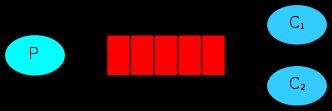
SpringBoot的RabbitMQ消息队列: 三、第二模式"Work queues"
上一节的两个工程,一个负责发送,一个负责接收,也就是一一对于的关系。
只要消息发出了,接收者就处理;当接收效率较低时,就会出现接收者处理不过来,我们就可能会处理不过来,于是我们就可能多配置接受者。这个模式就是"Work queues",它的结构如下
多个接收者,它们会出现什么情况呢?是否像大锅饭,有的人撑死,有的人饿死。这个通过例子验证。
一、再建一个接收者工程 HelloReceiving2
1、把HelloReceiver工程中的HelloRabbitConfig、HelloReceiver、logback.xml依次拷贝过去
2、修改application.properties为
#服务器配置
spring.application.name=rabbitmq-hello-receiving
server.port=9092
#rabbitmq连接参数
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=test
spring.rabbitmq.password=123456二、运行工程
1、在工程HelloSending所在文件夹打开cmd,运行mvn spring-boot:run
2、在工程HelloReceiving所在文件夹打开cmd,运行mvn spring-boot:run
3、在工程HelloReceiving2所在文件夹打开cmd,运行mvn spring-boot:run
4、在浏览器中输入http://localhost:9080/send/上帝1,http://localhost:9080/send/上帝2,http://localhost:9080/send/上帝3
观察两个Receiving的日志.
查看出不均衡吧,为了突出这个不公平,我们修改发送代码如下
package com.example;
import java.util.Date;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloSender {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloSender.class);
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public String send(String name) {
String context = "hello "+name+" --" + new Date();
String sendStr;
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){
sendStr="第["+i+"]个 hello "+name+" --" + new Date();
logger.debug("HelloSender: " + sendStr);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello", sendStr);
}
return context;
}
}再次http://localhost:9080/send/上帝,会发现更多的不公平。
三、Message acknowledgment 消息确认
1、默认情况下,RabbitMQ 会顺序的分发每个Message。当分发后,会将该Message删除,然后将下一个Message分发到下一个Consumer。这种分发方式叫做round-robin
2、每个Consumer可能需要一段时间才能处理完收到的数据。如果在这个过程中,Consumer出错了,异常退出了,而数据还没有处理完成,那么非常不幸,这段数据就丢失了。因为我们采用no-ack的方式进行确认,也就是说,每次Consumer接到数据后,而不管是否处理完成,RabbitMQ Server会立即把这个Message标记为完成,然后从queue中删除了。
3、如果一个Consumer异常退出了,它处理的数据能够被另外的Consumer处理,这样数据在这种情况下就不会丢失了(注意是这种情况下)。
4、为了保证数据不被丢失,RabbitMQ支持消息确认机制,即acknowledgments。为了保证数据能被正确处理而不仅仅是被Consumer收到,那么我们不能采用no-ack。而应该是在处理完数据后发送ack。
5、在处理数据后发送的ack,就是告诉RabbitMQ数据已经被接收,处理完成,RabbitMQ可以去安全的删除它了。
6、如果Consumer退出了但是没有发送ack,那么RabbitMQ就会把这个Message发送到下一个Consumer。这样就保证了在Consumer异常退出的情况下数据也不会丢失。
7、这里并没有用到超时机制。RabbitMQ仅仅通过Consumer的连接中断来确认该Message并没有被正确处理。也就是说,RabbitMQ给了Consumer足够长的时间来做数据处理。
消息确认,对于spring-boot来说,就是一个开关,它就是spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode
acknowledgeMode有三值:
A、NONE = no acks will be sent (incompatible with channelTransacted=true).
RabbitMQ calls this "autoack" because the broker assumes all messages are acked without any action from the consumer.
B、MANUAL = the listener must acknowledge all messages by calling Channel.basicAck().
C、AUTO = the container will acknowledge the message automatically, unless the MessageListener throws an exception.
Note that acknowledgeMode is complementary to channelTransacted - if the channel is transacted then the broker requires a commit notification in addition to the ack. This is the default mode. See also txSize.
非常简单,在application.properties中增加spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode=AUTO
为了更好的演示异常,我们把生产者、消费者都做了sleep.代码如下:
sending
package com.example;
import java.util.Date;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloSender {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloSender.class);
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public String send(String name) throws InterruptedException {
String context = "hello "+name+" --" + new Date();
String sendStr;
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){
sendStr="第["+i+"]个 hello "+name+" --" + new Date();
logger.debug("HelloSender: " + sendStr);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello", sendStr);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
return context;
}
}
package com.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello")
public class HelloReceiver {
protected static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloReceiver.class);
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String hello) {
logger.debug("HelloReceiver : " + hello);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Receiving2
package com.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello")
public class HelloReceiver {
protected static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloReceiver.class);
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String hello) {
logger.debug("HelloReceiver : " + hello);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、消息持久化
在上一节中我们知道了即使Consumer异常退出,Message也不会丢失。但是如果RabbitMQ Server退出呢?软件都有bug,即使RabbitMQ Server是完美毫无bug的(当然这是不可能的,是软件就有bug,没有bug的那不叫软件),它还是有可能退出的:被其它软件影响,或者系统重启了,系统panic了。。。
为了保证在RabbitMQ退出或者crash了数据仍没有丢失,需要将queue和Message都要持久化。
queue持久化,就是在实例时调用具有参数durable的构造函数.
package com.example;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class HelloRabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Queue helloQueue() {
return new Queue("hello",true);
}
}
五、单消费者,排他队列
消息只能一个消费者接收处理,其它消费者只能看着,这也是队列实例时调用具有参数exclusive 的构造函数。
/**
* Construct a new queue, given a name, durability, exclusive and auto-delete flags.
* @param name the name of the queue.
* @param durable true if we are declaring a durable queue (the queue will survive a server restart)
* @param exclusive true if we are declaring an exclusive queue (the queue will only be used by the declarer's
* connection)
* @param autoDelete true if the server should delete the queue when it is no longer in use
*/
public Queue(String name, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete) {
this(name, durable, exclusive, autoDelete, null);
}
六、参数
-
spring.rabbitmq.addresses指定client连接到的server的地址,多个以逗号分隔.
-
spring.rabbitmq.dynamic是否创建AmqpAdmin bean. 默认为: true)
-
spring.rabbitmq.host指定RabbitMQ host.默认为: localhost)
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.acknowledge-mode指定Acknowledge的模式.
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.auto-startup是否在启动时就启动mq,默认: true)
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.concurrency指定最小的消费者数量.
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.max-concurrency指定最大的消费者数量.
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.prefetch指定一个请求能处理多少个消息,如果有事务的话,必须大于等于transaction数量.
-
spring.rabbitmq.listener.transaction-size指定一个事务处理的消息数量,最好是小于等于prefetch的数量.
-
spring.rabbitmq.password指定broker的密码.
-
spring.rabbitmq.port指定RabbitMQ 的端口,默认: 5672)
-
spring.rabbitmq.requested-heartbeat指定心跳超时,0为不指定.
-
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.enabled是否开始SSL,默认: false)
-
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store指定持有SSL certificate的key store的路径
-
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.key-store-password指定访问key store的密码.
-
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store指定持有SSL certificates的Trust store.
-
spring.rabbitmq.ssl.trust-store-password指定访问trust store的密码.
-
spring.rabbitmq.username指定登陆broker的用户名.
-
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host指定连接到broker的Virtual host.