玩转MySQL -----处理大数据对象
一、大数据对象简介
1.LOB(Large Object,大型对象)类型的字段现在用得越来越多了。因为这种类型的字段,容量大(最多能容纳4GB的数据),且一个表中可以有多个这种类型的字段,很灵活,适用于数据量非常大的业务领域(如图象、档案等)。
2.LOB类型分为BLOB和CLOB两种:BLOB即二进制大型对象(Binary Large Object),适用于存贮非文本的字节流数据(如程序、图象、影音等)。
3.而CLOB,即字符型大型对象(Character Large Object),则与字符集相关,适于存贮文本型的数据(如历史档案、大部头著作等)。
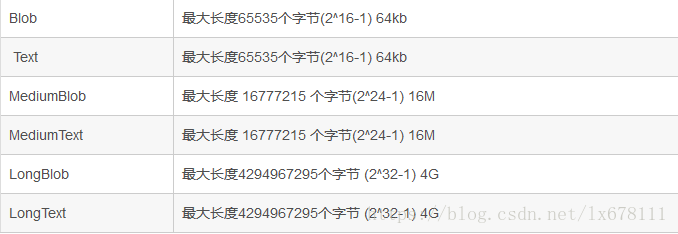
4. 四种类型的最大长度: tinyBlob:255, Blob:65k, MediumBlob:16M, LongBlob:4G text也是这4种类型,长度类似
create table note(
id int,
note text;
)
字段定义成 "note varchar(100000)" 时,数据库自动会把它转成 MediumText类型
CREATE TABLE img(
id INT,
img BLOB //MEDIUMBLOB
);
凡是要写入大数据字段,都只能使用PreparedStatement, 不能使用Statement。
读取大数据字段是可以用Statement的。
实例如下:
CLOB:
1.写入"文本大数据"字段
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
文本大数据字段的数据封装: pst.setAsciiStream(i, in)
public class JDBCLobDemo {
@Test
// 写入"文本大数据"字段
public void saveCLob() throws Exception {
Connection conn = ConnUtils.getConn();
String sql = "insert into note values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 2);
// 文本大数据字段的数据封装: pst.setAsciiStream(i, in)
File file = new File("./src/cn/hncu/jdbc/JDBCDemo2.java");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
pst.setAsciiStream(2, in);
pst.executeUpdate();
conn.close();
}
2.读取"文本大数据"字段
InputStream in = rs.getAsciiStream(2); // rs.getAsciiStream("note")
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String str = null;
while ((str = bf.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
@Test
// 读取"文本大数据"字段
public void readCLob() throws Exception {
Connection conn = ConnUtils.getConn();
String sql = "select * from note";
// PreparedStatement pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
System.out.println("id:" + id);
// 大文本数据字段的读取
InputStream in = rs.getAsciiStream(2); // rs.getAsciiStream("note")
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String str = null;
while ((str = bf.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
bf.close();
}
conn.close();
}
BLOB类型---二进制大数据字段---声音、图像、视频等
3 写入"二进制大数据"字段
文本大数据字段的数据封装: pst.setBinaryStream(i, in)
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f);
pst.setBinaryStream(2, in);
@Test
// 写入"二进制大数据"字段
public void saveBLob() throws Exception {
Connection conn = ConnUtils.getConn();
String sql = "insert into note values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//文本大数据字段的数据封装: pst.setBinaryStream(i, in)
File f = new File("d:/a/11.jpg");
pst.setInt(1, 1);
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(f);
pst.setBinaryStream(2, in);
pst.executeUpdate();
conn.close();
}4.读取"二进制大数据"字段
InputStream in=rs.getBinaryStream(2);
//自己用底层io技术把in中的数据存成一个独立文件
byte b[]=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("d:/a/abc.jpg");
while((len=in.read(b))!=-1){
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
@Test//读取"二进制大数据"字段
public void readBLob() throws Exception{
Connection conn = ConnUtils.getConn();
String sql = "select * from img";
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
System.out.println("id:"+id);
//二进制大数据字段的读取
InputStream in=rs.getBinaryStream(2);
//自己用底层io技术把in中的数据存成一个独立文件
byte b[]=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("d:/a/abc.jpg");
while((len=in.read(b))!=-1){
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
conn.close();
}CLOB结果: