// if tau < a < 1 then also check the color distortion
if( numerator <= denominator && numerator >= tau*denominator )
{
float a = numerator / denominator;
float dist2a = 0.0f;
for( int c = 0; c < nchannels; c++ )
{
float dD= a*mean_m[c] - data[c];
dist2a += dD*dD;
}
if (dist2a= m_nkNN)//shadow
return 2;
};
};
};
};
}
return 0;
};
CV_INLINE void
icvUpdatePixelBackgroundNP(const Mat& _src, Mat& _dst,
Mat& _bgmodel,
Mat& _nNextLongUpdate,
Mat& _nNextMidUpdate,
Mat& _nNextShortUpdate,
Mat& _aModelIndexLong,
Mat& _aModelIndexMid,
Mat& _aModelIndexShort,
int& _nLongCounter,
int& _nMidCounter,
int& _nShortCounter,
int _nN,
float _fAlphaT,
float _fTb,
int _nkNN,
float _fTau,
int _bShadowDetection,
uchar nShadowDetection
)
{
int nchannels = CV_MAT_CN(_src.type());
//model
uchar* m_aModel=_bgmodel.ptr(0);
uchar* m_nNextLongUpdate=_nNextLongUpdate.ptr(0);
uchar* m_nNextMidUpdate=_nNextMidUpdate.ptr(0);
uchar* m_nNextShortUpdate=_nNextShortUpdate.ptr(0);
uchar* m_aModelIndexLong=_aModelIndexLong.ptr(0);
uchar* m_aModelIndexMid=_aModelIndexMid.ptr(0);
uchar* m_aModelIndexShort=_aModelIndexShort.ptr(0);
//some constants
int m_nN=_nN;
float m_fAlphaT=_fAlphaT;
float m_fTb=_fTb;//Tb - threshold on the distance
float m_fTau=_fTau;
int m_nkNN=_nkNN;
int m_bShadowDetection=_bShadowDetection;
//recalculate update rates - in case alpha is changed
// calculate update parameters (using alpha)
int Kshort,Kmid,Klong;
// 这部分借鉴了GMM中有关权值自增至一定阈值的代数计算log(1-cf)/log(1-alpha)
//approximate exponential learning curve
Kshort=(int)(log(0.7)/log(1-m_fAlphaT))+1;//Kshort
Kmid=(int)(log(0.4)/log(1-m_fAlphaT))-Kshort+1;//Kmid
Klong=(int)(log(0.1)/log(1-m_fAlphaT))-Kshort-Kmid+1;//Klong
//refresh rates
// 不是连续保存帧信息,而是Kshort/Kmid/Klong帧中各自保存m_nN帧信息
int m_nShortUpdate = (Kshort/m_nN)+1;
int m_nMidUpdate = (Kmid/m_nN)+1;
int m_nLongUpdate = (Klong/m_nN)+1;
//int m_nShortUpdate = MAX((Kshort/m_nN),m_nN);
//int m_nMidUpdate = MAX((Kmid/m_nN),m_nN);
//int m_nLongUpdate = MAX((Klong/m_nN),m_nN);
//update counters for the refresh rate
int m_nLongCounter=_nLongCounter;
int m_nMidCounter=_nMidCounter;
int m_nShortCounter=_nShortCounter;
_nShortCounter++;//0,1,...,m_nShortUpdate-1
_nMidCounter++;
_nLongCounter++;// 随着处理帧数自增
if (_nShortCounter >= m_nShortUpdate) _nShortCounter = 0;
if (_nMidCounter >= m_nMidUpdate) _nMidCounter = 0;
if (_nLongCounter >= m_nLongUpdate) _nLongCounter = 0;
//go through the image
long i = 0;
for (long y = 0; y < _src.rows; y++)
{
for (long x = 0; x < _src.cols; x++)
{
const uchar* data = _src.ptr((int)y, (int)x);
//update model+ background subtract
uchar include=0;
// 先做前景/背景判断
int result= _cvCheckPixelBackgroundNP(i, data, nchannels,
m_nN, m_aModel, m_fTb,m_nkNN, m_fTau,m_bShadowDetection,include);
// 将该点加入历史信息
_cvUpdatePixelBackgroundNP(i,data,nchannels,
m_nN, m_aModel,
m_nNextLongUpdate,
m_nNextMidUpdate,
m_nNextShortUpdate,
m_aModelIndexLong,
m_aModelIndexMid,
m_aModelIndexShort,
m_nLongCounter,
m_nMidCounter,
m_nShortCounter,
m_nLongUpdate,
m_nMidUpdate,
m_nShortUpdate,
include
);
switch (result)
{
case 0:
//foreground
*_dst.ptr((int)y, (int)x) = 255;
break;
case 1:
//background
*_dst.ptr((int)y, (int)x) = 0;
break;
case 2:
//shadow
*_dst.ptr((int)y, (int)x) = nShadowDetection;
break;
}
i++;
}
}
};
void BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl::apply(InputArray _image, OutputArray _fgmask, double learningRate)
{
Mat image = _image.getMat();
bool needToInitialize = nframes == 0 || learningRate >= 1 || image.size() != frameSize || image.type() != frameType;
if( needToInitialize )
initialize(image.size(), image.type());
_fgmask.create( image.size(), CV_8U );
Mat fgmask = _fgmask.getMat();
++nframes;
learningRate = learningRate >= 0 && nframes > 1 ? learningRate : 1./std::min( 2*nframes, history );
CV_Assert(learningRate >= 0);
//parallel_for_(Range(0, image.rows),
// KNNInvoker(image, fgmask,
icvUpdatePixelBackgroundNP(image, fgmask,
bgmodel,
nNextLongUpdate,
nNextMidUpdate,
nNextShortUpdate,
aModelIndexLong,
aModelIndexMid,
aModelIndexShort,
nLongCounter,
nMidCounter,
nShortCounter,
nN,
(float)learningRate,
fTb,
nkNN,
fTau,
bShadowDetection,
nShadowDetection
);
}
void BackgroundSubtractorKNNImpl::getBackgroundImage(OutputArray backgroundImage) const
{
int nchannels = CV_MAT_CN(frameType);
//CV_Assert( nchannels == 3 );
Mat meanBackground(frameSize, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0));
int ndata=nchannels+1;
int modelstep=(ndata * nN * 3);
const uchar* pbgmodel=bgmodel.ptr(0);
for(int row=0; row(row, col) = Vec3b(mean_m);// 最近的判断为背景的历史像素值作为背景点
break;
}
}
pbgmodel=pbgmodel+modelstep;
}
}
switch(CV_MAT_CN(frameType))
{
case 1:
{
std::vector channels;
split(meanBackground, channels);
channels[0].copyTo(backgroundImage);
break;
}
case 3:
{
meanBackground.copyTo(backgroundImage);
break;
}
default:
CV_Error(Error::StsUnsupportedFormat, "");
}
}
Ptr createBackgroundSubtractorKNN(int _history, double _threshold2,
bool _bShadowDetection)
{
return makePtr(_history, (float)_threshold2, _bShadowDetection);
}
}
/* End of file. */